Abstract
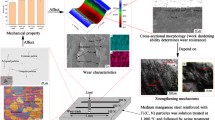
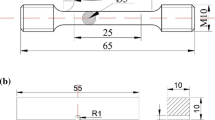
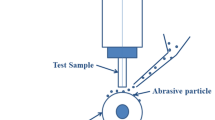
A high-manganese austenitic steel matrix (Mnl3) composite reinforced with TiN ceramic particles was synthesized by means of Vacuum-Evaporation Pattern Casting (V-EPC). The composite microstructure and interface bonding of TiN/matrix were analyzed utilizing optical microscope (OM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The effects of different volume fraction of TiN on impact wear resistance were evaluated by MLD-10 impact wear test. The results showed that TiN was evenly distributed in composite layer and had a good interface bonding with matrix when the volume fractions of TiN were 27% and 36%, respectively. However, cast defects and TiN agglomeration occurred when the TiN volume fraction increased to 48%. Compared with high-manganese austenitic steel (Mnl3), the impact wear resistance of the TiN-reinforced composite is better. In small impact load conditions, composite layer can effectively resist abrasives wear and TiN particles played an important role in determining impact wear resistance of composite layer. In large impact load, the synergistic roles of spalling of TiN particles and the increase of work hardening of Mn13 based material are responsible for impact wear resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashok Kumar Srivastava, Karabi Das. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of in Situ TiC and (Ti,W)C-Rein-forced High Manganese Austenitic Steel Matrix Composites [J]. Mat Sei Eng A Struct, 2009, 516: 1.
Ashok Kumar Srivastava, Karabi Das. The Abrasive Wear Resistance of TiC and (Ti, W) CReinforced Fe-17Mn Austenitic Steel Matrix Composites [J]. Tribol Int, 2010, 43: 944.
Ashok Kumar Srivastava, Karabi Das. Microstructure and Abrasive Wear Study of (Ti,W)C-Reinforced High-Manganese Austenitic Steel Matrix Composite [J]. Mater Lett, 2008, 62: 3947.
Pagounis E, Talvitie M, Lindroos V K. Influence of the Metal/Ceramic Interface on the Microsturcture and Mechanical Properties of HIPed Iron-Based Composites [J]. Compos Sei Technol, 1996, 56: 1329.
Hua M, Tam H Y, Ma H Y. Patterned PVD TiN Spot Coatings on M2 Steel: Tribological Behaviors Under Different Sliding Speeds [J]. Wear, 2006, 260: 1153.
Hu S B, Tu J P, Mei Z. Adhesion Strength and High Temperature Wear Behaviour of Ion Plating TiN Composite Coating With Electric Brush Plating Ni-W Interlayer [J]. Surf Coat Tech, 2001, 141: 174.
Hedengvist P, Olsson M, Wallen P. How TiN Coatings Improve the Performance of High Speed Steel Cutting Tools [J]. Surf Coat Tech, 1990, 41: 245.
Soliman F A, Abuzeid O A. On the Improvement of the Performance of High Speed Steel Turning Tools by TiN Coatings [J]. Wear, 1987, 119: 199.
LI Jing-guo, GAO Lian, GUO Jing-kun. Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of TiN-Al2O3 Nanocomposites [J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2003, 23: 69.
Kaptay G. The Threshold Pressure of Infiltration Into Fibrous Preforms Normal to the Fibres’ Axes [J]. Compos Sci Tech, 2008, 68: 228.
LIU Shi-liang, CAO Guoping, LI Guang-sheng. Refiner Disc Made With RE Cast-Infiltration Process and Its Application [J]. China Pulp and Paper, 2010, 29: 37 (in Chinese).
Markus Weiler. An Infiltration Model Based on Flow Variability in Macropores: Development, Sensitivity Analysis and Applications [J]. J Hydro, 2005, 310: 294.
HUANG Xi-gu. Metallurgy of Iron and Steel Principle [M]. Beijing; Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item: Item Sponsored by Office of Education of Shaanxi Province of China (08JK345); Programs for Industry Development of Shaanxi Province of China (2008K06-18)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Yp., Li, Xl., Wang, Ch. et al. Microstructure and Impact Wear Resistance of TiN Reinforced High Manganese Steel Matrix. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19, 60–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60114-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60114-9