Abstract
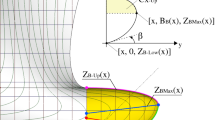
The parametric approach to design of hull form was studied in this work, which provides the means for quick generation and variation of hull form for the hydrodynamic optimization of hull form.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HARRIES S. Systematic optimization — A key for improving ship hydrodynamics[J]. Hansa, 2005, 142.
HARRIES S. Parametric design and hydrodynamic optimization of ship hull forms[D]. Ph. D. Thesis, Berlin, Germany: Technische Universität, 1998.
PIEGL L., TILLER W. The NURBS book[M]. Second Edition, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1997.
GAO Zhi-liang, ZOU Zao-jian. A three-dimensional desingularized high order panel method based on NURBS[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2008, 20(2): 137–146.
GAO Gao, MA Ling. A raised panel method based on NURBS for free-surface potential flows with forward speed[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 2003, 15(2): 112–120.
HARRIES S., ABT C. Parametric curve design applying fairness criteria[C]. International Workshop on Creating Fair and Shape-Preserving Curves and Surfaces, Network Fairshape. Berlin/Potsdam, Germany, 1998.
YANG You-zhong, YANG Yi and CHEN Wen-wei et al. The design of ship hull line[J]. Shanghai Shipbuilding, 2001, (2): 18–23(in Chinese).
HARRIES S., HINRICHSEN H. The InSAC — A new design feature for the improvement of transport efficiency[J]. Hansa, 2006, 143.
ABC C., BADE S. D. and BIRK L. Parametric hull form design—A step towards one week ship design[C]. 8th International Symposium on Practical Design of Ships and Other Floating Structures (PRADS 2001). Shanghai, 2001.
ABT C., HARRIES S. Friendship Framework-integrating ship-design modeling, simulation, and optimization[J]. The Naval Architect, RINA, 2007.
ABT C., Harries S. A new approach to integration of CAD and CFD for naval architects[C]. The 6th International Conference on Computer Applications and Information Technology in the Maritime Industries (COMPIT2007), Cortona, 2007.
PEREZ-ARRIBAS F., SUAREZ-SUAREZ J. A. and FERNANDEZ-JAMBRINA L. Auto surface modeling of a ship hull[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2006, 38: 584–594.
BIRMINGHAM R. W., SMITH T. A. G. Auto hull form generation, a practical tool for design and research[C]. In Practical Design of Ships and Mobile Units. Hague, 1998.
FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS. Imaging functionality for flexible shapes[J]. The Naval Architect, RINA, 2007.
HARRIES S. Fundamentals of advanced hydrodynamic design[J]. The Naval Architect, RINA, 2006.
HARRIES S., ABT C. and HOCHKIRCH K. Modeling meets simulation — Process integration to improve design[C]. Honorary Colloquium for Prof. Hagen, Prof. Schluter and Prof. Thiel. University of Duisburg-Essen, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: ZHANG Ping (1975- ), Female, Ph. D. Candidate, Senier Engineer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Zhu, Dx. & Leng, Wh. Parametric Approach to Design of Hull Forms. J Hydrodyn 20, 804–810 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(09)60019-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(09)60019-6