Abstract
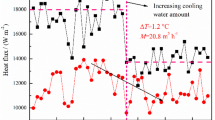
A monitoring method that has been designed for the first time for blast furnace wall with copper staves manufactured in China was introduced. Combining the method of “inverse problem” and the concept “non-inverse problem”, the monitoring program for blast furnace wall with copper staves has been realized, which can be used to calculate online the accretion thickness and temperature of hot surface of copper staves after obtaining the values of thermocouples of copper staves. The accretion state obtained in the actual investigation has proved that the result of the program is correct. The monitoring program shows that the accretion would easily fluctuate when the accretion layer is extremely thick or thin, thereby the stable and smooth operation of the blast furnace is hindered. By maintaining appropriate accretion thickness, both long campaigns and high productivity of the blast furnace can be achieved; furthermore, it can also optimize the operation of blast furnace and maximize its production. Approximately 30–50 mm in thickness of accretion layer is maintained on the wall of Shougang blast furnace 2, which can meet the requirement for obtaining both long campaign and high productivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHENG Su-sen, MA Xiang, YANG Tian-jun. Thermal Analysis Influence of Cooling Water Scale on Cooling Capacity of BF Stave [J]. Iron and Steel, 2002, 37(7): 16–19 (in Chinese).
CHENG Su-sen, YANG Tian-jun. Application of Heat Transfer Theory in Analysis and Research for Heat Load of Blast Furnace Wall [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2002, 14(2): 5–8 (in Chinese).
CHENG Su-sen, YANG Tian-jun, YANG Wei-guo, et al. Analysis of Heat Transfer and Temperature Field of Blast Furnace Copper Stave [J]. Iron and Steel, 2001, 36(2): 8–11 (in Chinese).
SHI Lin, CHENG Su-sen, ZHANG Li-jun. Thermal Distortion of Blast Furnace Copper Staves [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(12): 2040–2046 (in Chinese).
BAI Hao, CANG Da-qiang, ZONG Yan-bing. Experimental Study on Heat Transfer Characteristic of Blast Furnace Copper Stave [J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2002, 9(4): 258–259.
ZONG Yan-bin, CANG Da-qiang, CUI Heng. Experimental Study on the Copper Stave With Different Water Cooling Channels [J]. Metallurgy Research, 2005, 91–96.
LIU Qi. Adopting Copper Cooling Stave to prolong BF Campaign [J]. Ironmaking, 2002, 12(6): 7–10 (in Chinese).
QIAN Liang, CHENG Su-sen, LI Wei-guang, et al. Development of Model for Profile Control Based on the Inverse Problem in Heat Transfer of Wall With Copper Stave [J]. Ironmaking, 2006, 25(2): 18–22 (in Chinese).
QIAN Liang, CHENG Su-sen, ZHU Qing-tian. Monitoring of Copper Stave Supplied to Blast Furnace [J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2006, 30(4): 20–23 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (60472095)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Ss., Qian, L. & Zhao, Hb. Monitoring Method for Blast Furnace Wall With Copper Staves. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 14, 1–5 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(07)60048-X
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(07)60048-X