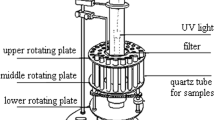
Abstract
Nitrite ions and ammonia are widespread forms of inorganic water pollutants. Nevertheless, the mechanisms of their photolytic and photocatalytic reactions under UV-A irradiation are still fully undisclosed, particularly, at different pH values under aerobic and inert atmospheres. Herein, we have studied the photolytic decomposition of nitrite ions under different conditions using 365 nm UV-A LED as a light source instead of mercury lamps that emit photons in the UV-B region and generate a lot of heat. The results indicated that the rate of nitrite disproportionation in the dark at pH ≤ 3.0 is remarkably high relative to the rate of the photolytic decomposition. At pH ˃ 3, the photolytic reaction is negligible and nitrite ions showed considerable stability. In contrast, the photocatalytic oxidation of nitrite ions over TiO2 photocatalysts, namely, TiO2P25, TiO2UV100, and TiO2 anatase/brookite mixture proceeds at pH ˃ 3.0. TiO2 P25 exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity at pH 5. Interestingly, the photolytic simultaneous removal of nitrite ions and ammonia was possible at pH 9.0 in the absence of oxygen (Ar atmosphere). A 42.69 ± 0.66%, 27.75 ± 1.7%, and 32.74 ± 0.59% of nitrogen calculated based on nitrite, ammonia, and both of them, respectively, can be removed after 6 h of UV-A irradiation. The selectivity of N2 evolution was 77.6%. The nitrogen removal rate was significantly reduced in the presence of TiO2 photocatalyst evincing that TiO2 photocatalysis is applicable for nitrite ions oxidation, whereas the photolytic process is better suited for the simultaneous removal of nitrite ions and ammonia.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kocour Kroupová, H., Valentová, O., Svobodová, Z., Šauer, P., & Máchová, J. (2018). Toxic effects of nitrite on freshwater organisms: A review. Reviews in Aquaculture, 10, 525–542.
Wang, P., Wang, M., Zhou, F., Yang, G., Qu, L., & Miao, X. (2017). Development of a paper-based, inexpensive, and disposable electrochemical sensing platform for nitrite detection. Electrochemistry Communications, 81, 74–78.
Rizvi, M., Gerengi, H., Kaya, S., Uygur, I., Yıldız, M., Sarıoglu, I., Cingiz, Z., Mielniczek, M., & El Ibrahimi, B. (2021). Sodium nitrite as a corrosion inhibitor of copper in simulated cooling water. Scientific Reports, 11, 8353.
Radhakrishnan, S., Krishnamoorthy, K., Sekar, C., Wilson, J., & Kim, S. J. (2014). A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for nitrite detection based on Fe2O3 nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 148–149, 22–28.
Balasubramanian, P., Settu, R., Chen, S.-M., Chen, T.-W., & Sharmila, G. (2018). A new electrochemical sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of nitrite in food samples based on sonochemical synthesized calcium ferrite (CaFe2O4) clusters modified screen printed carbon electrode. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 524, 417–426.
Altomare, M., & Selli, E. (2013). Effects of metal nanoparticles deposition on the photocatalytic oxidation of ammonia in TiO2 aqueous suspensions. Catalysis Today, 209, 127–133.
Fan, X., Zhou, Y., Zhang, G., Liu, T., & Dong, W. (2019). In situ photoelectrochemical activation of sulfite by MoS2 photoanode for enhanced removal of ammonium nitrogen from wastewater. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 244, 396–406.
Shavisi, Y., Sharifnia, S., Hosseini, S., & Khadivi, M. (2014). Application of TiO2/perlite photocatalysis for degradation of ammonia in wastewater. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 278–283.
Pretzer, L. A., Carlson, P. J., & Boyd, J. E. (2008). The effect of Pt oxidation state and concentration on the photocatalytic removal of aqueous ammonia with Pt-modified titania. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 200, 246–253.
Zhang, X., Ren, P., Li, W., Lei, Y., Yang, X., & Blatchley, E. R., III. (2019). Synergistic removal of ammonium by monochloramine photolysis. Water Research, 152, 226–233.
Mokhtar, B., Kandiel, T. A., Ahmed, A. Y., & Komy, Z. R. (2021). New application for TiO2 P25 photocatalyst: A case study of photoelectrochemical sensing of nitrite ions. Chemosphere, 268, 128847.
Gao, W., Chen, J., Guan, X., Jin, R., Zhang, F., & Guan, N. (2004). Catalytic reduction of nitrite ions in drinking water over Pd–Cu/TiO2 bimetallic catalyst. Catalysis Today, 93, 333–339.
Ye, J., Liu, S.-Q., Liu, W.-X., Meng, Z.-D., Luo, L., Chen, F., & Zhou, J. (2019). Photocatalytic simultaneous removal of nitrite and ammonia via a zinc ferrite/activated carbon hybrid catalyst under UV-visible irradiation. ACS Omega, 4, 6411–6420.
Rittmann, B. E., & McCarty, P. L. (2001). Environmental biotechnology: Principles and applications. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
De Clippeleir, H. E., Courtens, E., Mosquera, M., Vlaeminck, S. E., Smets, B. F., Boon, N., & Verstraete, W. (2012). Efficient total nitrogen removal in an ammonia gas biofilter through high-rate OLAND. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 8826–8833.
Vlaeminck, S. E., Terada, A., Smets, B. F., Linden, D. V. D., Boon, N., Verstraete, W., & Carballa, M. (2009). Nitrogen removal from digested black water by one-stage partial nitritation and anammox. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 5035–5041.
Liao, P., Chen, A., & Lo, K. (1995). Removal of nitrogen from swine manure wastewaters by ammonia stripping. Bioresource Technology, 54, 17–20.
Jorgensen, T., & Weatherley, L. (2003). Ammonia removal from wastewater by ion exchange in the presence of organic contaminants. Water Research, 37, 1723–1728.
Li, X., Zhao, Q., & Hao, X. (1999). Ammonium removal from landfill leachate by chemical precipitation. Waste Management, 19, 409–415.
Wang, J., Song, M., Chen, B., Wang, L., & Zhu, R. (2017). Effects of pH and H2O2 on ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate transformations during UV254nm irradiation: Implications to nitrogen removal and analysis. Chemosphere, 184, 1003–1011.
Cheng, X. F., Leng, W. H., Liu, D. P., Zhang, J. Q., & Cao, C. N. (2007). Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic performance of Zn-doped WO3 photocatalysts for nitrite ions degradation under visible light. Chemosphere, 68, 1976–1984.
Wang, H., Su, Y., Zhao, H., Yu, H., Chen, S., Zhang, Y., & Quan, X. (2014). Photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous ammonia using atomic single layer graphitic-C3N4. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 11984–11990.
Zhang, F., Pi, Y., Cui, J., Yang, Y., Zhang, X., & Guan, N. (2007). Unexpected selective photocatalytic reduction of nitrite to nitrogen on silver-doped titanium dioxide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111, 3756–3761.
Mack, J., & Bolton, J. R. (1999). Photochemistry of nitrite and nitrate in aqueous solution: A review. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 128, 1–13.
Wu, Y., Bu, L., Duan, X., Zhu, S., Kong, M., Zhu, N., & Zhou, S. (2020). Mini review on the roles of nitrate/nitrite in advanced oxidation processes: Radicals transformation and products formation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 273, 123065.
He, J., Yang, H., Chen, Y., Yan, Z., Zeng, Y., Luo, Z., Gao, W., & Wang, J. (2015). Solar light photocatalytic degradation of nitrite in aqueous solution over CdS embedded on metal–organic frameworks. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 226, 1–8.
Höller, V., Rådevik, K., Yuranov, I., Kiwi-Minsker, L., & Renken, A. (2001). Reduction of nitrite-ions in water over Pd-supported on structured fibrous materials. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 32, 143–150.
Kominami, H., Gekko, H., & Hashimoto, K. (2010). Photocatalytic disproportionation of nitrite to dinitrogen and nitrate in an aqueous suspension of metal-loaded titanium (IV) oxide nanoparticles. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 12, 15423–15427.
Zafra, A., Garcia, J., Milis, A., & Domènech, X. (1991). Kinetics of the catalytic oxidation of nitrite over illuminated aqueous suspensions of TiO2. Journal of Molecular Catalysis, 70, 343–349.
Ranjit, K., & Viswanathan, B. (1997). Photocatalytic reduction of nitrite and nitrate ions to ammonia on M/TiO2 catalysts. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 108, 73–78.
Xu, A.-W., Gao, Y., & Liu, H.-Q. (2002). The preparation, characterization, and their photocatalytic activities of rare-earth-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Journal of Catalysis, 207, 151–157.
Pandikumar, A., Manonmani, S., & Ramaraj, R. (2012). TiO2–Au nanocomposite materials embedded in polymer matrices and their application in the photocatalytic reduction of nitrite to ammonia. Catalysis Science and Technology, 2, 345–353.
Huang, S.-R., & Huang, P.-J. (2022). Visible-light driven graphene oxide/titanium dioxide hydrogels for photocatalytic reduction of nitrite. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10, 106902.
Zhang, Y.-Y., Jia, Y., Xu, G.-G., He, Y.-N., & Kang, W. (2015). Photocatalytic reduction of nitrite over TiO2–graphene oxide composites. Environmental Engineering Science, 32, 631–636.
Zhao, X., Xu, H., Huang, S., You, Y., Li, H., Xu, X., & Zhang, Y. (2019). The design of a polyaniline-decorated three dimensional W18O49 composite for full solar spectrum light driven photocatalytic removal of aqueous nitrite with high N2 selectivity. Science of The Total Environment, 660, 366–374.
An, B., He, H., Duan, B., Deng, J., & Liu, Y. (2021). Selective reduction of nitrite to nitrogen gas by CO2 anion radical from the activation of oxalate. Chemosphere, 278, 130388.
Shifu, C., & Gengyu, C. (2002). Photocatalytic oxidation of nitrite by sunlight using TiO2 supported on hollow glass microbeads. Solar Energy, 73, 15–21.
Zuo, Y., & Deng, Y. (1998). The near-UV absorption constants for nitrite ion in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 36, 181–188.
Tugaoen, H. O. N., Herckes, P., Hristovski, K., & Westerhoff, P. (2018). Influence of ultraviolet wavelengths on kinetics and selectivity for N-gases during TiO2 photocatalytic reduction of nitrate. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 220, 597–606.
Gonzalez, M., & Braun, A. (1995). VUV photolysis of aqueous solutions of nitrate and nitrite. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 21, 837–859.
Kandiel, T. A., Feldhoff, A., Robben, L., Dillert, R., & Bahnemann, D. W. (2010). Tailored titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Anatase nanoparticles and brookite nanorods as highly active photocatalysts. Chemistry of Materials, 22, 2050–2060.
Kosmulski, M. (2020). The pH dependent surface charging and points of zero charge. VII.I Update. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 275, 102064.
Salvador, P. (2011). Mechanisms of water photooxidation at n-TiO2 rutile single crystal oriented electrodes under UV illumination in competition with photocorrosion. Progress in Surface Science, 86, 41–58.
Zhu, X., Castleberry, S. R., Nanny, M. A., & Butler, E. C. (2005). Effects of pH and catalyst concentration on photocatalytic oxidation of aqueous ammonia and nitrite in titanium dioxide suspensions. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 3784–3791.
Qian, R., Zong, H., Schneider, J., Zhou, G., Zhao, T., Li, Y., Yang, J., Bahnemann, D. W., & Pan, J. H. (2019). Charge carrier trapping, recombination and transfer during TiO2 photocatalysis: An overview. Catalysis Today, 335, 78–90.
Ma, D., Schneider, J., Lee, W. I., & Pan, J. H. (2021). Controllable synthesis and self-template phase transition of hydrous TiO2 colloidal spheres for photo/electrochemical applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 295, 102493.
Nicodem, D., & Ferris, J. (1973). Ammonia photolysis on Jupiter. Icarus, 19, 495–498.
Kominami, H., Kitsui, K., Ishiyama, Y., & Hashimoto, K. (2014). Simultaneous removal of nitrite and ammonia as dinitrogen in aqueous suspensions of a titanium (iv) oxide photocatalyst under reagent-free and metal-free conditions at room temperature. RSC Advances, 4, 51576–51579.
Burg, A., Lozinsky, E., Cohen, H., & Meyerstein, D. (2004). Mechanism of reduction of the nitrite ion by CuI complexes. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2004, 3675–3680.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtar, B., Ahmed, A.Y. & Kandiel, T.A. Revisiting the mechanisms of nitrite ions and ammonia removal from aqueous solutions: photolysis versus photocatalysis. Photochem Photobiol Sci 21, 1833–1843 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-022-00260-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-022-00260-w