Abstract
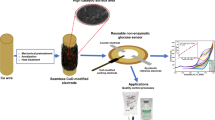
To minimize background interference in electrochemical enzymatic biosensors employing electron mediators, it is essential for the electrochemical oxidation of electroactive interfering species (ISs), such as ascorbic acid (AA), to proceed slowly, and for the redox reactions between electron mediators and ISs to occur at a low rate. In this study, we introduce a novel combination of a working electrode and an electron mediator that effectively mitigates interference effects. Compared to commonly used electrodes such as Au, glassy carbon, and indium tin oxide (ITO), boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes demonstrate significantly lower anodic current (i.e., lower background levels) in the presence of AA. Additionally, menadione (MD) exhibits notably slower reactivity with AA compared to other electron mediators such as Ru(NH3)63+, 4-amino-1-naphthol, and 1,4-naphthoquinone, primarily due to the lower formal potential of MD compared to AA. This synergistic combination of BDD electrode and MD is effectively applied in three biosensors: (i) glucose detection using electrochemical-enzymatic (EN) redox cycling, (ii) glucose detection using electrochemical-enzymatic-enzymatic (ENN) redox cycling, and (iii) lactate detection using ENN redox cycling. Our developed approach significantly outperforms the combination of ITO electrode and MD in minimizing IS interference. Glucose in artificial serum can be detected with detection limits of ~ 20 μM and ~ 3 μM in EN and ENN redox cycling, respectively. Furthermore, lactate in human serum can be detected with a detection limit of ~ 30 μM. This study demonstrates sensitive glucose and lactate detection with minimal interference, eliminating the need for (bio)chemical agents to remove interfering species.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
E.T. da Silva, D.E. Souto, J.T. Barragan, J. de F. Giarola, A.C. de Moraes, L.T. Kubota, ChemElectroChem (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201600758
G. Hernandez-Vargas, J.E. Sosa-Hernández, S. Saldarriaga-Hernandez, A.M. Villalba-Rodríguez, R. Parra-Saldivar, H.M. Iqbal, Biosens. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020029
A. Singh, A. Sharma, A. Ahmed, A.K. Sundramoorthy, H. Furukawa, S. Arya, A. Khosla, Biosens. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090336
N. Zare-Shehneh, F. Mollarasouli, M. Ghaedi, Critical. Rev. Anal. Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2021.1967719
Y. Zeng, Z. Zhu, D. Du, Y. Lin, J. Electroanal. Chem. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.10.030
M. R. Romero, M. L. Picchio (2020). Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials: Transducers and Modified Surfaces for Diagnostics. In: P. Chandra, R. Prakash (eds) Nanobiomaterial Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9437-1_4
B. Jurado-Sánchez (2023). Nanobioelectrochemical Sensors in Clinical Diagnosis. In: U. P. Azad, P. Chandra (eds) Handbook of Nanobioelectrochemistry. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9840-8_2
E.B. Aydın, M.K. Sezgintürk, Trends Anal. Chem. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.09.021
P. Nandhakumar, A.M. Ichzan, N.-S. Lee, Y.H. Yoon, S. Ma, S. Kim, H. Yang, ACS Senss (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b01448
S. Park, D.-E. Kwak, A.-M.J. Haque, N.-S. Lee, Y.H. Yoon, H. Yang, ACS Senss (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c02346
J. Kwon, J.H. Jeon, S.I. Yang, H. Yang, Electroanalysis (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202300063
M.R. Akanda, H.-A. Joung, V. Tamilavan, S. Park, S. Kim, M.H. Hyun, M.-G. Kim, H. Yang, Analyst (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN02328A
M.R. Akanda, Y.-L. Choe, H. Yang, Anal. Chem. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202638y
G. Dutta, S. Kim, S. Park, H. Yang, Anal. Chem. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5006487
M.R. Akanda, V. Tamilavan, S. Park, K. Jo, M.H. Hyun, H. Yang, Anal. Chem. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3028855
J. Jeong, J. Das, M. Choi, J. Jo, M.A. Aziz, H. Yang, Analyst (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN01174K
S. Noh, H. Yang, Electroanalysis (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201400383
F. Arslan, U. Beskan, Artif. Cells, Nanomed. Biotechnol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2013.812650
S. Liu, Y. Jia, Y. Li, P. Wang, Z. Xu, Q. Liu, Y. Li, Q. Wei, ACS Sens. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01695
Y. Wu, S. Ali, R.J. White, ACS Sens. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02363
S. Karuppiah, N.C. Mishra, W.-C. Tsai, W.-S. Liao, C.-F. Chou, ACS Sens. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c00851
S. Park, J. Kim, H. Ock, G. Dutta, J. Seo, E.-C. Shin, H. Yang, Analyst (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN01086A
K. Lee, G. Song, J. Kwon, J. Kim, H. Yang, Electroanalysis (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202200051
P. Nandhakumar, A.-M.J. Haque, N.-S. Lee, Y.H. Yoon, H. Yang, Anal. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02590
J. Kang, J. Shin, H. Yang, Electroanalysis (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800119
J. Xu, Y. Yokota, R.A. Wong, Y. Kim, Y. Einaga, J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b11183
T. Watanabe, Y. Honda, K. Kanda, Y. Einaga, Phys. Status Solidi (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201431455
J.V. Macpherson, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP04022H
C. Yamaguchi, K. Natsui, S. Iizuka, Y. Tateyama, Y. Einaga, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CP07402J
N. Yang, S. Yu, J.V. Macpherson, Y. Einaga, H. Zhao, G. Zhao, G.M. Swain, X. Jiang, Chem. Soc. Rev. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201901088
K. Muzyka, J. Sun, T.H. Fereja, Y. Lan, W. Zhang, G. Xu, Anal. Methods (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY02197J
M. Yence, A. Cetinkaya, G. Ozcelikay, S.I. Kaya, S.A. Ozkan, Critical. Rev. Anal. Chem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY02197J
Y. Qi, H. Long, L. Ma, Q. Wei, S. Li, Z. Yu, J. Hu, P. Liu, Y. Wang, L. Meng, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.08.158
J. Fei, L. Luo, S. Hu, Z. Gao, Electroanalysis (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/bkcs.12147
J. Shin, K. Park, S. Park, H. Yang, Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/bkcs.12147
J. Kwon, J.H. Jeon, S.I. Yang, H. Yang, Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/bkcs.12424
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (2022R1A4A2000778 and 2021R1A2C3012115).
Funding
National Research Foundation of Korea, 2022R1A4A2000778, Haesik Yang, 2021R1A2C3012115, Haesik Yang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NY and YJ are equally contributed. Conceptualization: NY, YJ, HY, Investigation: NY, YJ, Supervision: GK, JK, HY, Writing—original draft: NY, Writing—review & editing: NY, HY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, N., Jung, Y., Kim, G. et al. Low-interference and sensitive electrochemical detection of glucose and lactate using boron-doped diamond electrode and electron mediator menadione. ANAL. SCI. 40, 853–861 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00497-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00497-0