Abstract
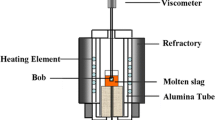
The relationship between the binary basicity (CaO/SiO2), TiO2, Na2O, Li2O, MgO, MnO, B2O3 and viscosity for fluoride-free and titanium-bearing mold fluxes were systematically researched. The rotating cylinder method was employed in the experiment to measure the viscosity of the slag. The results indicate that Li2O, B2O3 and Na2O play major roles in decreasing viscosity, especially Li2O, which is the most effective flux, while MgO and MnO exert little influence on viscosity. Meanwhile, it can be concluded that with increasing TiO2 content, the viscosity of fluoride-free and titanium-bearing mold fluxes increases at first but then falls when the amount of TiO2 is greater than 6.0%. Based on large amounts of experimental statistics of the viscosity of fluoride-free and titanium-bearing mold fluxes, an available model in literature for predicting the mold-slag viscosity was modified. This modified model can be used to predict the viscosity of fluoride-free and titanium-bearing mold fluxes. In fact, the predicted values approximate the observed values with a ±10.6% average deviation. Compared with the classical models, the average deviation is higher and it was found that the modified model can be used to estimate the viscosity of fluoride-free and titanium-bearing mold fluxes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WEN Guang-hua, Sridhar S. Development of Fluoride-Free Mold Powders for Peritectic Steel Slab Casting [J]. ISIJ International, 2007, 47: 1117.
Hideko N, Kazuhiro N. Crystallization of CaO-SiO2-TiO2 Slag as a Candidate for Fluorine Free Mold Flux [J]. ISIJ International, 2006, 46: 441.
ZHU Li-guang. Study on Viscosity of Mold Powders for High Speed Casting [J]. Iron and Steel, 2000, 35(6): 23 (in Chinese).
Riboud P V, Roux Y, Lucas L D. Improvement of Continuous Casting Powders [J]. Facber, Hüttenprax, Metallweiter Verarb, 1981, 19: 859.
Koyama K, Nagano K. Design for Chemical and Physical Properties of Continuous Casting Powders [J]. Nippon Steel Technical Report, 1987, 34: 41.
Mills K C, Sridhar S. Viscosities of Ironmaking and Steelmaking Slags [J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1999, 26: 262.
CHI Jing-hao, GAN Yong-nian. Mold Fluxes [M]. Shenyang: Northeastern University Press, 2000 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shanghai Baosteel Group (50374086)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, X., Wen, Gh. & Tang, P. Viscosity and Viscosity Estimate Model of Fluoride-Free and Titanium-Bearing Mold Fluxes. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17, 6–10 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60105-7
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60105-7