Abstract
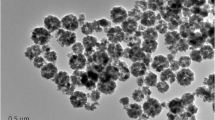
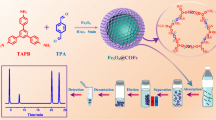
In this work, a novel magnetic covalent organic framework (COF (TpPa-NH2) @ Fe3O4) was prepared via two step by simple solvent method for the extraction of anionic azo dye residues in food. The as-prepared COF (TpPa-NH2) @ Fe3O4 nanocomposite was characterised by scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and vibrating sample magnetometer. Before high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection (HPLC-UV) determination, it was used as magnetic adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) to extract and pre-concentrate three anionic azo dyes in carbonated beverage samples. The several key extraction and desorption parameters affecting the extraction recovery rate were investigated, including extraction time, pH of the solution, amount of material, adsorption time, elution solvent, pH of elution solvent, type of elution solvent, elution volume and elution time. Under optimised conditions, this method has good linearity between 5 and 500 μg L–1 (correlation coefficient > 0.9986). The limit of detection was 2.3–3.4 μg L–1. The recoveries of the samples were between 87.5 and 96.9%, and the relative standard deviation lower than 4.6%. The developed method has broad application prospects for the analysis of anionic azo dyes in carbonated beverages.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Change history
07 May 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-024-00584-w
References
X.T. Zhang, J. Zhang, W.Q. Li, Y.X. Yang, P.G. Qin, X.B. Zhang, M.H. Lu, Food Addit. Contam. Part A 35(11), 2099–2110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2018.1526415
S. Dey, B.H. Nagababu, Food Chem. Adv. 1, 100019 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2022.100019
A. Downham, P. Collins, Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 35(1), 5–22 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2022.100019
S.I. Kaya, A. Cetinkaya, S.A. Ozkan, Food Chem. Toxicol. 156, 112524 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112524
S.N. Okafor, W. Obonga, M.A. Ezeokonkwo, J. Nurudeen, U. Orovwigho, J. Ahiabuike, Pharm. Biosci. J. (2016). https://doi.org/10.20510/ukjpb/4/i4/110639
M. Ramesh, A. Muthuraman, (Academic Press, 2018), pp. 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811518-3.00001-6
D. McCann, A. Barrett, A. Cooper, D. Crumpler, L. Dalen, K. Grimshaw, E. Kitchin, K. Lok, L. Porteous, E. Prince et al., Lancet 370(9598), 1560–1567 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61306-3
X.R. Wan, H.R. Dai, H.Y. Zhang, H. Yang, F. Li, Q. Xu, Sci. Total. Environ. 868, 161596 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107824
G.L. Dotto, T.R.S. Cadaval, L.A.A. Pinto, Process Biochem. 47(9), 1335–1343 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.04.029
Q.S. Zhang, X. Jiang, A.M. Kirillov, Y.W. Zhang, M.Y. Hu, W. Liu, L.Z. Yang, R. Fang, W.S. Liu, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7(3), 3203–3212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05146
X. Feng, X.S. Ding, D.L. Jiang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(18), 6010–6022 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CS35157A
J.R. Wang, J.J. Feng, Y.J. Lian, X. Sun, M.L. Wang, M. Sun, Food Chem. 405, 134818 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134818
P.J. Waller, F. Gándara, O.M. Yaghi, Acc. Chem. Res. 48(12), 3053–3063 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00369
T.T. Yang, C. Tian, X. Yan, R.Y. Xiao, Z. Lin, Environ. Sci. Nano 8(5), 1469–1480 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00059D
Q. Zhu, X. Wang, R. Clowes, P. Cui, L.J. Chen, M.A. Little, A.I. Cooper, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142(39), 16842–16848 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c07732
S. Li, J.P. Ma, G.G. Wu, J.H. Li, X.Y. Wang, L.X. Chen, J. Hazard. Mater. 424, 127687 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127687
Z. Chen, K. Wang, X.N. Hu, P.Z. Shi, Z.Y. Guo, H.B. Zhan, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(1), 1145–1151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c16116
W. Tan, X.H. Wu, W.R. Liu, F.G. Ye, S.L. Zhao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(3), 4352–4363 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18902
L.C. Wang, Y.Q. Tao, J.J. Wang, M. Tian, S.C. Liu, T. Quan, L.J. Yang, D.D. Wang, X. Li, D. Gao, Anal. Chim. Acta 1227, 340329 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.340329
S.P. Guan, H. Wu, L. Yang, Z.L. Wang, J.M. Wu, J. Sep. Sci. 43(19), 3775–3784 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202000616
H. Wu, S.P. Guan, L. Yang, D.R. Li, Anal. Lab. (2021). https://doi.org/10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2021.012301
W. Sun, Q. Xu, Q.L. Liu, T.L. Wang, Z.X. Liu, J. Chromatogr. A 1690, 463777 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2023.463777
J.L. Du, H. Wu, X. Jing, Y.H. Yu, Z.S. Yan, J.H. Zhang, Foods 11(19), 3130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11193130
G.Y. Li, L.L. Yao, Y.R. Jiang, K.L. Huang, P. Ding, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 320(1–3), 11–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.01.017
L. You, K. Xu, G. Ding, X. Shi, J. Li, S. Wang, J. Wang, J. Mol. Liq. 320, 114456 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114456
J.L. Liu, W.C. Qian, J.Z. Guo, Y. Shen, B. Li, Biores. Technol. 320, 124374 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124374
H. Molavi, A. Shojaei, A. Pourghaderi, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 524, 52–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.03.088
S. Ghorai, A.K. Sarkar, A.B. Panda, S. Pal, Biores. Technol. 144, 485–491 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.108
X.R. Shi, X.L. Chen, Y.L. Hao, L. Li, H.J. Xu, M.M. Wang, J. Chromatogr. B 1086, 146–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.04.022
R. Darabi, M. Shabani-Nooshabadi, Food Chem. 339, 127841 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127841
E. Kılınç, K.S. Çelik, H. Bilgetekin, Food Chem. 242, 533–537 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.039
M. Hemmati, M. Rajabi, Food Chem. 286, 185–190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.197
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Project of Shanxi Advanced Permanent Magnet Materials and Technology Provincial and Ministerial Collaborative Innovation Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no financial or non-financial conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
The original online version of this article was revised: With the authors’ decision to cancel Open Access the copyright of the article changed on 19 April 2024 to ©The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 2024.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, S., Wu, H., Lin, W. et al. Facile synthesis of amino-modified magnetic covalent organic framework for the efficient extraction and determination of anionic azo dyes in carbonated beverages. ANAL. SCI. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-024-00561-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-024-00561-3