Abstract
Purpose
In the present study, we aimed at assessing the effect of femoral and tibial coronal bowing on varus malalignment and Oxford knee score (OKS) at different grades of knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Materials and Methods
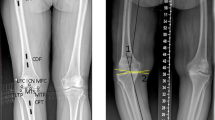
This prospective observational study was conducted at a tertiary referral centre in New Delhi, India. Consecutive patients presenting to the “knee OA” outpatient clinics were invited to take part in the study conducted over a 12-month period. All consented patients underwent long-leg standing alignment radiographs using standardised technique and patient reported knee pain and function were recorded using Oxford knee score. The following radiological parameters were measured from weight-bearing long-leg radiographs of 824 varus aligned limbs via a morphometric software (Matlab R2009a) (1) hip–knee–ankle angle (HKAA), (2) femoral bowing, (3) tibial bowing. The knees were graded according to Kellegren and Lawrence grade (K&L) and OKS was recorded. 3 groups of HKAA were made based on the angle, A (0° to − 3°), B (− 3° to − 10°) and C (< − 10°). Both the femoral and tibial bow were also categorized into three groups depending upon the angle; in-range (− 2° to + 2°), varus (< − 2°), valgus (> + 2°).
Results
The mean (± SD) of HKAA, femoral bow and tibial bow of the whole cohort was − 6.97° ± 5.64°, − 1.54° ± 4.31° and − 1.96° ± 3.5°, respectively. An increase in the lateral bow of both femur and tibia was seen with an increase in the severity of OA. A consequent increase in the varus malalignment was observed with an increase in the lateral bow of both femur as well as the tibia at all grades of OA, with significant correlation observed between HKAA with Femoral bowing and HKAA with tibial bowing. The mean OKS for femoral bow, in-range, varus and valgus was 30.6 ± 11.5, 21.3 ± 11.5 and 35.3 ± 11.4, respectively, and for tibial bow, in-range, varus and valgus was 27.6 ± 11.5, 26. ± 11.5 and 28 ± 11.4, respectively. The difference in the mean OKS was observed to be significant when the varus bow group was compared to in range as well as valgus group (p < 0.01) for both femur and tibia for all the grades of OA.
Conclusion
The present study shows a significant correlation between varus malalignment and the bowing of extremities. Varus coronal bowing of both femur and tibia were seen to have significantly lower mean OKS as compared to valgus bowing or in-range bowing at all grades of knee OA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salaffi, F., Carotti, M., Stancati, A., & Grassi, W. (2005). Health-related quality of life in older adults with symptomatic hip and knee osteoarthritis: A comparison with matched healthy controls. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 17(4), 255–263.
Thienpont, E., Schwab, P. E., Cornu, O., Bellemans, J., & Victor, J. (2017). Bone morphotypes of the varus and valgus knee. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 137(3), 393–400.
Howell, S. M., Kuznik, K., Hull, M. L., & Siston, R. A. (2010). Longitudinal shapes of the tibia and femur are unrelated and variable. Clinical Orthopaedics, 468(4), 1142–1148.
Sharma, L., Song, J., Felson, D. T., Cahue, S., Shamiyeh, E., & Dunlop, D. D. (2001). The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA, 286(2), 188–195.
Hunter, D. J., Zhang, Y., Niu, J., Tu, X., Amin, S., Goggins, J., et al. (2005). Structural factors associated with malalignment in knee osteoarthritis: The Boston osteoarthritis knee study. Journal of Rheumatology, 32(11), 2192–2199.
Cooke, T. D. V., Harrison, L., Khan, B., Scudamore, A., & Chaudhary, M. A. (2002). Analysis of limb alignment in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: A comparison of Saudi Arabian and Canadian cases. Rheumatology International, 22(4), 160–164.
Bellemans, J., Colyn, W., Vandenneucker, H., & Victor, J. (2012). The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clinical Orthopaedics, 470(1), 45–53.
Hsu, R. W., Himeno, S., Coventry, M. B., & Chao, E. Y. (1990). Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clinical Orthopaedics, 255, 215–227.
Moreland, J. R., Bassett, L. W., & Hanker, G. J. (1987). Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume, 69(5), 745–749.
Shetty, G. M., Mullaji, A., Bhayde, S., Nha, K. W., & Oh, H. K. (2014). Factors contributing to inherent varus alignment of lower limb in normal Asian adults: Role of tibial plateau inclination. The Knee, 21(2), 544–548.
Victor, J. M. K., Bassens, D., Bellemans, J., Gürsu, S., Dhollander, A. A. M., & Verdonk, P. C. M. (2014). Constitutional varus does not affect joint line orientation in the coronal plane. Clinical Orthopaedics, 472(1), 98–104.
Yau, W. P., Chiu, K. Y., Tang, W. M., & Ng, T. P. (2007). Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: Its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery (Hong Kong), 15(1), 32–36.
Lasam, M. P. G., Lee, K. J., Chang, C. B., Kang, Y. G., & Kim, T. K. (2013). Femoral lateral bowing and varus condylar orientation are prevalent and affect axial alignment of TKA in Koreans. Clinical Orthopaedics, 471(5), 1472–1483.
Mullaji, A. B., Marawar, S. V., & Mittal, V. (2009). A comparison of coronal plane axial femoral relationships in Asian patients with varus osteoarthritic knees and healthy knees. Journal of Arthroplasty, 24(6), 861–867.
Matsumoto, T., Hashimura, M., Takayama, K., Ishida, K., Kawakami, Y., Matsuzaki, T., et al. (2015). A radiographic analysis of alignment of the lower extremities—Initiation and progression of varus-type knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 23(2), 217–223.
Kobayashi, H., Akamatsu, Y., Kumagai, K., Kusayama, Y., Aratake, M., & Saito, T. (2017). Influence of coronal bowing on the lower alignment and the positioning of component in navigation and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Orthopaedics and Traumatology Surgery and Research (OTSR), 103(2), 251–256.
Doré, D. A., Winzenberg, T. M., Ding, C., Otahal, P., Pelletier, J.-P., Martel-Pelletier, J., et al. (2013). The association between objectively measured physical activity and knee structural change using MRI. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 72(7), 1170–1175.
Kellgren, J. H., & Lawrence, J. S. (1957). Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 16(4), 494–502.
Collins, N. J., Misra, D., Felson, D. T., Crossley, K. M., & Roos, E. M. (2011). Measures of knee function: International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) Subjective Knee Evaluation Form, Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score Physical Function Short Form (KOOS-PS), Knee Outcome Survey Activities of Daily Living Scale (KOS-ADL), Lysholm Knee Scoring Scale, Oxford Knee Score (OKS), Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), Activity Rating Scale (ARS), and Tegner Activity Score (TAS). Arthritis Care and Research, 63(Suppl 11), S208-228.
Dawson, J., Fitzpatrick, R., Murray, D., & Carr, A. (1998). Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about total knee replacement. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 80(1), 63–69.
Victor, J., Urlus, M., Bellemans, J., & Fabry, G. (1994). Femoral intramedullary instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty: The role of pre-operative X-ray analysis. The Knee, 1(2), 123–125.
Niki, Y., Matsumoto, H., Otani, T., Enomoto, H., Toyama, Y., & Suda, Y. (2010). Accuracy of implant positioning for minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty in patients with severe varus deformity. Journal of Arthroplasty, 25(3), 381–386.
Mullaji, A. B., Shetty, G. M., Lingaraju, A. P., & Bhayde, S. (2013). Which factors increase risk of malalignment of the hip-knee-ankle axis in TKA? Clinical Orthopaedics, 471(1), 134–141.
Kim, S. H., Oh, M. K., Namgung, R., & Park, M. J. (2014). Prevalence of 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency in Korean adolescents: Association with age, season and parental vitamin D status. Public Health Nutrition, 17(1), 122–130.
Saibaba, B., Dhillon, M. S., Chouhan, D. K., Kanojia, R. K., Prakash, M., & Bachhal, V. (2015). Significant incidence of extra-articular tibia vara affects radiological outcome of total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surgery and Related Research, 27(3), 173–180.
Kim, C.-W., & Lee, C.-R. (2018). Effects of femoral lateral bowing on coronal alignment and component position after total knee arthroplasty: A comparison of conventional and navigation-assisted surgery. Knee Surgery and Related Research, 30(1), 64–73.
Nagamine, R., Miura, H., Bravo, C. V., Urabe, K., Matsuda, S., Miyanishi, K., et al. (2000). Anatomic variations should be considered in total knee arthroplasty. Journal of Orthopaedic Science, 5(3), 232–237.
Akamatsu, Y., Kobayashi, H., Kusayama, Y., Kumagai, K., & Saito, T. (2016). Femoral shaft bowing in the coronal and sagittal planes on reconstructed computed tomography in women with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis: A comparison with radiograph and its predictive factors. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, 136(9), 1227–1232.
Akamatsu, Y., Mitsugi, N., Kobayashi, H., Kumagai, K., Kusayama, Y., & Saito, T. (2012). Relationship between shaft bowing in the femur and tibia and bone mineral density in women with varus knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 1(20), S219.
Moyer, R. F., Birmingham, T. B., Chesworth, B. M., Kean, C. O., & Giffin, J. R. (2010). Alignment, body mass and their interaction on dynamic knee joint load in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 18(7), 888–893.
Thambiah, M., Nathan, S., Seow, B., Liang, S., & Lingaraj, K. (2015). Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: An Asian perspective. Singapore Medical Journal, 56(05), 259–263.
Jacobs, C. A., & Christensen, C. P. (2014). Factors influencing patient satisfaction two to five years after primary total knee arthroplasty. Journal of Arthroplasty, 29(6), 1189–1191.
Bourne, R. B., Chesworth, B. M., Davis, A. M., Mahomed, N. N., & Charron, K. D. J. (2010). Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: Who is satisfied and who is not? Clinical Orthopaedics, 468(1), 57–63.
Lin, Y.-H., Chang, F.-S., Chen, K.-H., Huang, K.-C., & Su, K.-C. (2018). Mismatch between femur and tibia coronal alignment in the knee joint: Classification of five lower limb types according to femoral and tibial mechanical alignment. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 19(1), 411.
Slevin, O., Hirschmann, A., Schiapparelli, F. F., Amsler, F., Huegli, R. W., & Hirschmann, M. T. (2018). Neutral alignment leads to higher knee society scores after total knee arthroplasty in preoperatively non-varus patients: A prospective clinical study using 3D-CT. Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy, 26(6), 1602–1609.
Funding
The study was conducted under project approved by UK-India Education and Research Initiative (UKIERI) and funded by Department of Science and technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MN; Drafting of the article, Critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, Collection and assembly of data, Final approval of the article. VK; Conception and design, Provision of study materials or patients, Final approval of the article. RY; Collection of data, analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of article. DNS; Analysis and interpretation of the data, Critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, final approval of the article. HP; Conception and design, Final approval of the article. RM; Conception and design, Drafting of the article, Critical revision of the article for important intellectual content, final approval of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no potential conflicts of interest, including financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations, to disclose.
Ethical standard statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, M., Kumar, V., Yadav, R. et al. Lateral Coronal Bowing of Femur and/or Tibia Amplifies the Varus Malalignment of Lower Limb as well as Increases Functional Disability in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. JOIO 55 (Suppl 1), 88–96 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-020-00303-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-020-00303-3