Abstract
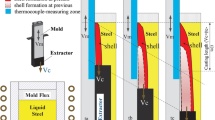
A computational model of thermal behavior of the top-surface slag layers in continuous casting mold was applied to interpret the thermal insulation of mold powder. The temperature drop of liquid steel caused by heat removal at the interface of molten steel and slag in mold was proposed to evaluate the thermal insulation of mold slag. The calculation results show that slag consumption is one of important factor influencing the temperature drop, while the casting speed has no obvious effect on it. With the increase of slag consumption, the temperature drop is increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinheiro C A, Samarasekera I V, Brimacombe J K. Mold Flux for Continuous Casting of Steel [J]. Iron and Steel Maker, 1995, 22(7): 41.
Goldschmit M B, Gonzalez J C, Dvorkin E N. Finite Element Model for Analyzing Liquid Slag Development During Continuous of Round Bars [J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1993, 20 (5): 379.
Neumann F, Neal J, Pedroza M A, et al. Mold Fluxes in High Speed Thin Slab Casting [C]//Iron and Steel Society. Proceedings of 79th Steelmaking Conference. Pittsburgh: ISS, 1996: 249.
Watanabe K, Suzuki M, Murakami K, et al. Development of Mold Powder for High Speed Casting of Middle Carbon Steel [C]// Iron and Steel Society. Proceedings of 79th Steelmaking Conference. Pittsburgh: ISS, 1996: 265.
Lidefelt H, Hasselstrom P. Characterization of the Functional Properties of Mold Powders for Continuous Casting of Steel [C]//Metals Society. 4th International Iron and Steel Congress Proceedings. London: Metals Society, 1982: 101.
LIU Cheng-jun, JIANG Mao-fa. Insulation Capacity of Mold Powder [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2002, 14(3): 1 (in Chinese).
Kishimoto M, Maeda M, Mori K, et al. Thermal Conductivity and Specific Heat of Metallurgical Slags [C]//Fine H A, Gaskell D R. Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Metallurgical Slags and Fluxes. Warrendale: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1984: 891.
Ponsford F H, Mills K C, Grievson P, et al. Physical and Thermal Properties of Aluminate Slag [C]//Institute of Metals. 3rd International Conference Molten Slags and Fluxes. Glasgow: Institute of Metals, 1988: 332.
Nagata K, Susa M, Goto K S. Thermal Conductivities of Slags for Ironmaking and Steelmaking [J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1983, 69: 1417 (in Japanese).
Nagata K, Goto K S. Heat Conductivity and Mean Free Path of Phonons in Metallurgical Slags [C]//Fine H A, Gaskell D R. Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Metallurgical Slags and Fluxes. Warrendale: Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1984: 875.
McDavid R M, Thomas B G. Flow and Thermal Behavior of the Top Surface Flux/Powder Layers in Continuous Casting Molds [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 1996, 27B(4): 672.
ZHANG Xian-zhuo. Metallurgical Transport Phenomena [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Engineering Press, 1988 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wu, Ym., Qiu, St. et al. Simulation of Thermal Insulation of Top-Surface Slag Layers in Continuous Casting Mold. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18, 29–33 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60018-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60018-1