Abstract
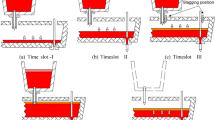
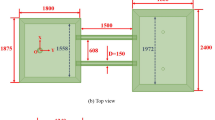
Fluid flow and mixing of molten steel in a twin-slab-strand continuous casting tundish were investigated using a mixing model under non-isothermal conditions, This model led to a set of ordinary differential equations that were solved with a Runge-Kutta algorithm. Steady state water modeling was carried out under non-isothermal conditions. Experimental data obtained from the water model were used to calibrate the mixing model. Owing to the presence of a mixed convection in the non-isothermal conditions, a channelizing flow would be created in the fluid inside the tundish. A mixing model was designed that was capable of predicting RTD (residence time distribution) curves for different cases in non-isothermal conditions. The relationship between RTD parameters and the Tu (tundish Richardson number) was obtained for various cases under non-isothermal conditions. The results show that the RTD parameters were completely different under isothermal and non-isothermal conditions. The comparison of the RTD curves between the isothermal and non-isothermal conditions presents that the extent of mixing in the tundish in non-isothermal conditions is lower than the mixing extent in isothermal conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A ext :
-
External surface of mixing box
- a, b:
-
Free parameters
- c P :
-
Specific heat, (J · kg−1 · K−1)
- f i :
-
Volume fraction of a given box
- g:
-
Gravitational acceleration, (m · s−2)
- h:
-
Heat transfer coefficient, (J · m−2 · s−1 · K−1)
- L:
-
Characteristic length, m
- Q 0 :
-
Volume flowrate entering branch 1, (m3 · s−1)
- Q c :
-
Volume flowrate entering branch 2, (m3 · s−1)
- Q d :
-
Volume flowrate entering dead zone, (m3 · s−1)
- Q i :
-
Volume flowrate leaving a given box, (m3 · s−1)
- Q in :
-
Volume flowrate entering tundish, (m3 · s−1)
- Q out :
-
Volume flowrate leaving each tundish outlet, (m3 · s−1)
- Re T :
-
Turbulent Reynolds number
- i:
-
Time, s
- t cp :
-
Time when traced first appearance in branch 2, s
- t p :
-
Time when traced first appearance in branch 1, s
- T 0 :
-
Initial temperature of fluid in the tundish, K
- T am :
-
Ambient temperature, K
- T d :
-
Temperature entering dead zone, K
- T i :
-
Temperature leaving a given box, K
- T in :
-
Temperature of incoming fluid, K
- T out :
-
Temperature at outlet, K
- Tu:
-
Tundish Richardson number
- U:
-
Characteristic velocity, (m · s−1)
- u:
-
Uniform velocity of fluid in plug-flow box, (m · s−1)
- V 0 :
-
Volume of fluid in branch 1, m3
- V c :
-
Volume of fluid in branch 2, m3
- V i :
-
Volume of a given box, m3
- V T :
-
Total volume of tundish, m3
- β:
-
Coefficient of volume expansion of water, β=2.95×10−4 K−1
- ΔT:
-
Temperature difference between Tin and T0
- θ:
-
Dimensionless temperature
- ρ0:
-
Fluid density entering branch 1, (kg · m−3)
- ρi:
-
Fluid density leaving a given box, (kg · m−3)
- cm1:
-
First mixing box in branch 2
- cm2:
-
Second mixing box in branch 2
- cp:
-
Plug flow box in branch 2
- d:
-
Dead zone
- m1:
-
First mixing box
- m2:
-
Second mixing box
- P:
-
Plug flow box in tundish mixing model
References
Sahai Y, Emi T. Melt Flow Characterization in Continuous Casting Tundishes [J]. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36(6): 667.
Butt J B. Reaction Kinetics and Reactor Design [M]. New Jersey, USA: Prentice-Hall Inc, 1980.
Mazumdar D, Guthrie R I L. The Physical and Mathematical Modelling of Continuous Casting Tundish Systems [J]. ISIJ Int, 1999, 39(6): 524.
Sheng D Y, Jonsson L. Investigation of Transient Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Continuous Casting Tundish by Numerical Analysis Verified With Nonisot hernial Water Model Experiments [J]. Metall Mater Trans, 1999, 30B(5): 979.
Sinha A K, Vassilicos A. Physical Modeling of Thermal Effects on Steel Flow and Mixing in Tundish [J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1998, 25(5): 387.
Morales R D, López-Ramírez S, Palafox Ramos J, et al. Mathematical Simulation of Effects of Flow Control Devices and Buoyancy Forces on Molten Steel Flow and Evolution of Output Temperatures in Tundish [J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2001, 28(1): 33.
Damle C, Sahai Y. The Effect of Tracer Density on Melt Flow Characterization in Continuous Casting Tundishes—A Modeling Study [J]. ISIJ Int, 1995, 35(2): 163.
Vargas-Zamora A, Morales R D, Diaz-Cruz M, et al. Heat and Mass Transfer of a Convection-Stratified Plow in a Trough Type Tundish [J]. Int J Heat and Mass Transfer, 2003, 46(16): 3029.
Szekely J, Llegbusi O J. The Physical and Mathematical Modeling of Tundish Operation [M]. New York, USA: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Damle C, Sahai Y. A Criterion for Water Modeling of Non-Isothermal Melt Flows in Continuous Casting Tundishes [J]. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36(6): 681.
Nauman E B, Buffham B A. Mixing in Continuous Flow System [M]. New York, USA: John Wiley and Sons Inc, 1983.
Nauman E B. Chemical Reactor Design [M]. New York, USA: John Wiley and Sons Inc, 1987.
Fan C M, Shie R J, Hwang W S. Studies by Mathematical and Physical Modeling of Fluid Flow and Inclusion Removal Phenomena in Slab Tundish for Casting Stainless Steel Using Various Flow Control Device Designs [J]. Ironmaking and Steel-making, 2003, 30(5): 341.
Sahai Y, Emi T. Criteria for Water Modeling of Melt Flow and Inclusion Removal in Continuous Casting Tundishes [J]. ISIJ Int, 1996, 36(9): 1166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alizadeh, M., Edris, H. & Shafyei, A. Fluid Flow and Mixing in Non-Isothermal Water Model of Continuous Casting Tundish. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 15, 7–13 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60022-9
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60022-9