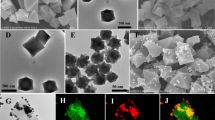
Abstract
In this work, a biological metal–organic framework@conductive covalent organic framework composite (bio-MOF@con-COF, denoted as Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF, here, Glu indicates L-glutamic acid, PT indicates 1,10-phenanthroline-2,9-dicarbaldehyde, and BD indicates benzene-1,4-diamine) was prepared and used as sensing material to fabricate aptasensor for trace detection of Staphylococcus aureus (SA). The Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF integrates the mesoporous structure and abundant defects of the MOF framework, the excellent conductivity of the COF framework, and high stability of the composite, providing abundant active sites to effectively anchor aptamers. As a result, the Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF-based aptasensor shows high sensitivity to detect SA via specific recognition between aptamer and SA, as well as the formation of aptamer–SA complex. Low detection limits of 2.0 and 1.0 CFU·mL−1 are deduced from the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and differential pulse voltammetry within a wide linear range of 10–108 CFU·mL−1 for SA, respectively. The Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF-based aptasensor also shows good selectivity, reproducibility, stability, regenerability, and applicability for real milk and honey samples. Therefore, the Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF-based aptasensor will be promising for fast screening of foodborne bacteria in food service industry.
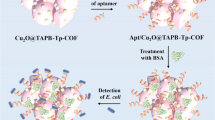
Graphical abstract
Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF composite was prepared and used as sensing material to fabricate aptasensor for trace detection of Staphylococcus aureus (SA). Low detection limits of 2.0 and 1.0 CFU·mL−1 are deduced from the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and differential pulse voltammetry within a wide linear range of 10–108 CFU·mL−1 for SA, respectively. The Zn-Glu@PTBD-COF-based aptasensor also shows good selectivity, reproducibility, stability, regenerability, and applicability for real milk and honey samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that all the experimental data are available.
References
Y. Wang, T.V. Duncan, Nanoscale sensors for assuring the safety of food products. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 44, 74–86 (2017)
Z. Zhang, F. Duan, L. He, D. Peng, F. Yan, M. Wang, W. Zong, C. Jia, Electrochemical clenbuterol immunosensor based on a gold electrode modified with zinc sulfide quantum dots and polyaniline. Microchim. Acta 183, 1089–1097 (2016)
T. Leal, L. Abrunhosa, L. Domingues, A. Venâncio, C. Oliveira, BSA-based sample clean-up columns for ochratoxin a determination in wine: Method development and validation. Food Chem. 300, 125204 (2019)
A.A. Chavan, H. Li, A. Scarpellini, S. Marras, L. Manna, A. Athanassiou, D. Fragouli, Elastomeric nanocomposite foams for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7, 14778–14784 (2015)
J. Hu, Z. Shen, L. Tan, J. Yuan, N. Gan, Electrochemical aptasensor for simultaneous detection of foodborne pathogens based on a double stirring bars-assisted signal amplification strategy. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 345, 130337 (2021)
H. Chen, X. Wang, J. Li, X. Wang, Cotton derived carbonaceous aerogels for the efficient removal of organic pollutants and heavy metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 6073–6081 (2015)
M. Al Mamun, Y.A. Wahab, M.M. Hossain, A. Hashem, M.R. Johan, Electrochemical biosensors with aptamer recognition layer for the diagnosis of pathogenic bacteria: barriers to commercialization and remediation. TrAC-Trend. Anal. Chem. 145, 116458 (2021)
V. Subjakova, V. Oravczova, M. Tatarko, T. Hianik, Advances in electrochemical aptasensors and immunosensors for detection of bacterial pathogens in food. Electrochim. Acta 389, 138724 (2021)
K.L. Lin, T. Yang, H.Y. Zou, Y.F. Li, C.Z. Huang, Graphitic C3N4 nanosheet and hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme-based label-free chemiluminescence aptasensing for biomarkers. Talanta 192, 400–406 (2019)
J. Li, L. Liu, Y. Ai, Y. Liu, H. Sun, Q. Liang, Self-polymerized dopamine-decorated Au NPs and coordinated with Fe-MOF as a dual binding sites and dual signal-amplifying electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of CEA. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12, 5500–5510 (2020)
K. Xiang, D. Wu, X. Deng, M. Li, S. Chen, P. Hao, X. Guo, J. Luo, X. Fu, Boosting H2 generation coupled with selective oxidation of methanol into value-added chemical over cobalt Hydroxide@Hydroxysulfide nanosheets electrocatalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1909610 (2020)
F. Duan, C. Guo, M. Hu, Y. Song, M. Wang, L. He, Z. Zhang, R. Pettinari, L. Zhou, Construction of the 0D/2D heterojunction of Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets and iron phthalocyanine quantum dots for the impedimetric aptasensing of microRNA-155. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 310, 127844 (2020)
T. Xu, H. Dai, Y. Jin, Electrochemical sensing of lead (II) by differential pulse voltammetry using conductive polypyrrole nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 187, 1–7 (2020)
J. Jiang, F. Li, S. Bai, Y. Wang, K. Xiang, H. Wang, J. Zou, J. Hsu, Carbonitride MXene Ti3CN(OH)x@MoS2 hybrids as efficient electrocatalyst for enhanced hydrogen evolution. Nano Res. 15, 1–8 (2022)
C. Gu, C. Guo, Z. Li, M. Wang, N. Zhou, L. He, Z. Zhang, M. Du, Bimetallic ZrHf-based metal-organic framework embedded with carbon dots: Ultra-sensitive platform for early diagnosis of HER2 and HER2-overexpressed living cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 134, 8–15 (2019)
J. Li, J. Zhao, S. Li, Y. Chen, W. Lv, J. Zhang, L. Zhang, Z. Zhang, X. Lu, Synergistic effect enhances the peroxidase-like activity in platinum nanoparticle-supported metal–organic framework hybrid nanozymes for ultrasensitive detection of glucose. Nano Res. 14, 4689–4695 (2021)
X. Ma, C. Pang, S. Li, Y. Xiong, J. Li, J. Luo, Y. Yang, Synthesis of Zr-coordinated amide porphyrin-based two-dimensional covalent organic framework at liquid-liquid interface for electrochemical sensing of tetracycline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 146, 111734 (2019)
Y. Deng, Y. Wang, Z. Di, M. Xie, F. Dai, S. Zhan, Z. Zhang, Confining Metal-Organic framework in the pore of covalent organic framework: a microscale Z-Scheme system for boosting photocatalytic performance. Small Methods 6, 2200265 (2022)
Y. Deng, Y. Wang, X. Xiao, B.J. Saucedo, Z. Zhu, M. Xie, X. Xu, K. Yao, Y. Zhai, Z. Zhang, J. Chen, Progress in hybridization of covalent organic frameworks and metal–organic frameworks. Small 18, 2202928 (2022)
R. Liu, K.T. Tan, Y. Gong, Y. Chen, Z. Li, S. Xie, T. He, Z. Lu, H. Yang, D. Jiang, Covalent organic frameworks: An ideal platform for designing ordered materials and advanced applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 120–242 (2021)
Y. Xue, S. Zheng, H. Xue, H. Pang, Metal–organic framework composites and their electrochemical applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 7301–7327 (2019)
X. Zhang, G. Xie, D. Gou, P. Luo, Y. Yao, H. Chen, A novel enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on high catalytic Cu-ZrMOF and conductive Super P. Biosens. Bioelectron. 142, 111486 (2019)
W. Wang, L. Tan, J. Wu, T. Li, H. Xie, D. Wu, N. Gan, A universal signal-on electrochemical assay for rapid on-site quantitation of vibrio parahaemolyticus using aptamer modified magnetic metal–organic framework and phenylboronic acid-ferrocene co-immobilized nanolabel. Anal. Chim. Acta 1133, 128–136 (2020)
J. Hu, D. Wu, T. Li, Y. Cao, X. Wang, N. Gan, Ratiometric electrochemical aptasensor for point-of-care testing Vibrio parahaemolyticus together with antimicrobial peptide-labeled nano metal-organic framework signal tag. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 352, 130987 (2022)
N. Li, J. Liu, J.J. Liu, L.Z. Dong, Z.F. Xin, Y.L. Teng, Y.Q. Lan, Adenine components in biomimetic metal–organic frameworks for efficient CO2 photoconversion. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 58, 5226–5231 (2019)
S. Hajra, M. Sahu, A.M. Padhan, I.S. Lee, D.K. Yi, P. Alagarsamy, S.S. Nanda, H.J. Kim, A green metal–organic framework-cyclodextrin mof: a novel multifunctional material based triboelectric nanogenerator for highly efficient mechanical energy harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2101829 (2021)
S. Wang, M. Wahiduzzaman, L. Davis, A. Tissot, W. Shepard, J. Marrot, C. Martineau-Corcos, D. Hamdane, G. Maurin, S. Devautour-Vinot, A robust zirconium amino acid metal-organic framework for proton conduction. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–8 (2018)
R. Nivetha, K. Gothandapani, V. Raghavan, Q. Van Le, S. Pitchaimuthu, M. Muthuramamoorty, S. Pandiaraj, A. Alodhayb, S. Kwan Jeong, A. Nirmala Grace, Nano‐MOF‐5 (Zn) Derived porous carbon as support electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ChemCatChem 13, 4342–4349 (2021)
A. Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, T. Jesionowski, Zinc oxide—from synthesis to application: a review. Materials 7, 2833–2881 (2014)
R. Huang, L. Wang, L. Guo, Highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence displacement method for the study of DNA/small molecule binding interactions. Anal. Chim. Acta 676, 41–45 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project (222102310493).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Y., Ma, Z., Huang, Y. et al. Construction of MOF@COF composite-based electrochemical aptasensor for detection of Staphylococcus aureus. ANAL. SCI. 39, 901–909 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00295-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00295-8