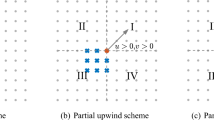
Abstract
In this paper, a hybrid finite-difference and finite-volume numerical scheme is developed to solve the 2-D Boussinesq equations. The governing equations are the extended version of Madsen and Sorensen’s formulations. The governing equations are firstly rearranged into a conservative form. The finite volume method with the HLLC Riemann solver is used to discretize the flux term while the remaining terms are discretized by using the finite difference method. The fourth order MUSCL-TVD scheme is employed to reconstruct the variables at the left and right states of the cell interface. The time marching is performed by using the explicit second-order MUSCL-Hancock scheme with the adaptive time step. The developed model is validated against various experimental measurements for wave propagation, breaking and runup on three dimensional bathymetries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LAKHAN V. C. Advances in coastal engineering[M]. Boston, USA: Elsevier, 2003, 1–41.
SORENSEN O. R., SCHAFFER H. A. and SORENSEN L. S. Boussinesq-type modelling using an unstructured finite element technique[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2004, 50(4): 181–198.
LI Yok-sheung, ZHAN Jie-min and SU Wei. Cheby-shev finite spectral method for 2-D extended Boussine-sq equations[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2011, 23(1): 1–11.
WEI G., KIRBY J. T. Time-dependent numerical code for extended boussinesq equations[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1995, 121(5): 251–261.
CHEN Q., KIRBY J. T. and DALRYMPLE R. A. et al. Boussinesq modeling of wave transformation, breaking, and runup. II: 2D[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 2000, 126(1): 48–56.
LYNETT P. J. Nearshore wave modeling with high-order Boussinesq-type equations[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 2006, 132(5): 348–357.
SHI F., KIRBY J. T. and HARRIS J. C. et al. A high-order adaptive time-stepping TVD solver for Boussinesq modeling of breaking waves and coastal inundation[J]. Ocean Modelling, 2012, 43–44: 36–51.
ERDURAN K. S., ILIC S. and KUTIJIA V. Hybrid finite-volume finite-difference scheme for the solution of boussinesq equations[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2005, 49(11): 1213–1232.
CIENFUEGOS R., BARTHELEMY E. and BONNE-TON P. A fourth-order compact finite volume scheme for fully nonlinear and weakly dispersive Boussinesq-type equations. Part I: Model development and analysis[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2006, 51(11): 1217–1253.
CIENFUEGOS R. A fourth-order compact finite volume scheme for fully nonlinear and weakly dispersive Boussinesq-type equations. Part Ii: Boundary conditions and validation[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2007, 53(9): 1423–1455.
ERDURAN K. S. Further application of hybrid solution to another form of boussinesq equations and comparisons[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2007, 53(5): 827–849.
SHIACH J. B., MINGHAM C. G. A temporally second-order accurate godunov-type scheme for solving the extended Boussinesq equations[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 56(1): 32–45.
ROEBER V., CHEUNG K. F. and KOBAYASHI M. H. Shock-capturing Boussinesq-type model for nearshore wave processes[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2010, 57(4): 407–423.
TONELLI M., PETTI M. Finite volume scheme for the solution of 2D extended Boussinesq equations in the surf zone[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2010, 37(7): 567–582.
ORSZAGHOVA J., BORTHWICK A. G. L. and TAYLOR P. H. From the paddle to the beach-a Boussinesq shallow water numerical wave tank based on madsen and Sørensen’s equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2012, 231(2): 328–344.
ROEBER V., CHEUNG K. F. Boussinesq-type model for energetic breaking waves in fringing reef enviro-nments[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2012, 70: 1–20.
TORO E. F. Riemann solvers and numerical methods for fluid dynamics, a pratical introduction[M]. Dordrecht, Heidelberg, London, New York: Springer, 2009.
KIM G., LEE C. and SUH K.-D. Extended Boussinesq equations for rapidly varying topography[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2009, 36(11): 842–851.
MADSEN P. A., SORENSEN S. R. A new form of the Boussinesq equations with improved linear dispersion characteristics. Part 2. A slowly-varying bathymetry[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1992, 18(3–4): 183–204.
HARTEN A., ENGQUIST B. and OSHER S. et al. Uniformly high order accurate essentially non-oscillatory schemes, III[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 131(1): 3–47.
BERKHOFF J. C. W., BOOY N. and RADDER A. C. Verification of numerical wave propagation models for simple harmonic linear waves[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1982, 6(3): 255–379.
BRIGGS M. J., SYNOLAKIS C. E. and HARKINS G. S., et al. Laboratory experiments of tsunami runup on a circular island[J]. Pageoph, 1995, 144(3–4): 569–593.
SWIGLE D. T. Laboratory study of the three-dimensional turbulence and kinematic properties associated with a breaking solitarywave[D]. Master Thesis, Texas, USA: Texas A&M University, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51009018, 51079042).
Biography: FANG Ke-zhao (1980-), Male, Ph. D., Lecturer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Kz., Zhang, Z., Zou, Zl. et al. Modelling of 2-D extended Boussinesq equations using a hybrid numerical scheme. J Hydrodyn 26, 187–198 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(14)60021-4
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(14)60021-4