Abstract
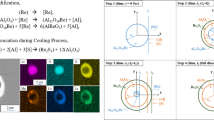
The experiments on adding Ce, Mn and S to molten iron have been carried out by means of the electric furnace, and the concentration of oxygen, the evolution of inclusions and microstructures of samples are analyzed, indicating that the concentration of dissolved oxygen decreases greatly after adding Ce. The calculated thermodynamics results at 1 273 K performed on Factsage show that Ce2O2S and CeAlO3 are formed with the increase of Ce content for w(Ce)>0.0002 and w(S)<0.0001, while three cerium sulphides (CeS, Ce3S4 and Ce2S3, in sequence), MnS and Ce2O2S are formed with the increase of S content and the decrease of Ce content for w(Ce)>0. 0002 and w(S)> 0. 000 1. These results are consistent with the SEM observations. Finally, some possible reasons are given to explain the formation of intragranular ferrite in the pure iron.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takamura J. Roles of Oxides in Steels Performance [C] // Proc 6th Inter Iron and Steel Cong. Nagoya: ISIJ. 1990: 591.
Mizoguchi S. Control of Oxides as Inoculants [C] // Proc 6th Inter Iron and Steel Cong. Nagoya: ISIJ, 1990s 598.
Sawai T. Effect of Zron the Precipitation of MnS in Low Carbon Steels [C] // Proc 6th Inter Iron and Steel Cong. Nagoya: ISIJ, 1990: 605.
Ogibayashi S. The Features of Oxides in Ti-Deoxidized Steel [C] // Ptoc 6th Inter Iron and Steel Cong. Nagoya: ISU, 1990: 612.
Guo AM, Li S, Guo, et al. Effect of Zirconium Addition on the Impact Toughness of the Heat Affected Zone in a High Strength Low Alloy Pipeline Steel [J]. Mater Char, 2008, 59: 134.
Oystein, Leiv, Casper E. Microstructure Control of Steels Through Dispersoid Metallurgy Using Novel Grain Refining Alloys [J]. ISIJ Int, 2006, 46(6): 824.
Babu S, David S A. Inclusion Formation and Microstructure Evolution in Low Alloy Steel Welds [J]. ISIJ Int, 2002, 42 (12): 1344.
Minagawa, Ishida, Funatsu Y. 390 MPa Yield Strength Steel Plate for Large Heat-Input Welding for Large Container Ships [J]. Nippon Steel Tech Rep, 2004, 380: 6.
Nagahara, Fukami H. 530 N/mm2 Tensile Strength Grade Steel Plate for Multi-Purpose Gas Carrier [J]. Nippon Steel Tech Rep, 2004, 380: 9.
Akihiko, Ken-Ichi, Tomohiko, et al. Development of High HAZ Toughness Steel Plates for Box Columns With High Heat Input Welding [J]. Nippon Steel Tech Rep, 2004, 380: 39.
Waudby P E. Rare Earth Additions to Steel [J]. Int Met Rev, 1978(2): 74.
Nuri, Ohashi, Hiromoto, et al. Solidification Micro-structure of Ingots and Continuously Cast Slabs Treated With Rare Earth Metal [J]. Trans ISIJ, 1982, 22: 399.
Li, McLean, Rutter J, et al. Influence of Rare Earth Metals on the Nucleation and Solidification Behavior of Iron and 1045 Steel [J]. Trans, 1988, 19B: 383.
Guo M, Suito H. Pinning of Austenite Grain Boundary of Fe-0. 09 to 0. 53 mass% C-0. 02 mass% P Alloys by Primary Inclusions of Ce2O3 and CeS [J]. ISIJ Int, 1999, 39(12): 1289.
Li C, Wang Y, Chen J, et al. Effects of Rare Earth on Microstructure of BNbRE Steel for Heavy Rail [J]. J Rare Earths, 2005, 23(4): 470.
Yang Q, Liao, Liu J, et al. Effect of Rare Earth Elements on Austenite Growth Dynamics of Steel 60CrMnMo [J]. J Rare Earths, 1998, 13(1): 32.
Manohar P, Chandra, Killmore C R. Continuous Cooling Transformation Behaviour of Microalloyed Steels Containing Ti, Nb, Mn and Mo [J]. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36(12): 1486.
Barritte G, Edmonds D V. Advances in the Physical Metallurgy and Applications of Steel [M]. London: The Met Society, 1981.
Zhang, Farrar R A. Role of Non-Metallic Inclusions in Formation of Acicular Ferrite in Low Alloy Weld Metals [J]. Mater Sci Technol, 1996, 12: 237.
Bramfitt B L. The Effect of Carbide and Nitride Additions on the Heterogeneous Nucleation Behavior of Liquid Iron [J]. Metal Trans, 1970, 7(1): 1987.
Yamamoto, Hasegawa, Takamura J. Effect of Boron on Intragranular Ferrite Formation in Ti-Oxide Bearing Steels [J]. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36(1): 80.
Mabuchi, Uemori, Fujioka M. The Role of Mn Depletion in Intra-Granular Ferrite Transformation in the Heat Affected Zone of Welded Joints With Large Heat Input in Structural Steels [J]. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36(11): 1406.
Shigesato, Sugiyama, Aihara, et al. Effect of Mn Depletion on Intra-Granular Ferrite Transformation in Heat Affected Zone of Welding in Low Alloy Steel [J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2001, 87(2): 93.(in Japanese).
Talas, Cochrane R C. Effects of Tion the Morphology of High Purity Iron Alloys [J]. J Alloys Comp, 2005, 396: 224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50734008) s Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities of China (FRF-MP-09-001A)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, B., Song, B., Pan, N. et al. Influence of Ce on Characteristics of Inclusions and Microstructure of Pure Iron. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18, 38–44 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(11)60021-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(11)60021-6