Abstract
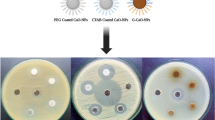
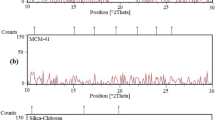
This study reports the preparation of Candida Antarctic lipase B (CalB) enzyme and nanofructosome encapsulated CalB enzyme (CalB@NF) immobilized silica coated magnetic nanoparticles (Si-MNPs) and demonstration of the enzymatic hydrolysis and acylation against p-nitrophenyl butyrate (p-NPB) and benzoic anhydride. Si-MNPs was prepared 60 nm of particle size with spherical shape, and the immobilization of CalB and CalB@NF was coupled by chlorosilane linker on the surface of Si-MNPs. The quantitative determination of CalB in Si-MNPs@CalB and Si-MNPs@CalB@NF was followed by Bradford assay. Various enzymatic kinetic parameters such as Km, Vmax, and Kcat were calculated using the Lineweaver-Burk equation and Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The hydrolysis of p-NPB with Si-MNPs@CalB@NF and Si-MNPS@CalB confirmed their utilization as effective catalysts. Furthermore, all four samples of native CalB, CalB@NF, Si-MNPs@CalB, and Si-MNPs@CalB@NF were successfully acylated to benzyl benzoate after column separation, and showed more than 99% conversion efficiency. The stability for pH and temperature of Si-MNPs@CalB and Si-MNPs@CalB@NF was optimized at 8 and 45 ℃, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
H.R. Lee, M.I. Kim, S.E. Hong, J.Y. Choi, Y.M. Kim, K.R. Yoon, S.H. Lee, S.H. Ha, Effect of functional group on activity and stability of lipase immobilized on silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles with different functional group, J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 105–113 (2016)
B. Staucha, S.J. Fisherc, M. Cianci, Open and closed states of candida antarctica lipase B: protonation and the mechanism of interfacial activation. J. Lipid Res. 56(12), 2348–2358 (2015)
H.Z. Maa, X.W. Yub, C. Songa, Q. Xuea, B. Jianga, Immobilization of candida antarctica lipase B on epoxy modified silica by sol-gel process. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 127, 76–81 (2016)
K.E. Jaeger, T. Eggert, Lipases for biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13, 390–397 (2002)
F.L.C. Almeida, M.P.J. Castro, B.M. Travalia, M.B.S. Forte, Trends in lipase immobilization: bibliometric review and patent analysis. Process. Biochem. 110, 37–51 (2021)
J.C. Cruz, K. Würges, M. Kramer, P.H. Pfromm, M.E. Rezac, P. Czermak, Immobilization of enzymes on fumed silica nanoparticles for applications in nonaqueous media, Methods Mol. Biol. 743 (2011)
E.T. Önera, L. Hernándezb, J. Combiec, Review of levan polysaccharide: from a century of past experiences to future prospects, Biotechnol. Adv. 34, 827–844 (2016)
P. Wiecinska, A. Zurawska, P. Falkowski, D.Y. Jeong, M. Szafran, Sweet ceramics: how saccharide–based compounds have changed colloidal processing of ceramic materials. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 57, 231–245 (2020)
C.S. Hundschell, F. Jakob, M. Wagemans, Molecular weight dependent structure of the exopolysaccharide levan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 161, 398–405 (2020)
E.M. Anderson, K.M. Larsson, O. Kirk, One biocatalyst–many applications: the use of candida antarctica B-lipase in organic synthesis. Biocatal. Biotransform. 16, 181–204 (2009)
D. Rotticci, J.C. Rotticci-Mulder, S. Denman, T. Norin, K. Hult, Improved enantioselectivity of a lipase by rational protein engineering, ChemBioChem. 2, 766–770 (2001)
J.H. Sohn, J.H. Bae, Levan-protein nanocomposites and their uses, KR Patent 1024159780000 (2022)
S.A. Arvidson, B.T. Rinehart, Francis Gadala-Maria,concentration regimes of solutions of levan polysaccharide from Bacillus sp. Carbohydr. Polym. 65, 144–149 (2006)
R. Srikanth, C.H.S.S. Sundhar Reddy, G. Siddartha, M.J. Ramaiah, K.B. Uppuluri, Review on production, characterization and applications of microbial levan. Carbohydr. Polym. 14, 0144–8617 (2014)
M.D. Kedzia, M. Ostrowska, A. Lewinska, Lukasazewicz recent developments and applications of microbial levan, a vrsatile polysaccharide-based biopolymer. Molecules. 28, 5407–5430 (2023)
H.J. Noh, W.Y. Lee, Synthesis of levan using recombinant levansucrase lmmobilized onto Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Korea Academia Industrial Soc. 24, 508–519 (2023)
R.A. Sheldon, Enzyme immobilization: the quest for optimum performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 349, 1289–1307 (2007)
S. Sharma, S. Gupta, S.K. Princy, A. Arya, Kaur, Enzyme immobilization: implementation of nanoparticles and an insight into polystyrene as the contemporary immobilization matrix. Process. Biochem. 120, 22–34 (2022)
C.H. Lee, E.S. Jin, J.H. Lee, E.T. Hwang, Immobilization and stabilization of enzyme in Biomineralized Calcium Carbonate Microspheres. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 553–591 (2020)
P. Zucca, E. Sanjust, Inorganic materials as supports for covalent enzyme immobilization: methods and mechanisms. Molecules. 19, 14139–14194 (2014)
O. Yemul, T. Imae, Covalent-bonded immobilization of lipase on poly(phenylene sulfide) dendrimers and their hydrolysis ability. Biomacromolecules. 6, 2809–2814 (2005)
T. Jesionowski, J. Zdarta, B. Krajewska, Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: a review. Adsorption. 20, 801–821 (2014)
K.H. Won, S.B. Kim, K.J. Kim, H.W. Park, S.J. Moon, Optimization of lipase entrapment in Ca-alginate gel beads. Process. Biochem. 40, 2149–2154 (2005)
U. Hanefeld, L. Gardossi, E. Magner, Understanding enzyme immobilisation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 453–468 (2009)
Y. Wu, Y. Wang, G. Luo, Y. Dai, In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles for lipase immobilization by cross-linking and oxidation in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol. 100, 3459–3464 (2009)
J.W. Lee, D.K. Kim, Carboxymethyl group activation of dextran cross–linked superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 58, 106–115 (2020)
A. Nikmah, A. Taufiq, A. Hidayat, Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. IOP Conf. Ser. : Earth Environ. Sci. 276, 012046 (2019)
D. Yang, J. Hu, S. Fu, Controlled synthesis of magnetite-silica nanocomposites via a seeded sol-gel approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 7646–7651 (2009)
C.G.C.M. Netto, H.E. Toma, L.H. Andrade, Superparamagnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers and supporting materials for enzymes. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 85–86, 71–92 (2013)
J.L. Campbell, J. Arora, S.F. Cowell, A. Garg, P. Eu, S.K. Bhargava, V. Bansal, “Quasi-cubic magnetite/silica core-shell nanoparticles as enhanced MRI contrast agents for cancer imaging” PLOS ONE 6 e21857 (2011)
P. Sricharoen, S. Chanthai, N. Lamaiphan, C. Sakaew, N. Limchoowong, P. Nuengmatcha, W.C. Oh, Sono–synthesized Fe3O4–GO–NH2 nanocomposite for highly efficient ultrasound–assisted magnetic dispersive solid–phase microextraction of hazardous dye Congo red from water samples. J. Korea Ceram. Soc. 58, 201–211 (2021)
F. Sharifianjazi, M. Irani, A. Esmaeilkhanian, L. Bazli, M.S. Asl, H.W. Jang, S.Y. Kim, S. Ramakrishna, M. Shokouhimehre, R.S. Varma, Polymer incorporated magnetic nanoparticles: applications for magnetoresponsive targeted drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Engineering: B 272, 115358 (2021)
N. Lamaiphan, C. Sakaew, P. Sricharoen, P. Nuengmatcha, S. Chanthai, N. Limchoowong, Highly efficient ultrasonic-assisted preconcentration of trace amounts of Ag(I), Pb(II), and Cd(II) ions using 3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane-functionalized graphene oxide–magnetic nanoparticles. J. Korea Ceram. Soc. 58, 314–329 (2021)
A. Noypha, Y. Areerob, S. Chanthai, P. Nuengmatcha, Fe2O3-graphene anchored Ag nanocomposite catalyst for enhanced sonocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Kor Ceram. Soc. 58, 297–306 (2021)
K.H. Kang, J.S. Choi, J.H. Nam, S.C. Lee, K.J. Kim, S.W. Lee, J.H. Chang, Preparation and characterization of chemically functionalized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles as a DNA separator, J. Phys. Chem. B 536–543 (2009)
M. Zhang, B.L. Cushing, C.J. O’Connor, Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse ultra-thin silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanotechnol. 19, 085601 (2008)
M.S. Park, A.R. Choi, S.K. Kim, W.Y. Shim, Y.J. Kim, Study of SiO2 coating and carboxylic surface–modifcation on Mg–based inorganic fber by one–step refux reaction. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 869–875 (2022)
S. Palakurthy, P.A. Azeem, K.V. Reddy, Sol–gel synthesis of soda lime silica–based bioceramics using biomass as renewable sources. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 76–85 (2022)
L.R. Arcot, M. Lundahl, O.J. Rojas, J. Laine, Asymmetric cellulose nanocrystals: thiolation of reducing end groups via NHS–EDC coupling. Cellulose. 21, 4209–4218 (2014)
S. Gámez, A. Magerat, E. Torre, E.M. Gaigneaux, functionalization of carbon black for Ru complexation towards the oxidative cleavage of oleic acid. J. Mol. Catal. 541, 113097 (2023)
M.J.E. Fischer, Amine coupling through EDC/NHS: a practical approach. Methods Mol. Biol. 627, 55–73 (2010)
P. Tengvall, E. Jansson, A. Askendal, P. Thomsen, C. Gretzer, Preparation of multilayer plasma protein films on silicon by EDC/NHS coupling chemistry. Colloids Surf. B 28, 261–272 (2003)
H.Y. Lee, W.Y. Jang, J.H. Chang, Reusable and rapid esterolysis of nitrophenyl alkanoates with CalB enzyme–immobilized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 527–535 (2022)
M. Song, J.H. Chang, Thermally stable and reusable ceramic encapsulated and cross-linked CalB enzyme particles for rapid hydrolysis and esterification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 2459 (2022)
N.J. Kruger, The Bradford method for protein quantitation, The Protein Protocols Handbook 17–24 (2009)
M.M. Bradford, A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 7, 248–254 (1976)
A. Mobinikhaledi, H. Moghanian, Z. Souri, Efficient synthesis of 2-amino-4H-chromene derivatives in the presence of piperazine-functionalized Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles as a new heterogeneous reusable catalyst under solvent-free conditions. Lett. Org. Chem. 11, 432–439 (2014)
S.Y. Lee, C.Y. Ahn, J.H. Lee, J.H. Lee, J.H. Chang, Rapid and selective separation for mixed proteins with thiol functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 279 (2012)
J.H. Lee, J.H. Chang, Facile and high-efficient immobilization of histidine-tagged multimeric protein G on magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 664 (2014)
A. Ulu, S.A.A. Noma, S. Koytepe, B. Ates, Chloro-modified magnetic Fe3O4@MCM-41 core–shell nanoparticles for L-asparaginase lmmobilization with improved catalytic activity, reusability, and storage stability. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 187, 938–956 (2019)
W.Y. Jang, J.H. Sohn, J.H. Chang, Thermally stable and reusable silica and nano-fructosome encapsulated CalB enzyme particles for rapid enzymatic hydrolysis and acylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 9838 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ01493802)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest with this work.
Ethical approval
This paper meets the ethical standards of this journal.
Research involving human and animals’ rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
All authors agree with the review of this paper in this journal.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Jang, W. & Chang, J.H. Nanofructosome encapsulated CalB enzyme immobilized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles for rapid enzymatic hydrolysis and acylation. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 61, 126–136 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00355-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00355-9