Abstract
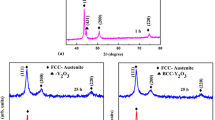
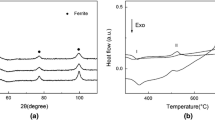
Preparation of nanocrystalline 430L stainless steel by both high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering technique has been investigated. The results have shown that the hardness can be improved markedly with an increase in sintering temperature and holding time. The lower the apparent porosity of nanocrystalline 430L stainless steel, the higher is the Vickers-hardness. The tensile strength reached a maximum value of 713 MPa when the sample was sintered at 1 173 K for 10 min, and then it evidently decreased with an increase in sintering temperature and holding time because of the growth of crystalline grain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch C C, Cavin O B, Mckamey C G, et al. Preparation of ‘a Morphous’ Ni60Nb40 by Mechanical Alloying [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1993, 43: 1017.
Kaibyshev O A. Grain Refinement in Commercial Alloys Due to High Plastic Deformations and Phase Transformations [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 117(3): 300.
LU K, WEI W D, WANG J T. The Mechanism of Crystalline Ni88 P12 [J]. Scripta Metall Matter, 1990, 24: 2319.
Claudio L, Castro De, Brain S Mitchell. Crystal Growth Kinetics of Nanocrystalline Aluminum Prepared by Mechanical Attrition in Nylon Media [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2005, 396A(1–2): 124.
Schlorke N, Eckert J, Schnltz L, et al. Synthesis of Multi-Component Fe-Based an Amorphous Alloys With Significant Super-Cooled Liquid Region by Mechanical Alloying [J]. Mater Sci and Eng, 1997, A226–228: 425.
Koch C C. Intermetallic Matrix Composites Prepared by Mechanical Alloying-a Review [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1998, 244A: 39.
Nagae T. Hot Compaction of Nanocrystalline Stainless Steel Powders by Spark-Plasma Sintering [J]. Metal Powder Report, 2003, 58(6): 53.
CHEN X H, LU J, LU L, et al. Tensile Properties of a Nanocrystalline 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52: 1039.
HE Hang, NI Hong-wei, LI Guang-qiang. Preparation of 430L Stainless Steel Nanocrystalline Grain Powders by High Energy Ball Milling [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006, Suppl(1): 23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by Young Talents Scientific Creative Team Foundation, Education Department of Hubei Province of China [(2003)7]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Hw., He, H., Li, Gq. et al. Preparation of nanocrystalline 430L stainless steel by HEBM and SPS. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 15, 73–76 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60147-8
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60147-8