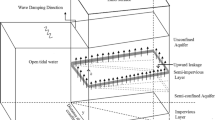
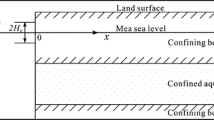
Abstract
In this article, a tide simulation system based on a two-way water pump technique is developed. Using this system and numerical simulations, the groundwater table fluctuation characteristics, relative over height of groundwater table, and influencing factors of over height are investigated. The experimental and numerical results indicate that the groundwater table fluctuation is of periodic, and of asymmetric. The amplitude of groundwater table fluctuations decreases with the increase of the onshore distances. There are phase lags of groundwater table fluctuations for different monitoring points. The tide can bring about remarkable over height of coastal groundwater table. The dominating factors bring about over height include the tide amplitude, aquifer thickness and tide frequency. Under experimental conditions, the relative tide amplitude over height may exceeded 50% of the maximal tide amplitude, and reach about 10% of aquifer thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HAN Long-xi, LI Wei and LU Yong-jun et al. Impact of artificial sand excavation on hydrodynamics and water environment of Dongjiang River network[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2005, 33(2): 123–126(in Chinese).
ZHOU Nian-qing, ZHU Xue-yu and QIAN Jia-zhong et al. The effect of tidal fluctuation on the unconfined aquifer of the site in the third phase of Qinshan nuclear power engineering[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. A, 2002, 17(3): 327–333(in Chinese).
LI Ling, BARRY D. A. and STAGNITTI F. et al. Submarine groundwater discharge and associated chemical input to a coastal sea[J]. Water Resource Research, 1999, 35(11): 3253–3259.
LI Yong, WANG Chao and YANG Lin-zhang et al. Influence of seepage face obliquity on discharge of groundwater and its pollutant into lake from a typical unconfined aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 2007, 19(6): 756–761.
LI Hai-long, JIAO J. J. Tide-induced seawater groundwater circulation in a mult-layered coastal leaky aquifer system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2003, 274(14): 211–224.
LI L., BARRY D. A. and PATTIARATCHI C. B. Numerical modeling of tide-induced beach water table fluctuations[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1997, 30(12): 105–123.
TURNER I. L. Simulating the influence of groundwater seepage on sediment transported by the sweep of the swash zone acrossmacro-tidal beaches[J]. Marine Geology, 1995, 125(12): 153–174.
ATAIE-ASHTIANI B., VOLKER R. E. and LOC-KINGTON D. A. Tidal effects on groundwater dynamics in unconfined aquifers[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2001, 15(4): 655–669.
TEO H. T., JENG D. S. and SEYMOUR B. R. et al. A new analytical solution for water table fluctuations in coastal aquifers with sloping beaches[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2003, 26(12): 1239–1247.
LI L., BARRY D. A. and STAGNITTI F. et al. Beach water table fluctuations due to spring-neap tides: Moving boundary effects[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2000, 23(8): 817–824.
SONG Zhi-yao, Li L. and NIELSEN P. et al. Quantification of tidal water table overheight in a coastal unconfined aquifer[J]. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2006, 56(4): 437–444.
ZHUANG Shui-ying, CHEN Juan and LI Ling. Numerical modeling of groundwater table fluctuations due to spring-neap tides in a coastal unconfined aquifer[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2006, 34(1): 10–12(in Chinese).
NIELSEN P., FENTON J. D. and ASEERVATHAM R. A. et al. Water table waves in aquifers of intermediate depths[J]. Advances Water Resources, 1997, 20(1): 37–43.
BAIRD A. J., HORN D. P. Monitoring and modelling groundwater behaviour in sandy beaches[J]. Coastal Research, 1996, 12(3): 630–640.
ZHANG Qian-fei, LAN Shou-qi and WANG Yan-ming et al. A new numerical method for groundwater flow and solute transport using velocity field[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 20(3): 356–364.
MA Xiu-yuan, LI Shu-guang and ZHU Wei-shen. A new method in groundwater flow modeling[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2009, 21(2): 245–254.
BAIRD A. J., MASON T. and HORN D. P. Validation of a Boussinesq model of beach groundwater behaviour[J]. Marine Geology, 1998,148(12): 55–69.
JENG D. S., LI L. and BARRY D. A. Analytical solution for tidal propagation in a coupled semi-confined/phreatic coastal aquifer[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(5): 577–584.
LI H. L., JIAO J. J. Analytical solutions of tidal groundwater flow in coastal two-aquifer system[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(4): 417–426.
LI H. L., JIAO J. J. Tidal groundwater level fluctuations in L-shaped leaky coastal aquifer system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 268(14): 234–243.
LI L., BARRY D. A. and CUNNINGHAM C. et al. A two-dimensional analytical solution of groundwater responses to tidal loading in an estuary and ocean[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2000, 23(8): 825–833.
NIELSEN P., ASEERVATHAM R. and FENTON J. D. et al. Groundwater waves in aquifers of intermediate depths[J]. Advances Water Resources, 1997, 20(1): 37–43.
RAUBENHEIMER B., GUZA R. T. and ELGAR S. Tidal water table fluctuations in a sandy beaches[J]. Water Resource Research, 1999, 35(8): 2313–2320.
HU Jian-wei, TANG Huai-ming. The numerical methods for the differential equations[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998, 282–289 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (Grant No. 0701006B).
Biography: WU Long-hua (1974- ), Male, Ph. D., Associate Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Lh., Zhuang, Sy. Experimental Investigation of Effect of Tide on Coastal Groundwater Table. J Hydrodyn 22, 66–72 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(09)60029-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(09)60029-9