Abstract
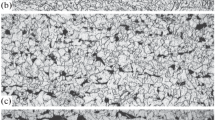
The microstructure characteristics and precipitation behavior of automobile beam steels produced by compact strip production (CSP) were investigated by use of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy. The result shows that the final microstructure is mainly composed of polygonal ferrite and small amount of pearlite, and the average ferrite grain size is about 3–6 μm. Small amount addition Ti to aluminium-killed steel can help to refine (the microstructure and improve the mechanical properties. A large number of fine precipitates have been observed in automobile beam steels. The mean particle size is about 10—30 nm. Remarkable strengthening and grain refinement can be obtained by these nano-particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flemming G, Hensger K. Extension of Product Range and Perspectives of CSP Technology [J]. MPT Inter, 2000(1): 54.
Yu H, Ren H, Kang Y L. Carbon Diffusion in Hot Strips of Low Carbon Steel Produced by CSP Line Under Different Thermal Histories [J]. J Mater Sci Technol, 2005, 21(1): 21.
Kang Y L, Yu H, Fu J. Morphology and Precipitation Kinetics of A1N in Hot Strip of Low Carbon Steel Produced by Compact Strip Production [J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2003(351): 265.
Yu H, Kang Y L, Wang K L. Study of Mechanism on Micro-structure Refinement During Compact Strip Production Process [J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2003(363): 86.
Gardiola B, Humbert M, Esling C. Determination and Prediction of the Inherited Ferrite Texture in a HSLA Steel Produced by Compact Strip Production [J]. Mater Sci Eng, 2001(303): 60.
Humbert M, Gardiola B, Esling C. Modeling of the Variant Selection Mechanism in the Phase Transformation of HSLA Steel Produced by Compact Strip Production [J]. Acta Mater, 2002, 50: 1741.
Yu H, Kang Y L, Xiong X Y. Quantitative Analysis on Strengthening Mechanism of Ultra-Thin Hot Strip of Low Carbon Steel Produced by CSP Technique [J]. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2004, 11(5): 425.
Kang Y L, Wang K L, Yu H. Microstructure Evolution and Precipitation Behavior of Low Carbon Steel Hot Strips Produced by CSP [J]. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2004, 11(4): 364.
Kunishige K, Nagao N. Strengthening and Toughening of Hot-Direct-Rolled Steels by Addition of a Small Amount of Titanium [J]. ISIJ Int, 1989, 29(11): 940.
Bai M Z, Liu D L, Lou Y Z. Effects of Ti Addition on Low Carbon Hot Strips Produced by CSP Process [J]. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2006, 13(3): 230.
Zhang L, Yang W Y, Zheng W W. Carbides/Nitrides Precipitates in a C-Mn Strip by CSP Technology [J]. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2005, 12(6): 517.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Science and Technology Support Program for 11th Five-Year Plan of China (2006BAE03A06)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Zz., Liu, J. & Zhao, Am. Analysis of microstructure characteristics and precipitation behavior of automobile beam steels produced by compact strip production. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17, 56–61 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60073-8
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60073-8