Abstract
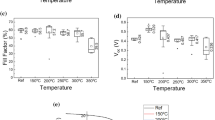
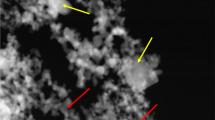
Sputter-deposited high-entropy materials, including high-entropy alloy (HEA) and high-entropy oxide (HEO), are demonstrated for use as selective solar absorber coatings (SSCs). Multi-layer SSC consists of CrFeCoNiAl HEA as the IR reflector layer, (CrFeCoNi)O medium-entropy oxide as the first layer absorber, and (CrMnFeCoNi)O HEO as the second layer absorber. The effects of phase and elemental concentration of the second layer absorber on the optical properties and thermal stability are addressed. The (CrMnFeCoNi)O HEO hematite has better spectral selectivity than the (CrMnFeCoNi)O HEO spinel. Meanwhile, from the X-Ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy analyses of the annealed samples, the (CrMnFeCoNi)O HEO spinel exhibits better thermal stability than (CrMnFeCoNi)O HEO hematite. This work provides guidance to create an effective solar absorber.
Graphical Abstract
(CrMnFeCoNi)O hematite solar absorber exhibits better spectral selectivity than (CrMnFeCoNi)O spinel. (CrMnFeCoNi)O spinel exhibits better thermal stability than (CrMnFeCoNi)O hematite. The thermal instability of the spinel originates from the metal diffusion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available on request.
References
M.A. Green, K. Emery, Y. Hishikawa, W. Warta, E.D. Dunlop, Solar cell efficiency tables (Version 45). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 23, 1–9 (2015)
D. Abbott, Keeping the energy debate clean: how do we supply the world’s energy needs? Proc. IEEE 98, 42–66 (2009)
N.S. Lewis, G. Crabtree, A.J. Nozik, M.R. Wasielewski, P. Alivisatos, H. Kung, J. Tsao, E. Chandler, W. Walukiewicz, M. Spitler, Basic Research Needs for Solar Energy Utilization. Report of the Basic Energy Sciences Workshop on Solar Energy Utilization, April 18–21, 2005. DOESC (USDOE Office of Science (SC)), (2005)
C.E. Kennedy, Review of mid- to high-temperature solar selective absorber materials. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (2002). https://doi.org/10.2172/15000706
C.K. Ho, A.R. Mahoney, A. Ambrosini, M. Bencomo, A. Hall, T.N. Lambert, Characterization of pyromark 2500 paint for high-temperature solar receivers. J. Sol. Energy Eng. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4024031
S. Hosseini, J.F. Torres, M. Taheri, A. Tricoli, W. Lipiński, J. Coventry, Long-term thermal stability and failure mechanisms of Pyromark 2500 for high-temperature solar thermal receivers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 246, 111898 (2022)
J. Liu, Thermodynamically stable, plasmonic transition metal oxide nanoparticle solar selective absorbers towards 95% optical-to-thermal conversion efficiency at 750 °C. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (2021). https://doi.org/10.2172/1890656
X. Wang, E. Lee, C. Xu, J. Liu, High-efficiency, air-stable manganese–iron oxide nanoparticle-pigmented solar selective absorber coatings toward concentrating solar power systems operating at 750 °C. Mater. Today Energy 19, 100609 (2021)
Y. Yin, Y. Pan, L. Hang, D. McKenzie, M. Bilek, Direct current reactive sputtering Cr–Cr2O3 cermet solar selective surfaces for solar hot water applications. Thin Solid Films 517, 1601–1606 (2009)
H. Liu, Q. Wan, B. Lin, L. Wang, X. Yang, R. Wang, D. Gong, Y. Wang, F. Ren, Y. Chen, The spectral properties and thermal stability of CrAlO-based solar selective absorbing nanocomposite coating. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 122, 226–232 (2014)
H. Liu, B. Yang, M. Mao, Y. Liu, Y. Chen, Y. Cai, D. Fu, F. Ren, Q. Wan, X. Hu, Enhanced thermal stability of solar selective absorber based on nano-multilayered TiAlON films deposited by cathodic arc evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 501, 144025 (2020)
N. Selvakumar, H.C. Barshilia, K. Rajam, A. Biswas, Structure, optical properties and thermal stability of pulsed sputter deposited high temperature HfOx/Mo/HfO2 solar selective absorbers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94, 1412–1420 (2010)
M.-H. Tsai, J.-W. Yeh, High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2, 107–123 (2014)
C.M. Rost, E. Sachet, T. Borman, A. Moballegh, E.C. Dickey, D. Hou, J.L. Jones, S. Curtarolo, J.-P. Maria, Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nat. Commun. 6, 8485 (2015)
A. Mao, F. Quan, H.-Z. Xiang, Z.-G. Zhang, K. Kuramoto, A.-L. Xia, Facile synthesis and ferrimagnetic property of spinel (CoCrFeMnNi) 3O4 high-entropy oxide nanocrystalline powder. J. Mol. Struct. 1194, 11–18 (2019)
Y. Dong, K. Ren, Y. Lu, Q. Wang, J. Liu, Y. Wang, High-entropy environmental barrier coating for the ceramic matrix composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 2574–2579 (2019)
D. Bérardan, S. Franger, D. Dragoe, A.K. Meena, N. Dragoe, Colossal dielectric constant in high entropy oxides. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 10, 328–333 (2016)
A. Radoń, Ł Hawełek, D. Łukowiec, J. Kubacki, P. Włodarczyk, Dielectric and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of high entropy (Zn, Fe, Ni, Mg, Cd) Fe 2 O 4 ferrite. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–13 (2019)
J. Dąbrowa, M. Stygar, A. Mikuła, A. Knapik, K. Mroczka, W. Tejchman, M. Danielewski, M. Martin, Synthesis and microstructure of the (Co, Cr, Fe, Mn, Ni) 3O4 high entropy oxide characterized by spinel structure. Mater. Lett. 216, 32–36 (2018)
M. Biesuz, L. Spiridigliozzi, G. Dell’Agli, M. Bortolotti, V.M. Sglavo, Synthesis and sintering of (Mg Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) O entropy-stabilized oxides obtained by wet chemical methods. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 8074–8085 (2018)
L. Spiridigliozzi, C. Ferone, R. Cioffi, G. Accardo, D. Frattini, G. Dell’Agli, Entropy-stabilized oxides owning fluorite structure obtained by hydrothermal treatment. Materials 13, 558 (2020)
D. Wang, Z. Liu, S. Du, Y. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Xiao, W. Chen, R. Chen, Y. Wang, Y. Zou, Low-temperature synthesis of small-sized high-entropy oxides for water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 24211–24216 (2019)
A. Sarkar, L. Velasco, D. Wang, Q. Wang, G. Talasila, L. de Biasi, C. Kübel, T. Brezesinski, S.S. Bhattacharya, H. Hahn, High entropy oxides for reversible energy storage. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–9 (2018)
A. Sarkar, R. Djenadic, N.J. Usharani, K.P. Sanghvi, V.S. Chakravadhanula, A.S. Gandhi, H. Hahn, S.S. Bhattacharya, Nanocrystalline multicomponent entropy stabilised transition metal oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 37, 747–754 (2017)
P. Meisenheimer, T. Kratofil, J. Heron, Giant enhancement of exchange coupling in entropy-stabilized oxide heterostructures. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–6 (2017)
C.-Y. He, X.-H. Gao, D.-M. Yu, X.-L. Qiu, H.-X. Guo, G. Liu, Scalable and highly efficient high temperature solar absorber coatings based on high entropy alloy nitride AlCrTaTiZrN with different antireflection layers. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 6413–6422 (2021)
C.-Y. He, X.-H. Gao, M. Dong, X.-L. Qiu, J.-H. An, H.-X. Guo, G. Liu, Further investigation of a novel high entropy alloy MoNbHfZrTi based solar absorber coating with double antireflective layers. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 217, 110709 (2020)
C.-Y. He, X.-H. Gao, D.-M. Yu, S.-S. Zhao, H.-X. Guo, G. Liu, Toward high-temperature thermal tolerance in solar selective absorber coatings: choosing high entropy ceramic HfNbTaTiZrN. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 21270–21280 (2021)
H.-X. Guo, C.-Y. He, X.-L. Qiu, Y.-Q. Shen, G. Liu, X.-H. Gao, A novel multilayer high temperature colored solar absorber coating based on high-entropy alloy MoNbHfZrTi: optimized preparation and chromaticity investigation. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 209, 110444 (2020)
S.-S. Zhao, C.-Y. He, X.-L. Qiu, P. Zhao, B.-H. Liu, G. Liu, X.-H. Gao, G.-K. Tian, High-entropy alloy nitride AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZrNx-based high-temperature solar absorber coating: structure, optical properties, and thermal stability. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 5, 9214–9224 (2022)
M. López-Herraiz, A.B. Fernández, N. Martinez, M. Gallas, Effect of the optical properties of the coating of a concentrated solar power central receiver on its thermal efficiency. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 159, 66–72 (2017)
X.-H. Gao, X.-L. Qiu, X.-T. Li, W. Theiss, B.-H. Chen, H.-X. Guo, T.-H. Zhou, G. Liu, Structure, thermal stability and optical simulation of ZrB2 based spectrally selective solar absorber coatings. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 193, 178–183 (2019)
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299–303 (2004)
K. Srinivas, M. Manivel Raja, D.V. Sridhara Rao, S.V. Kamat, Effect of sputtering pressure and power on composition, surface roughness, microstructure and magnetic properties of as-deposited Co2FeSi thin films. Thin Solid Films 558, 349–355 (2014)
Y. He, L. Zhang, H.W. Xiong, K.C. Zhou, X. Kang, The selective site occupation, structural and thermal stability of high entropy (CoCrFeMnNi)3O4 spinel. J. Alloys Comp. 965, 171428 (2023)
Z. Grzesik, G. Smoła, M. Miszczak, M. Stygar, J. Dąbrowa, M. Zajusz, K. Świerczek, M. Danielewski, Defect structure and transport properties of (Co, Cr, Fe, Mn, Ni)3O4 spinel-structured high entropy oxide. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40, 835–839 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Council under Grant Number NSTC 112-2224-E-006-003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Sari, F.N.I., Li, SY. et al. High-Entropy Oxide Solar Selective Absorber. High Entropy Alloys & Materials (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44210-024-00028-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44210-024-00028-0