Abstract
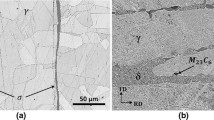
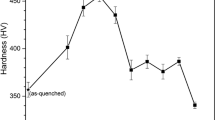
The paper discusses several aspects of degradation of Super 304H steel subjected to long-term aging up to 50,000 h at 650 and 750°C. The study includes microstructure examination by scanning and transmission electron microscopy along with X-ray microanalysis of a wide range of precipitates. The Super 304H steel has a structure characteristic for austenitic steels with annealing twins and single primary NBX precipitates of various sizes. Long-term aging leads to precipitation of several phases such as M23C6, MX carbides, σ phases, Z phase and ε-Cu phase. The precipitation processes lead to changes in the creep strength of the tested steel, the value of which strongly depends on the aging temperature used, which is measurably shown by the creep tests carried out with the elongation measured during the test.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Mesjasz-Lech A. Planning of production resources use and environmental effects on the example of a thermal power plant. Procd Soc Behv. 2015;213:539–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.11.447.
Golański G, Zielińska-Lipiec A, Zieliński A, Sroka M. Effect of long-term service on microstructure and mechanical properties of martensitic 9% Cr Steel. J Mater Eng Perform. 2017;26:1101–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2556-3.
Zieliński A, Golański G, Sroka M. Comparing the methods in determining residual life on the basis of creep tests of low-alloy Cr-Mo-V cast steels operated beyond the design service life. Int J Pres Ves Pip. 2017;152:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2017.03.002.
Golański G, Zieliński A, Sroka M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TP347HFG austenitic stainless steel after long-term service. Int J Pres Ves Pip. 2020;188: 104160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2020.104160.
Lu H, Xu F, Liu H, Wang J, Campbell DE, Ren H. Emergy-based analysis of the energy security of China. Energy. 2019;181:123–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.05.170.
Sroka M, Zieliński A, Mikuła J. The service life of the repair welded joint of Cr-Mo / Cr-Mo-V. Arch Metall Mater. 2016;61:969–74. https://doi.org/10.1515/amm-2016-0217.
Kępa J, Golański G, Zieliński A, Brodziak-Hyska A. Precipitation process in VM12 steel after ageing at 650°C temperature. J Vibroeng. 2012;14:143–50.
Rocha DHD, Silva RJ. Exergoenvironmental analysis of a ultra-supercritical coal-fired power plant. J Clean Prod. 2019;231:671–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.214.
Guo X, Sun W, Becker A, Morris A, Pavier M, Flewitt P, Tierney M, Wales C. Thermal and stress analyses of a novel coated steam dual pipe system for use in advanced ultra-supercritical power plant. Int J Pres Ves Pip. 2019;176: 103933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2019.103933.
Dudziak T, Deodeshmukh V, Backert L, Sobczak N, Witkowska M, Ratuszek W, Chruściel K, Zieliński A, Sobczak J, Bruzda G. Phase investigations under steam oxidation process at 800 °C for 1000 h of advanced steels and ni-based alloys. Oxid Met. 2017;87:139–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-016-9662-8.
Stevanovic VD, Petrovic MM, Wala T, Milivojevic S, Ilic M, Muszynski S. Efficiency and power upgrade at the aged lignite-fired power plant by flue gas waste heat utilization: high pressure versus low pressure economizer installation. Energy. 2019;187: 115980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.115980.
Lin C, Li Y, Tang Y, Shi Y, Wang Q, Yuan X, Kellett J. Integrated assessment of the environmental and economic effects of an ultra-clean flue gas treatment process in coal-fired power plant. J Clean Prod. 2018;199:359–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.174.
Golański G. Żarowytrzymałe stale austenityczne, Wydawnictwo Wydziału Inżynierii Produkcji i Technologii Materiałów, Częstochowa 2017 (in Polish).
Zieliński A, Sroka M, Dudziak T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 740h after long-term service. Materials. 2018;11:2130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112130.
Golański G, Merda A, Zieliński A, Urbańczyk P, Słania J, Kierat M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of HR6W alloy dedicated for manufacturing of pressure elements in supercritical and ultrasupercritical power units. E3S Web Conf. 2019;82:01005. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20198201005.
Zieliński A, Dobrzański J, Purzyńska H, Sikora R, Dziuba-Kałuża M, Kania Z. Evaluation of creep strength of heterogeneous welded joint in HR6W alloy and Sanicro 25 steel. Arch Metall Mater. 2017;62:2057–64. https://doi.org/10.1515/amm-2017-0305.
Sroka M, Nabiałek M, Szota M, Zieliński A. The influence of the temperature and ageing time on the NiCr23Co12Mo alloy microstructure. Rev Chim-Bucharest. 2017;68:737–41. https://doi.org/10.37358/RC.17.4.5541.
Viswanathan R, Henry JF, Tanzosh J, Stanko G, Shingledecker J, Vitalis B, Purgert R. U.S. program on materials technology for ultra-supercritical coal power plants. J Mater Eng Perform. 2005;14:281–92. https://doi.org/10.1361/10599490524039.
Maziasz PJ, Shingledecker JP, Evans ND. Developing new cast austenitic stainless steels with improved high-temperature creep resistance. J Press Vess-T ASME. 2009;131:051404. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3141437.
Iseda A, Okada H. Creep properties and Microstructuren of Super 304H, TP347HFG, HR3C. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference Advances in Materials Technology for Fossil Power Plants EPRI, Marco Island, USA; 2007, p. 61–62.
Abe F. Research and development of heat-resistant materials for advanced USC power plants with steam temperatures of 700 °C and above. Engineering. 2015;1:211–24. https://doi.org/10.15302/j-eng-2015031.
Di Gianfrancesco A. Materials for ultra-supercritical and advanced ultra-supercritical power plants. 1st ed. Sawston: Woodhead Publishing; 2016.
Zieliński A, Dobrzański J, Purzyńska H, Golański G. Properties, structure and creep resistance of austenitic steel Super 304H. Mater Test. 2015;57:859–65. https://doi.org/10.3139/120.110791.
Zhong Z, Gu Y, Yuan Y. Microstructural stability and mechanical properties of a newly developed Ni–Fe-base superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct. 2015;622:101–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.11.010.
Zieliński A, Sroka M, Miczka M, Śliwa A. Forecasting the particle diameter size distribution in P92 (X10CrWMoVNb9-2) steel after long-term ageing at 600 and 650°C. Arch Metall Mater. 2016;61:753–60. https://doi.org/10.1515/amm-2016-0128.
Horváth J, Janovec J, Junek M. The changes in mechanical properties of austenitic creep resistant steels SUPER 304H and HR3C caused by medium-term isothermal ageing. Solid State Phenom. 2017;258:639–42. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.258.639.
Yoo K-B, He Y, Lee H-S, Bae S-Y, Kim D-S, Shin K. Study of the scale formed on super 304H boiler tube steels after long-term steam oxidation at high temperatures. Mater Charact. 2018;146:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.09.045.
Li Y, Wang S, Wang L, Yu P, Yang J. Corrosion behavior of austenitic steel 304 in nearcritical aqueous solutions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Energy Science and Chemical Engineering, Atlantis Press; 2015. https://doi.org/10.2991/isesce-15.2015.38
Liang Z, Zhao Q, Deng J, Wang Y. Influence of aging treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of T92/Super 304H dissimilar metal welds. Mater High Temp. 2018;35(4):327–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603409.2017.1334857.
Rizvi SA, Tewari SP. Effect of different Welding Parameters on the mechanical and microstructural properties of Stainless Steel 304H welded joints. Int J Eng Trans A. 2017;31(10):150–60. https://doi.org/10.5829/ije.2017.30.10a.21.
Oua P, Xing H, Wang X, Sun J, Cui Z, Yang Ch. Coarsening and hardening behaviors of Cu – rich precipitates in Super304H austenitic steel. Metall Mater Trans A. 2015;46:3909–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3004-3.
Ou P, Xing H, Wang XL, Sun J. Tensile yield behavior and precipitation strengthening mechanism in Super304H steel. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct. 2014;600:171–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.085.
Chen AY, Hu WF, Wang D, Zhu YK, Wang P, Yang H, Wang XY, Gu JF, Lu J. Improving the intergranular corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel by high density twinned structure. Scripta Mater. 2017;13:264–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.032.
Zieliński A, Golański G, Sroka M. Evolution of the microstructure and mechanical properties of HR3C austenitic stainless steel after ageing for up to 30 000 h at 650–750°C. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct. 2020;796: 139944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139944.
Chi Ch-Y, Yu H-Y, Dong J-X, Liu W-Q, Cheng J-Ch, Liu Z-D, Xie X-S. The precipitation strengthening behavior of Cu- rich phase in Nb contained advanced Fe-Cr-Ni type austenitic heat resistant steel for USC power plant application. Prog Nat Sci. 2012;22:175–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2012.05.002.
Zieliński A, Wersta R. Structure of S304H steel after 10 000 hours of aging. Energetyka. 2018;11:648–50.
Noskovich OI, Rabkin EI, Semenov VN, Straumal BB, Shvindlerman LS. Wetting and premelting phase transitions in 38° [100] tilt grain boundary in (Fe-12 at.% Si)-Zn alloy in the vicinity of the A2–B2 bulk ordering in Fe-12 at.% Si alloy. Acta Metall Mater. 1991;39:3091–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-7151(91)90042-y.
Straumal B, Kogtenkova O, Bulatov M, Nekrasov A, Baranchikov A, Baretzky B, Straumal A. Wetting of grain boundary triple junctions by intermetallic delta-phase in the Cu–In alloys. J Mater Sci. 2021;56:7840–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05674-4.
Chang L-S, Rabkin E, Straumal B, Lejček P, Hofmann S, Gust W. Temperature dependence of the grain boundary segregation of Bi in Cu polycrystals. Scripta Mater. 1997;37(6):729–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6462(97)00171-1.
Jin X, Xia X, Li Y, Zhao Y, Xue F, Zhang G. Quantitative study of microstructure evolution and the effect on mechanical properties of Super304H during aging. Mater High Temp. 2019;36(5):459–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603409.2019.1632508.
Yu H, Chi Ch. Precipitation behaviour of Cu-rich phase in 18Cr9Ni3CuNbN austenitic heat - resistant steel at early aging state, Chin. J Mater Res. 2015;29:195–200. https://doi.org/10.11901/1005.3093.2014.610.
Chi CY, Yu HY, Dong JX, Liu WQ, Cheng SC, Liu ZD, Xie XS. The precipitation strengthening behavior of Cu-rich phase in Nb contained advanced Fe–Cr–Ni type austenitic heat resistant steel for USC power plant application. Prog Nat Sci. 2012;22(3):175–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2012.05.002.
Padilha AF, Machado IF, Plaut RI. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Fe-15%Cr-15%Ni austenitic stainless steels containing different levels of niobium additions submitted to various processing stages. J Mater Process Tech. 2005;170(1–2):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.05.002.
Farooq M. Strengthening and mechanism degradation in austenitic stainless steels at elevated temperature. PhD thesis. Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm; 2013
Ji YS, Park J, Lee SY, Kim JW, Lee SM, Nam J, Hwang B, Suh JY, Shim JHJMC. Long-term evolution ofσphase in 304H austenitic stainless steel: experimental andcomputational investigation. Mater Charact. 2017;128:23–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2017.03.030.
Kuboň Z, Stejskalová Š, Kander L. Effect of sigma phase on fracture behavior of steels and weld joints of components in power industry working at supercritical conditions. Austenitic Stainl Steels New Aspects. 2017. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71569.
Hsieh C-C, Wu W. Overview of intermetallic sigma (σ) phase precipitation in stainless steels. ISRN Metall. 2012;2012:1–16. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/732471.
Golański G., Zieliński A., Purzyńska H. Precipitation process in creep-resistant austenitic steels. Austenitic stainless steels. London: InTech Publication; 2017, p. 93–112. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.70941
Padilha AF, Rios PR. Decomposition of austenite in austenite stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 2002;42:325–37. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.42.325.
Barcik J. Mechanism of σ-phase precipitation in Cr-Ni austenitic steels. Mater Sci Technol. 1988;4:5–15. https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1988.4.1.5.
Wang X, Li Y, Chen D, Sun J. Precipitate evolution during the aging of Super304H steel and its influence on impact toughness. Mater Sci Eng A-Struct. 2019;754:238–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.03.086.
Jiang J, Liu Z, Gao Q, Zhang H, Hao A, Qu F, Li H. The effect of isothermal aging on creep behavior of modified 2.5 Al alumina-forming austenitic steel. Mater Sci Eng A Struct. 2020;797:140219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140219.
Sklenicka V, Kucharova K, Svobodova M, Kral P, Kvapilova M, Dvorak J. The effect of a prior short-term ageing on mechanical and creep properties of P92 steel. Mater Charact. 2018;136:388–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.01.008.
Acknowledgements
The results in this publication were obtained as a part of research co-financed by the National Science Centre under contract 2011/01/D/ST8/07219 – Project: “Creep test application to model lifetime of materials for modern power generation industry”, and co-financed rector's grant in the area of scientific research and development works, Silesian University of Technology, 10/010/RGJ21/1032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zieliński, A., Wersta, R. & Sroka, M. The study of the evolution of the microstructure and creep properties of Super 304H austenitic stainless steel after aging for up to 50,000 h. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 22, 89 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00408-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-022-00408-6