Abstract
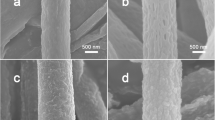
Nanostructured titania (TiO2) fibers such as nonporous, macroporous, hollow, and hollow macroporous fibers were successfully prepared by electrospinning using titanium diisopropoxide bis (acetylacetonate) (TDIP) as starting material. Hollow TiO2 fibers were fabricated using two syringe pumps and dual concentric nozzle to prepare hollow microstructure inside the fibrous materials. Oil was supplied to core of nozzle and polymeric mixture containing the titania precursor was injected into outer layer of nozzle. Then, oil from electro-spun fibers was removed by washing with organic solvent to obtain hollow microstructure. Macroporous hollow titania fibers could be also fabricated from spinning solution composed of the titania precursor and PS nanospheres as sacrificial templates. Thickness of fiber walls of macroporous hollow titania fibers became thinner from 425.5 to 353.5 nm, when flow rate of titania precursor solution was adjusted from 15 to 10 μL/min. SEM, XRD, and FT-IR analysis were employed to characterize morphologies, crystallinity, and compositions of the fibers, respectively. Photocatalytic removal of methylene blue under UV light illumination was performed using four different kinds of the titania fibers to compare their photocatalytic activity. Rate constant of the degradation reaction could be estimated from experimental data during photocatalytic degradation, assuming first-order kinetics. The rate constant of hollow titania fiber (0.0772 min−1) was estimated as the highest value among various kinds of the nanostructured fibers, showing the best photocatalytic ability for decomposition of organic dyes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
K.-K. Kefeni, B.-B. Mamba, Photocatalytic application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites in wastewater treatment: Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 23, e00140 (2020)
J. Wang, G. Wang, B. Cheng, J. Yu, J. Fan, Sulfur-doped g-C3N4/TiO2 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for Congo Red photodegradation. Chin. J. Catal. 42(1), 56–68 (2021)
P. Kuang, J. Low, B. Cheng, J. Yu, J. Fan, MXene-based photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 56(1), 18–44 (2020)
Z. Wang, J. Fan, B. Cheng, J. Yu, J. Xu, Nickel-based cocatalysts for photocatalysis: Hydrogen evolution, overall water splitting and CO2 reduction. Mater. Today Phys. 5, 100279 (2020)
F. Xu, H. Tan, J. Fan, B. Cheng, J. Yu, J. Xu (2021) Electrospun TiO2-based photocatalysts. Sol.RRL. 5:2000571
T.-H. Yun, C. Yim, Uniform fabrication of hollow titania using anionic modified acrylated polymer template for phase composition effect as photocatalyst and infrared reflective coating. Nanomaterials 11, 2845 (2021)
M.-R. Hoffmann, S.-T. Martin, W. Choi, D.-W. Bahnemann, Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96 (1995)
A. Fujishima, X. Zhang, T.-A. Donald, Heterogeneous photocatalysis: From water photolysis to applications in environmental cleanup. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 32, 2664–2672 (2007)
A. Fujishima, K. Honda, Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238, 37–38 (1972)
K. Maeda, Photocatalytic water splitting using semiconductorparticles: History and recent developments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 12, 237–268 (2011)
R. Abe, Recent progress on photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting under visible light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 11, 179–209 (2010)
W. Choi, A. Termin, M.-R. Hoffmann, The role of metal ion dopants in quantum sized TiO2: correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 13669–13679 (1994)
M. Nasr, C. Eid, R. Habchi, P. Miele, M. Bechelany, Recent progress on titanium dioxide nanomaterials for photocatalytic applications. Chemsuschem 11(18), 3023–3047 (2018)
S.-M. Pasini, A. Valério, G. Yin, J. Wang, S.-M.-A.-G.-U. Souza, D. Hotza, A.-A.-U. Souza, An overview on nanostructured TiO2–containing fibers for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater treatment. J. Water Process. Eng. 40, 101827 (2021)
F.-D. Utami, D.-Y. Rahman, K. Sutisna, D.-O. Margareta, M. Abdullah, Photocatalyst based on TiO2 and its application in organic wastewater treatment using simple spray method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1204, 012086 (2019)
H.L. An, L. Kang, H.-J. Ahn, Y.-H. Choa, Ch.G. Lee, Synthesis and characterization of TiO2/CuS nanocomposite fibers as a visible light-driven photocatalyst. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 55(3), 267–274 (2018)
K. Sharma, V. Sharma, S.-S. Sharma, Dye-sensitized solar cells: Fundamentals and status. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 381 (2018)
T. Ochiai, A. Fujishima, Photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 photocatalyst and its applications for environmental purification. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 13, 247–262 (2012)
S.-E. Sherbiny, F. Morsy, M. Samir, O.-A. Fouad, Synthesis, characterization, and application of TiO2 nanopowders as special paper coating pigment. Appl. Nanosci. 4, 305–313 (2014)
K. Kamiya, K. Tanimoto, T. Yoko, Preparation of TiO2 fibres by hydrolysis and polycondensation of Ti(O—i-C3H7)4. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 5, 402–404 (1986)
Y.-F. Chen, C.-Y. Lee, M.-Y. Yeng, H.-T. Chiu, Preparing titanium oxide with various morphologies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 81, 39–44 (2003)
W. Huang, A. Duan, Z. Zhao, G. Wan, G. Jiang, T. Dou, K.-H. Chung, J. Liu, Ti-modified alumina supports prepared by sol–gel method used for deep HDS catalysts. Catal. Today 131, 314–321 (2008)
K.C. Hui, H. Suhaimi, N.-S. Sambudi, Electrospun-based TiO2 nanofibers for organic pollutant photodegradation: a comprehensive review. J. Rev. Chem. Eng. 38, 641–668 (2021)
S. Park, D.-Y. Lee, M.-H. Lee, S.-J. Lee, B.-Y. Kim, Fabrication of electrospun titania nanofiber. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 42(8), 548–553 (2005)
J. Xie, Y. Xia, Electrospinning: an enabling technique for nanostructured materials. Material Matters 3(1), 19 (2008)
J. Xue, T. Wu, Y. Dai, Y. Xia, Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 119(8), 5298–5415 (2019)
H.-H. Nguyen, T.-T.-H. Nguyen, Y.-S. Cho, Fabrication and surface modification of macroporous silica fibers by electrospinning for super adsorbent of oil. Korean J. Met. Mater. 60(10), 732–743 (2022)
S. Agarw, J.-H. Wendorff, A. Greiner, Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 49(26), 5603–5621 (2008)
M. Baca, K. Wenelska, E. Mijowska, R.-J. Kaleńczuk, B. Zielińska, Physicochemical and photocatalytic characterization of mesoporous carbon/ titanium dioxide spheres. Diam. Relat. Mater. 101, 107551 (2020)
E. Ersöz, O.-A. Yildirim, Green synthesis and characterization of Ag-doped ZnO nanofibers for photodegradation of MB, RhB and MO dye molecules. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59(5), 655–670 (2022)
M.-C. Chang, Nitrogen doping in polycrystalline anatase TiO2 ceramics by atmosphere controlled firing. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 56(4), 374–386 (2019)
X. Li, Z. Zhang, F.-J. Zhang, J. Liu, J. Ye, W.-C. Oh, Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of TiO2/BiVO4 layered films under visible light irradiation. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 53(6), 665–669 (2016)
M. Rashidzadeh, Synthesis of high-thermal stable titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Photoenergy. 245981, 1–4 (2008)
B. Vafakish, M. Barari, E. Jafari, Biodiesel production by transesterification of tallow fat using heterogeneous catalysis. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 47(2), 558–564 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2017R1A6A1A03015562) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1F1A1047451).
Funding
Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), NRF-2017R1A6A1A03015562, Young-Sang Cho, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT), No. 2021R1F1A1047451, Young-Sang Cho.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This paper meets the ethical standards of this journal.
Consent to participate
All authors agree with the review of this paper in this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.T.H., Nguyen, H.H. & Cho, YS. Fabrication of hollow titania fibers by electro-spinning for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 60, 702–711 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00302-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00302-8