Abstract
Introduction
This study was to evaluate the efficacy of multiple platelet-rich plasma injections in reflex sympathetic dystrophy following distal radius fracture after previous various treatments have failed.
Materials and methods
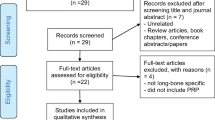
This comparative prospective study was designed for 64 patients of reflex sympathetic dystrophy developed following distal radius fracture, from January 2009 to December 2020 were enrolled in this study. This cohort of patient was given either four multiple subcutaneous platelet-rich plasma injections at weekly interval (n = 32) or two injections in a month with 15 days interval (n = 32). The primary outcome measure assessed with patient rated wrist evaluation questionnaire score. The secondary outcome was a visual analogue scale pain score. The final follow up was at 2 years. p ≤ 0.05 is considered statistically.
Results
The patient rated wrist evaluation score for usual and specific activities and EQ-VAS for pain level showed statistically significant greater improvement in group A (42 \(\pm\)21%) compared to group B (19 \(\pm\) 24%), (p = 0.37). Patients also had improvement in wrist movements with no statistically significant differences in both groups. The standard difference in means of all three functional scores was almost similar between both groups A and B (standard difference in means = 0.032; 95% CI 0.236–0.830; p = 0.495), considered clinically meaningful.
Conclusion
This study results suggest autologous platelet-rich plasma injections seem to be safe, cost effective, efficacious algorithm treatment for reflex sympathetic dystrophy following distal radius fracture patients where previous treatments have failed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birklein, F., & Dimova, V. (2017). Complex regional pain syndrome-up-to-date. Pain Reports, 2, e624.
Geertzen, J. H. B., Dukstra, P. U., Groothof, J. W., Jan, H., & ten duis, W Heisma. (1998). Reflex sympathetic dystrophy of the upper extremity— a 5.5-year follow-up. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.1998.11744781
Yh, J. O., Kim, K. W., Lee, B. G., et al. (2019). Incidence of risk factors for complex regional pain syndrome type 1 after surgery for distal radius fractures: A population based study. Science and Reports, 9(1), 1–7.
Harden, R. N., McCabe, C. S., Goebel, A., Massey, M., Suvar, T., Grieve, S., et al. (2022). Complex regional pain syndrome: Practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines 5 edition. Pain Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnac046
Fang, J., Wang, X., Jiang, W., et al. (2020). Platelet – rich plasma therapy in the treatment of disease associated with orthopedic injuries. Tissue Engineering. Part B, Reviews, 26, 571–585.
Chable, J., Cinque, M. E., Piuzzi, N. S., et al. (2017). A call for standardization in platelet-rich plasma preparation protocols and composition reporting a systematic review of the legal orthopaedic literature. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 99, 1769–1779.
Frey, C., Yeh, P. C., & Jayaram, P. (2020). Effects of antiplatelet and nonsteroidal ani-inflammatory medications on platelet – rich plasma: A systematic review. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine, 8(4), 2325967120912841.
Olomi, J., & Munthali, V. (2024). Complex regional pain syndrome diagnostic challenges and favorable response to prednisolone. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-024-07333-0
Taylor, S.-S., Noor, N., Urits, I., Paladini, A., Sadhu, M. S., Gibb, C., Carlson, T., Myrcik, D., Varrassi, G., & Viswanath, O. (2021). Complex regional pain syndrome: A comprehensive review. Pain and Therapy, 10, 875–892.
Vannala, V., Palaian, S., & Shankar, P. R. (2020). Therapeutic dimensions of biphosphonates: A clinical update. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 11, 166.
Neumeister, M. W., & Romaelli, M. R. (2020). Complex regional pain syndrome. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 47(2), P305-310.
Hunt, J. A., & Lake, M. A. (2021). Reviewing the physiology, pharmacology and therapeutic uses of ketamine. Nursing Standard, 36(9), 77–81.
Iolascon, G., Snichelotto, F., & Moretti, A. (2024). An update on the pharmacotherapeutic options for complex regional pain syndrome. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 24(2), 177–190.
Ghaly, L., Bargnes, V., Rahman, S., Tawfik, G.-A., Bergese, S., & Caldwell, W. (2023). Interventional treatment of complex regional pain syndrome. Biomedicines, 11(8), 2263.
Ghosh, P., & Gungor, S. (2020). Utilization of concurrent dorsal root ganglion stimulation and dorsal column spinal cord stimulation in complex regional pain syndrome [Mar 11]. Neuromodulation, 10, 1–5.
Shermon, S., Fazio, K. M., Shim, R., Abd-Elsayed, A., & Kim, C. H. (2023). Prescription trends in complex regional pain syndrome: A retrospective case-control study. Brain Sciences, 13(7), 1012.
Vowles, K. E., Pielech, M., Edwards, K. A., McEntee, M. L., & Bailey, R. W. (2021). A comparative meta-analysis of unidisciplinary psychology and interdisciplinary treatment outcomes following acceptance and commitment therapy for adults with chronic pain. The Journal of Pain, 21, 529–545.
Hussain, N., Johal, H., & Bhandari, M. (2017). An evidence – based evaluation on the use of platelet rich plasma in orthopedics – a review of the literature. SICOT-J, 3, 57.
Kulkarni, R. S. (2002). Reflex sympathetic dystrophy following Colle’s fracture. Indian Journal Orthopaedics, 36, 182–184.
Dejnek, M., Moreira, H., Placzkowska, S., Barg, E., Reichert, P., & Krolikowska, A. (2022). Leukocyte-rich plasma platelet – rich plasma as an effective source of molecules that modulate local immune and inflammatory cell responses. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, 8059622.
Everts, P., Onishi, K., Jayaram, P., & Lana, J. F. (2020). Platelet - rich plasma : New performance understanding and therapeutic considerations in 2020. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 7794.
Kulkarni R.S. (2004). Reflex sympathetic dystrophy following Colle’s Fracture. Orthopaedics Today, 131–136.
Sebbagh, P., Cannone, A., Gremion, G., et al. (2023). Current status of PRP manufacturing requirements & European regulatory frameworks : Practical tools for the appropriate implementation of PRP therapies in musculoskeletal regenerative medicine. Bioengineering (Basel), 10, 3–292.
Zavarro, A. C., De Girolamo, L., Laver, L., Sánchez, M., Tischer, T., Filardo, G., Sabatier, F., & Magalon, J. (2022). The top 100 most cited articles on platelet rich plasma use in regenerative medicine a bibliometric analysis from the esska orthobiologic initiative. Bioengineering (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100580
Magalon, J., Brandin, T., Francois, P., et al. (2021). Technical and biological review of authorized medical devices for platelets — rich plasma preparation in the field of regenerative medicine. Pletelets, 32(2), 200–208.
Tey, R. V., Joshi, H. P., & VR, Raj R. (2022). Variability in platelet – rich plasma preparations used in regenerative medicine a comparative analysis. Stem Cells Int, 2022, 3852898.
Bacevich, B. M., Smith, R. D. J., Reihi, A. M., & Mazzocca, A. D. (2024). Advances with platelet-rich plasma for bone healing. Biologics Targets Therapy, 18, 29–59.
Rout, A., Thakur, K., & Choubey, A. K. (2023). Subcutaneous platelet rich plasma therapy for management of hyperalgesia in complex regional pain syndrome. Indian Journal Pain, 37(2), 106–109.
Barnett, J., Borin, M., Barry, L., Katayama, E., Patel, A., Cvetanovich, G., Bishop, J., & Rauck, R. (2024). The utility of platelet rich plasma in modern orthopedic practices a review of the literature. Journal Orthopaedics Experience Innovation. https://doi.org/10.60118/001c.87963
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript. No funding was received for conducting this study. No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Raghavendra Shankar Kulkarni and Rachana Raghavendra Kulkarni; methodology: SriRam Raghavendra Kulkarni; frmal analysis and investigation: Rachana Raghavendra Kulkarni; writing—original draft preparation: Ranjani Raghavendra Kulkarni and Raghavendra Shankar Kulkarni and SriRam Raghavendra Kulkarni; writing—review and editing: Raghavendra Shankar Kulkarni and SriRam Raghavendra Kulkarni; supervision: Rachana Raghavendra Kulkarni and Ranjani Raghavendra Kulkarni.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The treatment protocols were approved by the local hospital Ethical Committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kulkarni, R.S., Kulkarni, S.R., Kulkarni, R.A. et al. Does Platelet-Rich Plasma Deserve a Role in Accelerating the Recovery of Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Following Distal Radius Fracture?. JOIO (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-024-01171-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-024-01171-x