Abstract
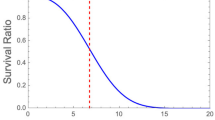
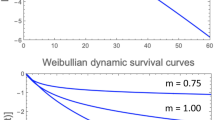
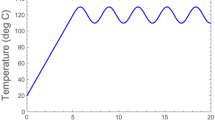
When the isothermal semi-logarithmic survival curves of heat inactivated microbial cells or spores are known to be linear it is possible to calculate their survival parameters from curves obtained under nonisothermal conditions, provided that the temperature history (’profile’) satisfies certain simple mathematical requirements. These requirements have been identified. The concept was tested by retrieving the survival parameters of a Listeria-like organism from generated survival curves for linear and nonlinear heating profiles on which noise had been superimposed. The availability of such a procedure eliminates the need to determine the survival parameters under perfect isothermal conditions, which are difficult to create for technical reasons. It will also enable determination of the survival parameters in the actual medium of interest, which may contain particles or may be too viscous to be treated in a capillary or narrow tube as is currently done. The method can also be used to assess survival parameters in nonthermal inactivation. A treatment with a dissipating chemical agent or anti-microbial is an example. In principle, the concept can be extended to the more general situation where the isothermal or iso-concentration semi-logarithmic survival curves are clearly nonlinear, but this will require a modification of the model and a different numerical calculation procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, W. F., P. J. McClure, A. C. Baird-Parker and M. B. Cole (1996). The application of a log-logistic model to describe the thermal inactivation of C. botulinum 213B at temperatures below 121.1 °C. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 80, 283–290.
Augustin, J. C., V. Carlier and J. Rozjier (1998). Mathematical modeling of the heat resistance of L. monocytogenes. Appl. Microbiol. 84, 185–191.
Brock, T. D., M. T. Madigan, J. M. Martinko and J. Parker (1994). Biology of Microorganisms, 7th edn, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Campanella, O. H. and M. Peleg (2001). Theoretical comparison of a new and the traditional method to calculate C. botulinum survival during thermal inactivation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 81, 1069–1076.
Casolari, A. (1988). Microbial death, in Physiological Models in Microbiology, M.J. Bazin and J.I. Prosser (Eds), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 1–44.
Davis, B. D., R. Dulbeco, H. N. Eisen and H. S. Ginsberg (1990). Microbiology, 4th edn, Philadelphia, PA: J.B. Lippincott.
Jay, J. M. (1996). Modern Food Microbiology, New York: Chapman and Hall.
Linton, R. H., W. H. Carter, M. D. Pierson, C. R. Hackney and J. D. Eifert (1996). Use of a modified Gompertz equation to model non linear survival curves of Listeria monocytogenes Scott A. J. Food Protec. 59, 16–23.
Mattick, K. L., J. D. Legan, T. J. Humphrey and M. Peleg (2001). Calculating Salmonella inactivation in non-isothermal heat treatments from isothermal non-linear survival curves. Food Res. Int. 34, 383–388.
Peleg, M. (2002). Modeling and simulation of microbial survival during treatments with a dissipating lethal chemical agent. Food Res. Int. 32, 327–336.
Peleg, M. and M. B. Cole (1998). Reinterpretation of microbial survival curves. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 38, 353–380.
Peleg, M. and C. M. Penchina (2000). Modeling microbial survival during exposure to a lethal agent with varying intensity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 40, 159–172.
Peleg, M., C. M. Penchina and M. B. Cole (2001). Estimation of the survival curve of Listeria monocytogenes during treatments from non-linear isothermal survival curves. J. Food Protec. 64, 606–613.
Prescot, L. M., J. P. Harley and D. A. Klein (1996). Microbiology, 3rd edn, Duboque IA: WCB.
Stephens, P. J., M. B. Cole and M. V. Jones (1994). Effect of heating rate on the thermal inactivation of Listeria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 77, 702–710.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peleg, M., Normand, M.D. & Campanella, O.H. Estimating microbial inactivation parameters from survival curves obtained under varying conditions—The linear case. Bull. Math. Biol. 65, 219–234 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8240(02)00097-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8240(02)00097-6