Abstract
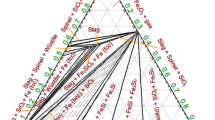
The activity model of CaO-FeO-SiO2-WO3 quarternary system is built according to the coexistence theory of slag structure and the reduction thermodynamics of scheelite is discussed by using this model. The activities of SiO2 and WO3 decrease, while the activity of CaO increases with increasing the basicity of slag. Among SiC, carbon and silicon reactants, the reducing capability of SiC is the strongest, while that of carbon is the poorest at high temperature (about 1873 K). Increasing the content of silicon or carbon is beneficial for increasing the yield of tungsten. Oxidizability of slag has a significant effect on the yield of tungsten. Controlling basicity and oxidizability of slag can decrease the oxidation loss of tungsten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GUO Pei-min. Study on Making Alloy Steel by Direct Reduction and Alloying of Scheelite and Molybdenum Oxide [D]. Beijing: Central Iron and Steel Research Institute. 2001 (in Chinese).
LI Zheng-bang, GUO Pei-min, ZHANG He-sheng, et al. Theoretic Analysis and Industrial Trial of Direct Reducing and Alloying of Scheelite and Molybdenum Oxide [J]. Iron and Steel, 1999, 34(10): 20 (in Chinese).
GUO Pei-min, LI Zheng-bang, LIN Gong-wen, et al. Kinetic Analysis of Smelting Alloy Steel With Scheelite [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2000, 12(4): 10 (in Chinese).
LI Zheng-bang, GUO Pei-min, ZHANG He-sheng. Thermodynamic Analysis of Smelting Alloy Steels With Scheelite, Molybdenum Oxide and Vanadium Slag [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1999, 11(3): 14 (in Chinese).
GUO Pei-min, LI Zheng-bang, LIN Gong-wen. Developing Technology of Direct Alloying of Scheelite, Molybdenum Oxide and Vanadium Slag [J]. Special Steel, 2000, 21(4): 23 (in Chinese).
GUO Pei-min, LI Zheng-bang, LIN Gong-wen. Effect of Ingredient on Melting Point of Scheelite Fluxes [J]. Special Steel, 2002, 23(4): 16 (in Chinese).
GUO Pei-min, LI Zheng-bang, LIN Gong-wen. Activity Model and Its Application in CaO-FeO-SiO2-MoO3 Quarternary System [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2004, 11(5): 406 (in Chinese).
GUO Pei-min, ZHAO Pei. Activity Model and Application of Quarternary System CaO-FeO-SiO2-V2 O3 [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2005, 26(3): 1 (in Chinese).
ZHANG Jian. Computing Thermodynamics of Metallurgical Melt [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation ltem: Item Sponsored by National Science and Technology Support Program for 11th Five-Year Plan of China (2006BAE03A12. 2006BAE03A05)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Pm., Li, Zb. & Zhao, P. Activity model and its application in quarternary system CaO-FeO-SiO2-WO3. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17, 12–17 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60037-4
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60037-4