Abstract
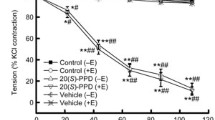
Cardiovascular diseases are a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, necessitating the development of novel therapeutic molecules and strategies. A triterpene isolated from the leaves of Licania cruegeriana Urb., Chrysobalanaceae, 6-hydroxybetulinic acid exerts hypotensive effects in hypertensive rats. In this study, we aimed to investigate the vasorelaxant effects of this triterpene in rat aortic rings and determine its possible mechanism of action. The activity of 6-hydroxybetulinic acid was evaluated on contractile responses of isolated aorta to KCl and phenylephrine. 6-Hydroxybetulinic acid induced a concentration-dependent relaxation both in endothelium-intact and endothelium-denuded aortic rings precontracted by phenylephrine (1 µM) and KCl (50 µM). Pretreatment of the aortic rings with N-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (100 µM), methylene blue (100 µM), or 4-aminopyridine (1 mM), completely prevented 6-hydroxybetulinic acid-induced vasorelaxation, while indomethacin (10 µM) did not affect response. We found that 6-hydroxybetulinic acid exerted its vasorelaxant effects in rat aortic rings in vascular endothelium-dependent and -independent manners by blocking extracellular Ca2+ influx. Moreover, its effects were mediated by the activation of the nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway and opening of 4-aminopyridine-sensitive K+ channels. As vascular tone is a determinant of blood pressure in mammals, our findings partially explain the hypotensive effects of 6-hydroxybetulinic acid in vivo.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The experimental data are available and can be requested from the corresponding author.
References
Brayden JE (1996) Potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 23:1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2016.07.001
Di Giulio C, Gonzalez Guzman JM, Dutra Gomes JV, Choi YH, Magalhães PO, Fonseca-Bazzo YM, Silveira D, Estrada O (2023) A new lignan from Annona squamosa L. (Annonaceae) demonstrates vasorelaxant effects in vitro. Molecules 28:4256. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114256
Estrada O, Contreras W, Acha G, Lucena E, Venturini W, Cardozo A, Alvarado-Castillo C (2014) Chemical constituents from Licania cruegeriana and their cardiovascular and antiplatelet effects. Molecules 19:21215–21225. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191221215
Mashour NH, Lin GI, Frishman WH (1998) Herbal medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular disease: clinical considerations. Arch Intern Med 158:2225–2234. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.158.20.2225
Moosmang S, Schulla V, Welling A, Feil R, Feil S, Wegener JW, Klugbauer N (2003) Dominant role of smooth muscle L-type calcium channel Cav1. 2 for blood pressure regulation. EMBO J 22:6027–6034. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg583
Nakatsu K, Diamond J (1989) Role of cGMP in relaxation of vascular and other smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 67:251–262. https://doi.org/10.1139/y89-042
Sausbier M, Schubert R, Voigt V, Hirneiss C, Pfeifer A, Korth M, Hofmann F (2000) Mechanisms of NO/cGMP-dependent vasorelaxation. Circ Res 87:825–830. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.87.9.825
Seccia T, Brasilina C, Adler G, Maiolino G, Cesari M, Rossi GP (2017) Arterial hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and hyperaldosteronism, the triple trouble. Hypertension 69:545–550. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08956
Souza DS, Menezes-Filho JER, Santos-Miranda A, Jesus ICG, Silva Neto JA, Guatimosim S, Cruz JS, Vasconcelos CML (2019) Calcium overload-induced arrhythmia is suppressed by farnesol in rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol 859:172488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172488
Tabares-Guevara JH, Jaramillo JC, Ospina-Quintero L, Piedrahíta-Ochoa CA, García-Valencia N, Bautista-Erazo DE, Caro-Gómez E, Covián C, Retamal-Díaz A, Duarte LF, González PA, Bueno SM, Riedel CA, Kalergis AM, Ramírez-Pineda JR (2021) IL-10-Dependent amelioration of chronic inflammatory disease by microdose subcutaneous delivery of a prototypic immunoregulatory small molecule. Front Immunol 12:708955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.708955
WHO. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). WHO; 2021 [cited 2021 11 June 2021]; Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti E, Azizi M, Burnier M, Clement D, Coca A, de Simone G, Dominiczak A (2018) ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens 36:1953–2041. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000001940
Zhao C, Li S, Zhang J, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhao F, Huang L (2020) Current state and future perspective of cardiovascular medicines derived from natural products. Pharmacol Ther 216:107698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107698
Funding
Financial support for this project was provided by Fondo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia, Venezuela (FONACIT), grant number: 20071585.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OE conceived the study and revised the final manuscript. OE and AC prepared figures and tables and wrote the manuscript. OE and AC helped with the performance of experiments. The final version of the manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The authors declare that the experiments with animals were performed in compliance with international rules on the care and use of laboratory animals. The animal studies were evaluated and approved by the Bioethics Commission for Investigations in Animals at the IVIC (Protocol 201417, approval on November 2017), by the Code on Bioethics and Biosecurity (2008) established by the Bioethics Commission National Fund on Science and Technology (FONACIT), under the national legislation.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Carocci, A., Estrada, O. Vasorelaxant Effect of 6β-Hydroxybetulinic Acid. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 34, 647–653 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-024-00515-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-024-00515-w