Abstract
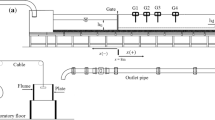
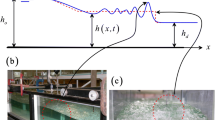
The one-dimensional steep slope shallow water equations are used to model the dam-break flow down a uniform slope with arbitrary inclination, and analytical solutions are derived by the hodograph transformation and the Riemann’s method in terms of evaluated integrals. An implicit analytical solution is obtained to evaluate the spatio-temporal distributions of dam-break flood hydrographs along the slope. For convenience, the solution for representative wave profiles and velocity distributions is shown in charts. Comparing with the Dressler’s solution and WES experimental data, the analytical solution is seen reasonable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SHIGEMATSU T., LIU P. L. F. and ODA K. Numerical modeling of the initial stages of dam-break waves[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2004, 42(2): 183–195
LEVEQUE R. J. Finite volume methods for hyperbolic problems [M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2002.
ZOPPOU C., ROBERTS S. Explicit schemes for dambreak simulations[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 2003, 129(1): 11–34
MACCHIONE F., MORELLI M. A. Practical aspects in comparing shock-capturing schemes for dam break problems[ J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 2003, 129(3): 187–195
HOGG A. J., PRITCHARD D. The effects of hydraulic resistance on dam-break and other shallow inertial flows[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2004, 501: 179–212.
ADDUCE C., SCIORTINO G. and PROIETTI S. Gravity currents produced by lock exchanges: Experiments and simulations with a two-layer shallow-water model with entrainment[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 2011, 138(2): 111–121
GOATER A. J. N., HOGG A. J. Bounded dam-break flows with tailwaters[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2011, 686: 160–186
HUANG Guo-fu, WU Chao and ZHANG Yi-fei et al. Analytical solutions for 1-D dam-break flood on sloping channel bed[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2005, 20(5): 597–603
ANCEY C., COCHARD S. The dam-break problem for Herschel-Bulkley viscoplastic fluids down steep flumes[ J]. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 2009, 158(1): 18–35
CHANSON H. Analytical solutions of laminar and turbulent dam break wave[C]. International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics River Flow. Lisbon, Portugal, 2006, 1: 465–474
BALDOCK T. E., HUGHES M. G. and DAY K. et al. Swash overtopping and sediment overwash on a truncated beach[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2005, 52(7): 633–645.
ANTUON M., HOGG A. J. Run-up and backwash bore formation from dam-break flow on an inclined plane[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2009, 640: 151–164
ANCEY C., IVERSON R. M. and RENTSCHLER M. et al. An exact solution for ideal dam-break floods on steep slopes[J]. Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(1): 1–10
FERNANDEZ-FERIA R. Dam-break flow for arbitrary slopes of the bottom[J]. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2006, 54(4): 319–331
DELESTRE O., LUCAS C. and KSINANT P. A. et al. SWASHES: A compilation of shallow water analytic solutions for hydraulic and environmental studies[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2013, 72(3): 269–300
MANGENEY A., HEINRICH P. and ROCHE R. Analytical solution for testing debris avalanche numerical models[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2000, 157(6–8): 1081–1096
EMMETT M., MOODIE T. B. Sediment transport via dam-break flows over sloping erodible beds[J]. Studies in Applied Mathematics, 2009, 123(3): 257–290
MARRA D., EARL T. and ANCEY C. Experimental investigations of dam break flows down an inclined channel[C]. Proceedings of the 34th World Congress of the International Association for Hydro-Environment Research and Engineering: 33rd Hydrology and Water Resources Symposium and 10th Conference on Hydraulics in Water Engineering. Brisbane, Australia, 2011.
PILOTTI M., TOMIROTTI M. and VALERIO G. et al. Simplified method for the characterization of the hydrograph following a sudden partial dam break[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE, 2010, 136(10): 693–704.
CHANG T. J., KAO H. M. and CHANG K. H. et al. Numerical simulation of shallow-water dam break flows in open channels using smoothed particle hydrodynamics[ J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 408(1): 78–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Major Program of the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51079130), the Fujian Provincial Major Course of Hydraulic.
Biography: WANG Li-hui (1972-), Male, Ph. D., Senior Engineer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Lh., Pan, Ch. An analysis of dam-break flow on slope. J Hydrodyn 26, 902–911 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(14)60099-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(14)60099-8