Abstract
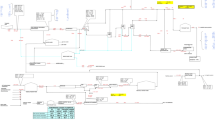
Two new integrated processes, gas-energy-management (GEM)—electrochemical catalytic oxidation (ECO)—membrane bioreactor (MBR) and ultrafiltration (UF)—ECO—MBR, in industrial-scale test for treating cold-rolling mill emulsion wastewater with water quantity of 200 L/h to 3 000 L/h were studied. The former was put forward firstly and the latter was applied initially in this field. The operation conditions and mechanisms of each module in the integrated processes were analyzed and the influences of operational parameters of two processes on chemical oxygen demand (CODCr) removal efficiency were comparatively investigated. The test results showed that the ultimate water quality from the two processes after treatment could meet the requirement for reuse. However, the quality of effluent treated by GEM—ECO—MBR was more stable than that of UF—ECO—MBR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakrabarty B, Ghoshal A K, Purkait M K. Ultra-Filtration of Stable Oil-in-Water Emulsion by Polysulfone Membrane [J]. J Membrane Sci, 2008, 325(1): 427.
YI Ning, HU Wei. Some Treatment in the Cold Rolling Emulsion Wastewater in Iron and Steel Plants [J]. J Metallurgical Power, 2004, 22(5): 58.
LIU Fu-xing, LI Yi-jiu. Mechanism and Development of Electrochemical Catalytic Oxidation in Degradation of Organic Pollutants [J]. J SiChuan Environment, 2005, 24(1): 52 (in Chi-nese).
Panizza M, Bocca C, Cerisola G. Electrochemical Treatment of Wastewater Containing Polyaromatic Organic Pollutants [J]. J Water Res, 2000, 34(9): 2601.
WU Ke-ming, ZHANG Cheng-zhou, LIU Hong. Treatment of Emulsifying Wastewater From Cold Rolling With Compound Flocculent [J]. J Chemical Engineers, 2005, 113(2): 1.
Miroslav Colic, Wade Morse. The Development and Application of Centrifugal Flotation Systems in Wastewater Treatment [J]. Int J Environment and Pollution, 2007, 30(2): 296.
Brillas E, Calpe J C, Casado J. Mineralization of 2, 4-D by Advanced Electrochemical Oxidation Processes [J]. J Water Res, 2000, 34(8): 2253.
CUI Yan-ping, YANG Cang-zhu. Application of Electrochemical Oxidation Process in the Bio-Refractory Organic Wastewater Treatment [J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2004, 30(6): 12 (in Chinese).
TANG Wei-wen, WANG Zhen-zhen, XU Jing-cheng, et al. Effects of Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen on Biological Activated-Carbon Treating Drainage From Steel and Iron Industry [J]. Industrial Water and Wastewater, 2008, 39(2): 32 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by Preferred Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of China ([2007]170)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Yh., Gan, Fx., Li, M. et al. New Integrated Processes for Treating Cold-Rolling Mill Emulsion Wastewater. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17, 32–35 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60110-0
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60110-0