Abstracts
Background
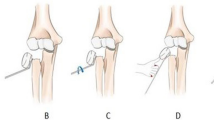
Although most paediatric radial neck fractures can be treated with closed reduction, some severely displaced fractures require open reduction. The purpose of this study is to compare the effects of ESIN and KW fixation in open reduction of radial neck fracture in children.
Methods
Twenty-four patients with mean age of 8.5 years were included. Four of the patients had a Judet type III fracture and 20 had a Judet type IV fracture. Ten patients who underwent percutaneous KW fixation were assigned to group A, while 14 patients who underwent ESIN fixation were assigned to group B. Variables of interest included age, sex, fracture type, associated lesions, surgical time, fracture reduction, cost, follow-up, healing time, X-rays, clinical outcomes, and complications.
Results
There were no significant between-group differences in sex, age, additional injuries, fracture type, and quality of reduction. Costs were significantly lower in Group A. Fracture healing was achieved in 23 of 24 patients (10/10 in group A and 13/14 in group B). In a postoperative elbow function assessment based on the Steele and Graham classification, 80% of patients in group A had a score of excellent or good, compared to 78.6% of patients in group B. Two cases of nail shifting and joint protrusion were observed in group B, one of which also presented with nonunion during follow-up.
Conclusions
Both KW and ESIN may achieve good clinical outcomes, but KW is associated with lower costs, easier implant removal (without the need for a secondary surgery), and lower iatrogenic complications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESIN:
-
Elastic stable intramedullary nail
- KW:
-
Kirschner wire
- AP:
-
Anteroposterior
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Tibone, J. E., & Stoltz, M. (1981). Fractures of the radial head and neck in children. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 63(1), 100–106.
Erickson, M., Frick. S. (2015). Fractures of the proximal radius and ulna. In: Beaty JH, Kasser JR, eds: Rockwood & Wilkins’ Fractures in Children, ed 7, Philadelphia, Wolters Kluwer Health. pp 406–445
Pring, M. E. (2012). Pediatric radial neck fractures: When and how to fix. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 32(Suppl 1), S14-21.
Stiefel. D., Meuli, M., Altermatt, S. (2001). Fractures of the neck of the radius in children. Early experience with intramedullary pinning. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British 83(4):536–541
Nicholson, L. T., & Skaggs, D. L. (2019). Proximal radius fractures in children. Journal of American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 27(19), e876–e886.
Métaizeau, J. P. (2005). Reduction and osteosynthesis of radial neck fractures in children by centromedullary pinning. Injury, 36(Suppl 1), A75–A77.
Song, K. S., Kim, B. S., & Lee, S. W. (2015). Percutaneous leverage reduction for severely displaced radial neck fractures in children. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 35(4), e26-30.
Brandão, G. F., Soares, C. B., Teixeira, L. E., & Boechat, L. C. (2010). Displaced radial neck fractures in children: Association of the Métaizeau and Böhler surgical techniques. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 30(2), 110–114.
Basmajian, H.G., Choi, P.D., Huh, K., Sankar, W.N., Wells, L., Arkader, A. (2014). Radial neck fractures in children: experience from two level-1 trauma centers. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics 23(4):369
Gutiérrez-de la Iglesia, D., Pérez-López, L.M., Cabrera-González, M., Knörr-Giménez, J. (2017). Surgical techniques for displaced radial neck fractures: predictive factors of functional results. Journal of Pediatr Orthopedics 37(3):159–165
Klitscher, D., Richter, S., Bodenschatz, K., Hückstädt, T., Weltzien, A., Müller, L. P., Schier, F., & Rommens, P. M. (2009). Evaluation of severely displaced radial neck fractures in children treated with elastic stable intramedullary nailing. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 29(7), 698–703.
Caputo, A. E., Mazzocca, A. D., & Santoro, V. M. (1998). The nonarticulating portion of the radial head: Anatomic and clinical correlations for internal fixation. Journal of Hand Surgery Am., 23(6), 1082–1090.
Metaizeau, J. P., Lascombes, P., Lemelle, J. L., Finlayson, D., & Prevot, J. (1993). Reduction and fixation of displaced radial neck fractures by closed intramedullary pinning. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 13(3), 355–360.
Steele, J. A., Graham, H.K. (1992). Angulated radial neck fractures in children. A prospective study of percutaneous reduction. Journal of Bone Joint Surgery British. 1992;74(5):760–764
Falciglia, F., Giordano, M., Aulisa, A. G., Di Lazzaro, A., & Guzzanti, V. (2014). Radial neck fractures in children: Results when open reduction is indicated. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 34(8), 756–762.
De Mattos, C. B., Ramski, D. E., Kushare, I. V., Angsanuntsukh, C., & Flynn, J. M. (2016). Radial neck fractures in children and adolescents: an examination of operative and nonoperative treatment and outcomes. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 36(1), 6–12.
Kaiser Margarita, Eberl Robert, Castellani Christoph et al. (2016). Judet type-IV radial neck fractures in children: Comparison of the outcome of fractures with and without bony contact. Journal of Acta Orthopedics 87: 529–532
Zhang, F. Y., Wang, X. D., Zhen, Y. F., Guo, Z. X., Dai, J., Zhu, L.Q. (2016). Treatment of severely displaced radial neck fractures in children with percutaneous k-wire leverage and closed intramedullary pinning. Medicine (Baltimore). 95(1): e2346
Waters, P. M., & Stewart, S. L. (2001). Radial Neck Fracture Nonunion in Children[J]. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 21(5), 570–576.
Su, Y., Xie, Y., Qin, J., Wang, Z., Cai, W., & Nan, G. (2016). Internal fixation with absorbable rods for the treatment of displaced radial neck fractures in children. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 36(8), 797–802.
Nisar Aamer, Bhosale Abhijit, Madan Sanjeev S. et al. (2013). Complications of Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing for treating paediatric long bone fractures. Journal of Orthopedics 10: 17–24
Murphy Hamadi, A., Jain Viral, V., Parikh Shital N. et al. (2019). Extensor tendon injury associated with dorsal entry flexible nailing of radial shaft fractures in children: a report of 5 new cases and review of the literature. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 39: 163–168
Pogorelić, Z., Gulin, M., Jukić, M., Biliškov, A. N., & Furlan, D. (2020). Elastic stable intramedullary nailing for treatment of pediatric forearm fractures: A 15-year single centre retrospective study of 173 cases. Acta Orthopaedica et Traumatologica Turcica, 54(4), 378–384. https://doi.org/10.5152/j.aott.2020.19128
Frigg Arno, Rillmann Paavo, Perren Thomas et al. (2009). Intramedullary nailing of clavicular midshaft fractures with the titanium elastic nail: problems and complications. American Journal of Sports Medicine, 37: 352–359
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: YL, L-QZ, F-YZ; data collection: YL, T-TZ; analysis and interpretation of results: YL, Y-FZ; draft manuscript preparation: YL, F-YZ, Y-FZ. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Ethics Committee of the Children’s Hospital of Soochow University.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhu, LQ., Zhang, FY. et al. Open Reduction of Displaced Radial Neck Fractures in Children by Internal Fixation Techniques: Comparison of Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring and Elastic Stable Intramedullary Nailing. JOIO 56, 1192–1198 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-022-00631-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-022-00631-6