Abstract
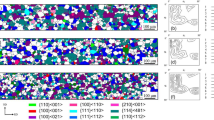
Goss texture or (110)[100] crystallographic orientation of the grains is typical grain structure of grain oriented silicon steel used for transformer. This type of texture is one of the most important parameters determining the magnetic properties of the laminated steel plates. The formation and growth of Goss texture in three steel samples are investigated. Two of them are prepared under laboratory conditions and one under industrial conditions. The emphasis is put on the effects of hot lamination temperature and time, primary and secondary recrystallization temperatures during cold lamination on developing of the Goss texture in correlation with other texture components. Also in all steel processing stages, the influence of the chemical composition on the occurrence of Goss texture is examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimanaka H, Ito Y, Matsumura K, et al. Recent Development on Non-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheets [J]. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1982, 26(1–3): 57.
Masui H, Matsuo Y, Mizokami M. Relation Between Magnetostriction and Magnetic Domain in Changing Directions of Grain Oriented Silicon Steel Sheet [R]. Digests of INTERMAG Magnetics, 1997, 1–4: EQ-09.
Doniga A. Recrystallization Influence on the Texture and Microstructure of the Microalloyed 3%Si Steel [J]. Metalurgia International, 2005, 2: 30.
Iwanaga J, Masui H, Harase J, et al. Effect of Initial Texture on Secondary Recrystallization of Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel [J]. Materials Engineering and Performance, 1994, 3 (2): 223.
Jayanth C S, Nash P. Factors Affecting Particle-Coarsening Kinetics and Size Distribution [J]. Materials Science, 1989, 24 (9): 3041.
Barnettm M R, Jonas J J. Influence of Ferrite Rolling Temperature on Grain Size and Texture in Annealed Low C and IF Steels [J]. ISIJ International, 1997, 37(7): 706.
Zhu G, Subramanian S V. Recrystallization Behavior Design for Controlling Grain Size in Strip Rolling Process [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2008, 15(1): 39.
Sánchez-Araiza M, Godet S, Jonas J J. Effect of Rolling Temperature, Reduction and Alloying Additions on the Texture of Warm Rolled Steels [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 495–497: 501.
Azzil M, Reza Batenil M, Szpunar J A, et al. The Effect of Texture on Friction of AISI304 Stainless Steel [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 495–497: 1579.
Gheorghies C, Gheorghies L. Control of Material Texture by X Ray [M]. Bucharest: Technical Publishing House, 1994 (in Romanian).
Morawiec A. Orientations and Rotations Computations in Crystallographic Textures [J]. Cryst Res Technol, 2005, 40 (3): 283.
Kuber R, Berveiller M, Cherkaoui M, et al. Transformation Textures in Unstable Austenitic Steel [J], Engineering Materials and Technology, 2003, 125(1): 12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gheorghies, C., Doniga, A. Evolution of texture in grain oriented silicon steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 16, 78–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(09)60065-0
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(09)60065-0