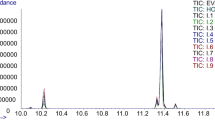
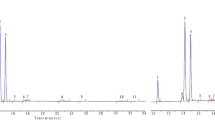
Abstract
Liquid chromatography‒mass spectrometry employing porous graphite carbon columns and an n-octane-isopropanol mobile phase was utilized for the separation of triacylglycerols (TAGs) in various edible oils, aiming to identify lard adulteration in soybean, corn, and sunflower seed oils. Experiments were conducted using a Hypercarb column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 5 µm) and an n-octane-isopropanol (70:30, V/V) mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.25 mL· min−1 and a column temperature of 60 °C. Detection was achieved through atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry. Analysis of diverse edible oil samples revealed that oils of the same type shared similar TAG compositions, while different types exhibited distinct TAG profiles. Distinct variations in triglyceride composition were observed across different edible oils. Based on liquid chromatography‒mass spectrometry analysis, the characteristic component 1-stearic acid-2-palmitic acid-3-oleic acid glyceride (SPO), which may also include PSO, was identified in lard through principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis. This component served as a marker for detecting as low as 0.1% lard adulteration in soybean, corn, and sunflower seed oils. The technique offers a precise and effective approach for the identification of lard adulteration in these edible oils.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Change history
09 May 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-024-00580-0
References
Y.B. Che Man, A. Rohman, T.S.T. Mansor, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 88, 187 (2011)
K.A. Al-Rashood, E.M. Abdel-Moety, A. Rauf, R.R. Abou-Shaaban, K.I. Al-Khamis, J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 18, 2661 (1995)
W.M. Cao, X.H. Sun, F.X. Chen, B. Xue, X.G. Wang, China. Oils. Fats. 37, 1 (2012)
F. Munir, S.G. Musharraf, S.T.H. Sherazi, M.I. Malik, M.I. Bhanger, Turk. J. Chem. 43, 1098 (2019)
A. Rohman, Y.B.C. Man, Food Res. Int. 43, 886 (2010)
N. Vanstone, A. Moore, P. Martos, S. Neethirajan, Food Qual. Saf. 2, 189 (2018)
A.A. Christy, S. Kasemsumran, Y. Du, Y. Ozaki, Anal. Sci. 20, 935 (2004)
Z. Hai, J. Wang, Sens. Actuat. B: Chem. 119, 449 (2006)
Z. Hai, J. Wang, Eur. J. Lipid. Sci. Tech. 108, 116 (2006)
M. Hajimahmoodi, Y. Vander Heyden, N. Sadeghi, B. Jannat, M.R. Oveisi, S. Shahbazian, Talanta 66, 1108 (2005)
C.R. Xing, X.Y. Yuan, X.Y. Wu, X.L. Shao, J. Yuan, W.J. Yan, LWT-Food Sci Technol. 108, 437 (2019)
J. Jin, L.X. Wang, J.P. Chen, Y.Z. Tian, L.L. Zou, B.Q. Zhang, S.Q. Wang, X.F. Wang, Chin. J. Chromatogr. 30, 1100 (2012)
S.C. Cunha, M. Oliveira, Food Chem. 95, 518 (2006)
N. Carranco, M. Farrés-Cebrián, J. Saurina, O. Núñez, Foods. 7, 44 (2018)
L.X. Wang, J. Jin, S.Q. Wang, X.F. Wang, Y.Z. Tian, J.P. Chen, Chin. J. Chromatogr. 30, 1094 (2012)
R.R. Catharino, R. Haddad, L.G. Cabrini, I.B.S. Cunha, A.C.H.F. Saway, M.N. Eberlin, Anal. Chem. 77, 7429 (2005)
I.M. Lorenzo, J.L.P. Pavón, M.E.F. Laespada, C.G. Pinto, B.M. Cordero, J. Chromatogr. A 945, 221 (2002)
K.I. Poulli, G.A. Mousdis, C.A. Georgiou, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 386, 1571 (2006)
D. Šmejkalová, A. Piccolo, Food Chem. 118, 153 (2010)
A. Cataldo, E. Piuzzi, G. Cannazza, E. De Benedetto, L. Tarricone, Measurement 43, 1031 (2010)
S. Indelicato, D. Bongiorno, R. Pitonzo, V.D. Stefano, V. Calabrese, S. Indelicato, G. Avellone, J. Chromatogr. A 1515, 1 (2017)
P. Dugo, T. Kumm, A. Fazio, G. Dugo, L. Mondello, J. Sep. Sci. 29, 567 (2006)
Y.X. Zeng, P. Araujo, Z.Y. Du, T.T. Nguyen, L. Frøyland, B. Grung, Talanta 82, 1261 (2010)
X.P. Wang, P.W. Li, X. Liu, Y.Q. Liu, Q. Zhang, L.X. Zhang, B. Matthäus, Eur. J. Lipid. Sci. Tech. 121, 1900029 (2019)
F. Wei, N. Hu, X. Lv, X.Y. Dong, H. Chen, J. Chromatogr. A 1404, 60 (2015)
R. He, X.L. Shan, F.Y. Dong, X. Xu, Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 43, 1377 (2015)
S.D. Zhang, C. Gong, Y. Lu, X. Xu, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 95, 1253 (2018)
X.T. Lu, S.D. Zhang, C. Gong, X. Xu, Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 48, 1084 (2020)
K. Xiao, C. Gong, Q.S. Guo, X. Xu, Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 48, 802 (2020)
M. Buchgraber, F. Ulberth, H. Emons, E. Anklam, Eur. J. Lipid. Sci. Tech. 106(621–648), 1438 (2004)
R.A. Coleman, D.P. Lee, Prog. Lipid Res. 43, 134 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 31671928), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (15ZR1440800), and Science and Technology Development Foundation of Shanghai Institute of Technology (KJFZ2023-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Xu Xu, Xiang-Ting Lu, Can Gong, Methodology: Can Gong, Xiang-Ting Lu, Xu Xu, Investigation: Xiang-Ting Lu, Can Gong, Shi-Ding Zhang, Kun Xiao, Funding acquisition: Xu Xu. Software; Xiang-Ting Lu, Can Gong, Supervision: Xu Xu, Writing—original draft: Can Gong, Xiang-Ting Lu, Writing—review & editing: Can Gong, Xu Xu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, C., Lu, XT., Zhang, SD. et al. Detection of lard adulteration in 3 kinds of vegetable oils by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry with porous graphite carbon column. ANAL. SCI. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-024-00560-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-024-00560-4