Abstract
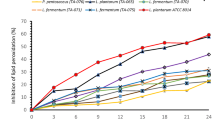
This study highlights the production and characterization of siderophore from probiotic bacteria, aiming to evaluate its suitability as a carrier to treat iron deficiency anemia. Organisms were previously isolated from Chhurpi (Himalayan traditional fermented food) and their probiotic characteristics were reported. Among the, Bacillus subtilis L9 that produced catecholate and Pediococcus pentosaceus BAC L7 synthesized hydroxymate and catecholate type of siderophore. After optimization (pH 6.0, 100 rpm agitation speed and 15% inoculums volume) B. subtilis L9 and P. pentosaceus BAC L7 produced 89 and 73% siderophore unit respectively, after 72 h of incubation at simulated gastro-intestinal condition. Owing to better siderophore production and spore forming capability B. subtilis L9 was selected and physico-chemical characteristics of its siderophore were studied by FTIR, NMR and mass spectrometric analysis. The purified siderophore (2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl glycine) from B. subtilis L9 exhibited a high iron scavenging activity (89.76%). The study was penlights the exploration of probiotic microorganism present in the indigenous fermented food and their capability to biosynthesize siderophore that could be an effective therapeutic aid for maximum absorption of dietary iron and alleviation anemia like micronutrient deficiency diseases as well as to combat hypoxia among the high altitude residents.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silva B, Faustino P. An overview of molecular basis of iron metabolism regulation and the associated pathologies. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis Disease. 2015;1852:1347.
Milto IV, Suhodolo IV, Prokopieva VD, Klimenteva TK. Molecular and cellular bases of iron metabolism in humans. Biochem (Mosc). 2016;81:549–64.
Goswami D, Mondal S, Hor PK, Santra S, Jana H, Gauri SS, Halder SK, Mondal KC. Bioprospecting of probiotic bacteria from traditional food of high-altitude himalayan region. Food Biosci. 2023;30:103257.
Bajaj JS. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16(4);235 – 46.
Andrabi ST, Bhat B, Gupta M, Bajaj BK. Phytase-producing potential and other functional attributes of lactic acid bacteria isolates for prospective probiotic applications. Probiotics Antimicrob. 2016;8:121–9.
Venkatesh U, Sharma A, Ananthan VA, Subbiah P, Durga R. Micronutrient’s deficiency in India: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Sci. 2021;10:e110.
González A, Gálvez N, Martín J, Reyes F, Pérez-Victoria I, Dominguez-Vera JM. Identification of the key excreted molecule by Lactobacillus fermentum related to host iron absorption. Food Chem. 2017;228:374.
Wilson BR, Bogdan AR, Miyazawa M, Hashimoto K, Tsuji Y. Siderophores in iron metabolism: from mechanism to therapy potential. Trends Mol Med. 2016;22:1077.
Ellermann M, Arthur JC. Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition and modulation of host-bacterial interactions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;105:68.
Li X, Liang H. Effects of Lactobacillus casei on iron metabolism and intestinal microflora in rats exposed to alcohol and iron. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2022;33:470.
Muckenthaler MU, Mairbäurl H, Gassmann M. Iron metabolism in high-altitude residents. J Appl Physiol. 2020;129(4):920–5.
Ray M, Hor PK, Singh SN, Mondal KC. Screening of health beneficial microbes with potential probiotic characteristics from the traditional rice-based alcoholic beverage, haria. Acta Biol Szeged. 2017;61:51.
Panda SH, Goli JK, Das S, Mohanty N. Production, optimization and probiotic characterization of potential lactic acid bacteria producing siderophores. AIMS Microbiol. 2017;3:88.
Yang YW, Chen MK, Yang BY, Huang XJ, Zhang XR, He LQ, Zhang J, Hua ZC. Use of 16S rRNA gene-targeted group-specific primers for real-time PCR analysis of predominant bacteria in mouse feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81:6749.
Schwyn B, Neilands JB. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem. 1987;160:47.
Ferreira CM, Vilas-Boas Â, Sousa CA, Soares HM, Soares EV. Comparison of five bacterial strains producing siderophores with the ability to chelate iron under alkaline conditions. AMB Express. 2019;9:78.
Ahire JJ, Patil KP, Chaudhari BL, Chincholkar SB. A potential probiotic culture ST2 produces siderophore 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoylserine under intestinal conditions. Food Chem. 2011;127:387.
Mondal S, Santra S, Rakshit S, Halder SK, Hossain M, Mondal KC. Saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass using an enzymatic cocktail of fungal origin and successive production of butanol by. Clostridium acetobutylicum Bioresour Technol. 2022;343:126093.
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr AL, Randall R. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.
Skrypnik K, Bogdański P, Schmidt M, Suliburska J. The effect of multispecies probiotic supplementation on iron status in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;192:234.
Ruiz Sella SR, Bueno T, de Oliveira AA, Karp SG, Soccol CR. Bacillus subtilis natto as a potential probiotic in animal nutrition. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2021;41:355.
Patel AK, Deshattiwar MK, Chaudhari BL, Chincholkar SB. Production, purification and chemical characterization of the catecholate siderophore from potent probiotic strains of Bacillus spp. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100:368.
Campana R, van Hemert S, Baffone W. Strain-specific probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria and their interference with human intestinal pathogens invasion. Gut Pathog. 2017;9(1):1.
Payne SM. Detection, isolation, and characterization of siderophores. Methods Enzymol. 1994;235:329.
Patel AK, Ahire JJ, Pawar S, Chaudhari BL, et al. Comparative accounts of probiotic characteristics of Bacillus spp. isolated from food wastes. Food Res Int. 2009;42:505–10.
Zhu H, Yang H. Isolation and characterization of a highly siderophore producing Bacillus subtilis strain. In Advances in Applied Biotechnology: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Biotechnology. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2015;pp.83–92.
Li J, Hirimuthugoda MU, Li H, Yao S. Cloning and sequencing of the Fur gene from marine probiotic Alteromonas aurantia A18 and its possible role in siderophore production. Trop Agr Res Ext. 2010;19:11.
Bendale MS, Chaudhari BL, Chincholkar SB. Influence of environmental factors on siderophore production by Streptomyces fulvissimus ATCC 27431. Pharmainfo Net. 2010;16:36.
Balgir PP, Kaur B, Kaur T. A preliminary clinical evaluation of probiotics Pediococcus acidilactici MTCC5101 and Bacillus coagulans MTCC492 on young anemic women. Int J Fermented Foods. 2014;3:45.
Mark R, Lyu X, Lee JJ, Parra-Saldívar R, Chen WN. Sustainable production of natural phenolics for functional food applications. J Funct Foods. 2019;57:233.
Roy EM, Griffith KL. Characterization of a novel iron acquisition activity that coordinates the iron response with population density under iron-replete conditions in. Bacillus subtilis J Bacteriol. 2017;199:10.
Kontoghiorghes GJ, Kontoghiorghe CN. Iron and chelation in biochemistry and medicine: new approaches to controlling iron metabolism and treating related diseases. Cells. 2020;9(6):1456.
Wandersman C, Delepelaire P. Bacterial iron sources: from siderophores to hemophores. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004;58:611.
Yu X, Ai C, Xin L, Zhou G. The siderophore-producing bacterium, Bacillus subtilis CAS15, has a biocontrol effect on Fusarium wilt and promotes the growth of pepper. Eur J Soil Biol. 2011;47:138.
Ollinger J, Song KB, Antelmann H, Hecker M, Helmann JD. Role of the Fur regulon in iron transport in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:3664.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the DST, Govt. of West Bengal, India for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict among the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Goswami, D., Halder, S.K. & Mondal, K.C. Characterization of siderophore from probiotic Bacillus spp. strain isolated from traditional fermented food of the Himalaya. Syst Microbiol and Biomanuf (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-024-00257-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-024-00257-9