Abstract
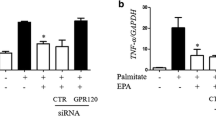
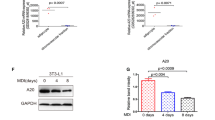
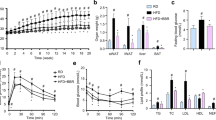
Fatty acid binding protein 4 is predominantly expressed in adipose tissue and functions as an important mediator of inflammation. However, small molecules that regulate its expression in adipocytes have not been adequately characterized. In this study, we found that trilobatin dose-dependently attenuates the mRNA expression and protein levels of fatty acid binding protein 4 induced by lipopolysaccharide in the differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Meanwhile, trilobatin also reduced the mRNA and protein levels of fatty acid binding protein 4 in the epididymal white adipose tissue and the contents of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-6 in the serum of obese-hyperglycemic mice. In addition, trilobatin protected against the decrease of microRNA precursors, including premiR-375, premiR-338, and premiR-129, but only miR-375 inhibitor prohibited the role of trilobatin on the expression of fatty acid binding protein 4, suggesting that miR-375 might be involved in trilobatin regulating this protein expression in LPS-treated differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. All these findings suggest that trilobatin might be a promising compound for the management of obesity due to its anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing the expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 in adipocytes.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data and materials of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Dou HX, Wang T, Su HX, Gao DD, Xu YC, Li YX, Wang HY (2020) Exogenous fabp4 interferes with differentiation, promotes lipolysis and inflammation in adipocytes. Endocrine 67:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-02157-8
Fan X, Zhang Y, Dong H, Wang B, Ji H, Liu X (2015) Trilobatin attenuates the lps-mediated inflammatory response by suppressing the nf-kappab signaling pathway. Food Chem 166:609–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.06.022
Fu Y, Luo L, Luo N, Garvey WT (2006) Lipid metabolism mediated by adipocyte lipid binding protein (albp/ap2) gene expression in human thp-1 macrophages. Atherosclerosis 188:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.10.041
Gao J, Chen N, Li N, Xu F, Wang W, Lei Y, Shi J, Gong Q (2020) Neuroprotective effects of trilobatin, a novel naturally occurring sirt3 agonist from Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd., mitigate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of tlr4/nf-kappab and nrf2/keap-1 signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 33:117–143. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2019.7825
Liu M, Wang L, Li X, Wu Y, Yin F, Liu J (2020) Trilobatin ameliorates insulin resistance through irs-akt-glut4 signaling pathway in c2c12 myotubes and ob/ob mice. Chin Med 15:110–122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-020-00390-2
Queipo-Ortuno MI, Escote X, Ceperuelo-Mallafre V, Garrido-Sanchez L, Miranda M, Clemente-Postigo M, Perez-Perez R, Peral B, Cardona F, Fernandez-Real JM, Tinahones FJ, Vendrell J (2012) Fabp4 dynamics in obesity: discrepancies in adipose tissue and liver expression regarding circulating plasma levels. PLoS ONE 7:e48605. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048605
Shen H, Huang L, Dou H, Yang Y, Wu H (2021) Effect of trilobatin from Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd on gut microbiota of obese rats induced by a high-fat diet. Nutrients 13:891. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030891
Steen KA, Xu H, Bernlohr DA (2017) Fabp4/ap2 regulates macrophage redox signaling and inflammasome activation via control of ucp2. Mol Cell Biol 37. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00282-16
Stolarczyk E (2017) Adipose tissue inflammation in obesity: a metabolic or immune response? Curr Opin Pharmacol 37:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2017.08.006
Thumser AE, Moore JB, Plant NJ (2014) Fatty acid binding proteins: tissue-specific functions in health and disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 17:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000031
Wang J, Huang Y, Li K, Chen Y, Vanegas D, McLamore ES, Shen Y (2016) Leaf extract from Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd. promote glycogen synthesis in t2dm mice. PLoS One 11:e0166557. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166557
Won YW, Adhikary PP, Lim KS, Kim HJ, Kim JK, Kim YH (2014) Oligopeptide complex for targeted non-viral gene delivery to adipocytes. Nat Mater 13:1157–1164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4092
Wu H, Ballantyne CM (2020) Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Circ Res 126:1549–1564. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315896
Yudkin JS (2007) Inflammation, obesity, and the metabolic syndrome. Horm Metab Res 39:707–709. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-985898
Zhang M, Zhu W, Li Y (2014) Small molecule inhibitors of human adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (fabp4). Med Chem 10:339–347. https://doi.org/10.2174/15734064113096660045
Zhang XM, Guo L, Chi MH, Sun HM, Chen XW (2015) Identification of active mirna and transcription factor regulatory pathways in human obesity-related inflammation. BMC Bioinformatics 16:76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0512-5
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Grant, KJZD-K202101102, KJQN201901139) and Chongqing Science & Technology Bureau (cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0427).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LXG and WYC performed research and analyzed results. YF performed statistical analysis. LJH, YF, and YL wrote and edited the manuscript. LJH and YL designed the project and contributed the research questions. All authors have read the final version of this paper and approved its publication.
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wu, Y., Jiang, X. et al. Trilobatin Ameliorates Inflammatory Response by Regulating the miR375-Mediated Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Expression in Adipocytes. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 33, 214–221 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00356-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-022-00356-5