Abstract
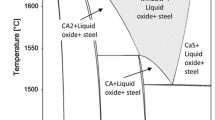
Strategies based on thermodynamic calculations can be used to overcome the problems associated with oxides encountered in steel plant operations, which can lead to certain difficulties in the process such as clogging of submerged entry nozzle during continuous casting. Approaches to producing high alloy steels by continuous casting have been taken. One of the strategies to avoid the oxidation of chromium is to add a small amount of other elements (subject to other constraints), which do not cause subsequent problems. The problem has been studied using the Thermo-CalcR software, with related databases; and the results obtained for different process conditions or generic compositions have been presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peri Reddy V. Thermodynamic Assessment of Oxide Systems (Phase I ) [R]. National Institute of Technology Tiruchirappalli, 2007.
Peri Reddy V. Thermodynamic Assessment of Oxide Systems (Phase II) [R]. National Institute of Technology Tiruchirappalli, 2008.
User’s Guide and Manuals, Thermo-CalcR Software and Databases, Thermo-Calc Software [M]. Stockholm, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peri, V.R., Sankaranarayanan, S.R. Thermodynamic modeling as a strategy for casting high alloy steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 16, 29–31 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60006-4
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60006-4