Abstract
Background
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent age-dependent neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive impairment of memory and cognitive functions. Cyclic nucleotides like cAMP and cGMP are well-known to play an important role in learning and memory functions. Enhancement of cAMP and cGMP levels in the hippocampus by phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors might be a novel therapeutic approach for AD. Thus, the present study was planned to explore the therapeutic potential of roflumilast (RFM) and tadalafil (TDF) phosphodiesterase inhibitors in intracerebroventricular (ICV) Aβ1–42 induced AD in rats.
Methods
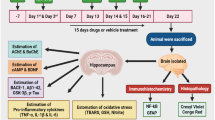
ICV Aβ1–42 was administered in rats followed by treatment with RFM (0.05 mg/kg) and TDF (0.51 mg/kg) for 15 days. Novel object recognition (NOR), and Morris water maze (MWM) test were performed during the drug treatment schedule. On the day, 22 rats were sacrificed, and hippocampus was separated for biochemical, neuroinflammation, and histopathological analysis.
Results
Aβ1–42 infused rats were induce behavioral impairment and increased AChE, BACE-1, Aβ1–42, GSK-3β, phosphorylated tau (p-Tau), pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) levels, oxidative stress (increased MDA, Nitrite and decreased GSH), histopathological changes, and reduced cAMP, cGMP, and BDNF levels. RFM and TDF significantly attenuated Aβ1–42 induced memory deficits and neuropathological alterations in the hippocampus.
Conclusion
The outcomes of the current study indicate that RFM and TDF lead to memory enhancement through upregulation of cAMP/cGMP/BDNF pathway, thus they may have a therapeutic potential in cognitive deficits associated with AD.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 July 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00511-2
References
Eratne D, Loi SM, Farrand S, Kelso W, Velakoulis D, Looi JC. Alzheimer’s disease: clinical update on epidemiology, pathophysiology and diagnosis. Australas Psychiatry. 2018;26:347–57.
Husain I, Akhtar M, Madaan T, Vohora D, Abdin MZ, Islamuddin M, et al. Tannins enriched fraction of Emblica officinalis fruits alleviates high-salt and cholesterol diet-induced cognitive impairment in rats via Nrf2–ARE pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:23.
Kelly MP. Cyclic nucleotide signaling changes associated with normal aging and age-related diseases of the brain. Cell Signal. 2018;42:281–91.
Akhtar A, Bishnoi M, Sah SP. Sodium orthovanadate improves learning and memory in intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin rat model of Alzheimer’s disease through modulation of brain insulin resistance induced tau pathology. Brain Res Bull. 2020;164:83–97.
Sengoku R. Aging and Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Neuropathology. 2020;40:22–9.
Vijayan D, Chandra R. Amyloid beta hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: major culprits and recent therapeutic strategies. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21:148–66.
Baby N, Alagappan N, Dheen ST, Sajikumar S. MicroRNA-134-5p inhibition rescues long-term plasticity and synaptic tagging/capture in an Aβ (1–42)-induced model of Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell. 2020;19:e13046.
Ivashko-Pachima Y, Gozes I. NAP protects against tau hyperphosphorylation through GSK3. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:3868–77.
Hu X, Li X, Zhao M, Gottesdiener A, Luo W, Paul S. Tau pathogenesis is promoted by Aβ1-42 but not Aβ1-40. Mol Neurodegener. 2014;9:1–11.
Guzmán BC-F, Chaffey TE, Palpagama TH, Waters S, Boix J, Tate WP, et al. The interplay between beta-amyloid 1–42 (Aβ1–42)-induced hippocampal inflammatory response, p-tau, vascular pathology, and their synergistic contributions to neuronal death and behavioral deficits. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020;13:522073.
Heckman P, Blokland A, Bollen E, Prickaerts J. Phosphodiesterase inhibition and modulation of corticostriatal and hippocampal circuits: clinical overview and translational considerations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;87:233–54.
Kaundal M, Zameer S, Najmi AK, Parvez S, Akhtar M. Betulinic acid, a natural PDE inhibitor restores hippocampal cAMP/cGMP and BDNF, improve cerebral blood flow and recover memory deficits in permanent BCCAO induced vascular dementia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;832:56–66.
Bollen E, Akkerman S, Puzzo D, Gulisano W, Palmeri A, D’Hooge R, et al. Object memory enhancement by combining sub-efficacious doses of specific phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Neuropharmacology. 2015;95:361–6.
Gulisano W, Tropea MR, Arancio O, Palmeri A, Puzzo D. Sub-efficacious doses of phosphodiesterase 4 and 5 inhibitors improve memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 2018;138:151–9.
Wedzicha JA, Calverley PM, Rabe KF. Roflumilast: a review of its use in the treatment of COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:81.
Goyal A, Garabadu D. Roflumilast attenuates cognitive deficits in estrogen insufficient rats. Behav Pharmacol. 2020;31:671–87.
Bhatia P, Singh N. Tadalafil ameliorates memory deficits, oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and neuropathological changes in rat model of hyperhomocysteinemia induced vascular dementia. Int J Neurosci. 2020;2020:1–13.
Zuccarello E, Acquarone E, Calcagno E, Argyrousi EK, Deng S-X, Landry DW, et al. Development of novel phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;176:113818.
Santiago A, Soares LM, Schepers M, Milani H, Vanmierlo T, Prickaerts J, et al. Roflumilast promotes memory recovery and attenuates white matter injury in aged rats subjected to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neuropharmacology. 2018;138:360–70.
Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates: hard cover edition. Elsevier; 2006.
Jan A, Hartley DM, Lashuel HA. Preparation and characterization of toxic Aβ aggregates for structural and functional studies in Alzheimer’s disease research. Nat Protoc. 2010;5:1186–209.
Sharma S, Verma S, Kapoor M, Saini A, Nehru B. Alzheimer’s disease like pathology induced six weeks after aggregated amyloid-beta injection in rats: increased oxidative stress and impaired long-term memory with anxiety-like behavior. Neurol Res. 2016;38:838–50.
Jan A, Gokce O, Luthi-Carter R, Lashuel HA. The ratio of monomeric to aggregated forms of Aβ40 and Aβ42 is an important determinant of amyloid-β aggregation, fibrillogenesis, and toxicity. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:28176–89.
Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016;7:27.
Deshmukh R, Kaundal M, Bansal V. Caffeic acid attenuates oxidative stress, learning and memory deficit in intra-cerebroventricular streptozotocin induced experimental dementia in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;81:56–62.
Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1984;11:47–60.
Wang D, Wang C, Liu L, Li S. Protective effects of evodiamine in experimental paradigm of Alzheimer’s disease. Cogn Neurodyn. 2018;12:303–13.
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961;7:88–95.
Zameer S, Alam M, Hussain S, Vohora D, Ali J, Najmi AK, et al. Neuroprotective role of alendronate against APP processing and neuroinflammation in mice fed a high fat diet. Brain Res Bull. 2020;161:197–212.
Kaundal M, Deshmukh R, Akhtar M. Protective effect of betulinic acid against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced cognitive impairment and neuronal damage in rats: possible neurotransmitters and neuroinflammatory mechanism. Pharmacol Rep. 2018;70:540–8.
Wills E. Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1966;99:667.
Ahuja S, Uniyal A, Akhtar A, Sah SP. Alpha lipoic acid and metformin alleviates experimentally induced insulin resistance and cognitive deficit by modulation of TLR2 signalling. Pharmacol Rep. 2019;71:614–23.
Ellman GL. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959;82:70–7.
Akhtar A, Dhaliwal J, Saroj P, Uniyal A, Bishnoi M, Sah SP. Chromium picolinate attenuates cognitive deficit in ICV-STZ rat paradigm of sporadic Alzheimer’s-like dementia via targeting neuroinflammatory and IRS-1/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;2020:1–16.
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982;126:131–8.
Richa R, Yadawa AK, Chaturvedi CM. Hyperglycemia and high nitric oxide level induced oxidative stress in the brain and molecular alteration in the neurons and glial cells of laboratory mouse. Mus Musculus Neurochem Int. 2017;104:64–79.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.
Vyas P, Tulsawani RK, Vohora D. Loss of protection by antiepileptic drugs in lipopolysaccharide-primed pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus is mediated via inflammatory signalling. Neuroscience. 2020;442:1–16.
Zameer S, Kaundal M, Vohora D, Ali J, Najmi AK, Akhtar M. Ameliorative effect of alendronate against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced alteration in neurobehavioral, neuroinflammation and biochemical parameters with emphasis on Aβ and BACE-1. Neurotoxicology. 2019;70:122–34.
Xu Y, Zhu N, Xu W, Ye H, Liu K, Wu F, et al. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 reverses Aβ-induced memory impairment by regulation of HPA axis related cAMP signaling. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:204.
Sanders O, Rajagopal L. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors for alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review of clinical trials and epidemiology with a mechanistic rationale. J Alzheimer’s Dis Rep. 2020;4:185–215.
Rahman SO, Panda BP, Parvez S, Kaundal M, Hussain S, Akhtar M, et al. Neuroprotective role of astaxanthin in hippocampal insulin resistance induced by Aβ peptides in animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;110:47–58.
Sachdeva AK, Chopra K. Lycopene abrogates Aβ (1–42)-mediated neuroinflammatory cascade in an experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Biochem. 2015;26:736–44.
García-Barroso C, Ricobaraza A, Pascual-Lucas M, Unceta N, Rico AJ, Goicolea MA, et al. Tadalafil crosses the blood–brain barrier and reverses cognitive dysfunction in a mouse model of AD. Neuropharmacology. 2013;64:114–23.
Gilleen J, Farah Y, Davison C, Kerins S, Valdearenas L, Uz T, et al. An experimental medicine study of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, roflumilast, on working memory-related brain activity and episodic memory in schizophrenia patients. Psychopharmacology. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5134-y.
Gauthier S, Molinuevo JL. Benefits of combined cholinesterase inhibitor and memantine treatment in moderate–severe Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:326–31.
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Dekundy A, Pulte I. Memantine and cholinesterase inhibitors: complementary mechanisms in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res. 2013;24:358–69.
Kametani F, Hasegawa M. Reconsideration of amyloid hypothesis and tau hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:25.
Zhao N, Sun C, Zheng M, Liu S, Shi R. Amentoflavone suppresses amyloid β1–42 neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease through the inhibition of pyroptosis. Life Sci. 2019;239:117043.
Bloom GS. Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71:505–8.
Lauretti E, Dincer O, Praticò D. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophysic Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020;1867:118664.
Wang Y-J, Ren Q-G, Gong W-G, Wu D, Tang X, Li X-L, et al. Escitalopram attenuates β-amyloid-induced tau hyperphosphorylation in primary hippocampal neurons through the 5-HT1A receptor mediated Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Oncotarget. 2016;7:13328.
Nemoto T, Toyoshima-Aoyama F, Yanagita T, Maruta T, Fujita H, Koshida T, et al. New insights concerning insulin synthesis and its secretion in rat hippocampus and cerebral cortex: Amyloid-β1–42-induced reduction of proinsulin level via glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Cell Signal. 2014;26:253–9.
Ly PT, Wu Y, Zou H, Wang R, Zhou W, Kinoshita A, et al. Inhibition of GSK3β-mediated BACE1 expression reduces Alzheimer-associated phenotypes. J Clin Investig. 2012;123:224–35.
Chami L, Checler F. BACE1 is at the crossroad of a toxic vicious cycle involving cellular stress and β-amyloid production in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2012;7:1–15.
Teich AF, Nicholls RE, Puzzo D, Fiorito J, Purgatorio R, Arancio O. Synaptic therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: a CREB-centric approach. Neurotherapeutics. 2015;12:29–41.
Bitner RS. Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation: a mechanistic marker in the development of memory enhancing Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:705–14.
Begni V, Riva MA, Cattaneo A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci. 2017;131:123–38.
Bathina S, Das UN. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch Medical Sci. 2015;11:1164.
Postu PA, Noumedem JA, Cioanca O, Hancianu M, Mihasan M, Ciorpac M, et al. Lactuca capensis reverses memory deficits in Aβ1-42-induced an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:111–22.
Wang L, Xiaokaiti Y, Wang G, Xu X, Chen L, Huang X, et al. Inhibition of PDE2 reverses beta amyloid induced memory impairment through regulation of PKA/PKG-dependent neuro-inflammatory and apoptotic pathways. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1–12.
Feng H, Wang C, He W, Wu X, Li S, Zeng Z, et al. Roflumilast ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling and anti-neuroinflammatory effects. Metab Brain Dis. 2019;34:583–91.
França MER, Ramos RKLG, Oliveira WH, Duarte-Silva E, Araújo SMR, Los DB, et al. Tadalafil restores long-term memory and synaptic plasticity in mice with hepatic encephalopathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;379:114673.
Amani M, Zolghadrnasab M, Salari A-A. NMDA receptor in the hippocampus alters neurobehavioral phenotypes through inflammatory cytokines in rats with sporadic Alzheimer-like disease. Physiol Behav. 2019;202:52–61.
Stamouli EC, Politis AM. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatriki. 2016;27:264–75.
Huang Z, Ji H, Shi J, Zhu X, Zhi Z. Engeletin attenuates Aβ1–42-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation by keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Inflammation. 2020;43(5):1759–71.
Abdel Moneim AE. Oxidant/antioxidant imbalance and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2015;12:335–49.
Mangialasche F, Polidori MC, Monastero R, Ercolani S, Camarda C, Cecchetti R, et al. Biomarkers of oxidative and nitrosative damage in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Ageing Res Rev. 2009;8:285–305.
Sadiki FZ, El Idrissi M, Cioanca O, Trifan A, Hancianu M, Hritcu L, et al. Tetraclinis articulata essential oil mitigates cognitive deficits and brain oxidative stress in an Alzheimer’s disease amyloidosis model. Phytomedicine. 2019;56:57–63.
Kaundal M, Akhtar M, Deshmukh R. Lupeol isolated from Betula alnoides ameliorates amyloid beta induced neuronal damage via targeting various pathological events and alteration in neurotransmitter levels in rat’s brain. J Neurol Neurosci. 2017;8:195.
Gulati P, Singh N. Neuroprotective effect of tadalafil, a PDE-5 inhibitor, and its modulation by L-NAME in mouse model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Surg Res. 2014;186:475–83.
Ozdegirmenci O, Kucukozkan T, Akdag E, Topal T, Haberal A, Kayir H, et al. Effects of sildenafil and tadalafil on ischemia/reperfusion injury in fetal rat brain. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;24:317–23.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the DST-PURSE program of the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India. We express our gratitude to Neurotoxicology Lab, Department of Medical Elementology and Toxicology, School of Chemical and Life Sciences, Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi India, and also to Neurobehavioral Pharmacology Lab, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Jamia Hamdard New Delhi India for providing necessary facilities used during this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00511-2
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, N., Zameer, S., Najmi, A.K. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Roflumilast and tadalafil improve learning and memory deficits in intracerebroventricular Aβ1–42 rat model of Alzheimer’s disease through modulations of hippocampal cAMP/cGMP/BDNF signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Rep 73, 1287–1302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00264-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00264-w