Abstract
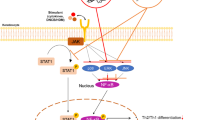
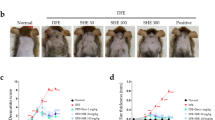
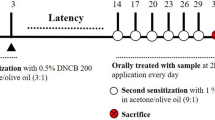
The risk of atopic dermatitis (AD)-like skin lesions has increased due to the elevated levels of allergens worldwide. Natural-origin agents, which are effective and safe, show promise for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory conditions. Orostachys japonicus (OJ) A. Berger is an ingredient of traditional herbal medicines for fever, gingivitis, and cancer in Korea, China, and Japan. However, the effect of OJ on AD-like skin lesions is unknown. Therefore, we investigated the effect of OJ ethanol extract (OJEE) on AD-like skin symptoms in mice and cells. OJEE reduced the 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced AD severity, serum levels of IgE and TARC, and mRNA levels of TARC, TNF-α, and IL-4 in NC/Nga mice. Histopathological analysis showed that OJEE reduced the thickness of the epidermis/dermis and dermal infiltration of inflammatory cells in ear tissue. Furthermore, OJEE suppressed the TNF-α/IFN-γ-increased TARC mRNA level by inhibiting NF-κB and STAT1 activation in HaCaT cells. Taken together, our findings show that OJEE reduced the risk of AD-like skin symptoms by decreasing TARC expression via inhibiting NF-κB and STAT1 activation in skin keratinocytes and thus shows promise as an alternative therapy for AD-like skin lesions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung DY (2000) Atopic dermatitis: new insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105:860–876
Udompataikul M, Limpa-o-vart D (2012) Comparative trial of 5% dexpanthenol in water-in-oil formulation with 1% hydrocortisone ointment in the treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. J Drugs Dermatol 11:366–374
Margolis JS, Abuabara K, Bilker W, Hoffstad O, Margolis DJ (2014) Persistence of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol 150:593–600
Liu FT, Goodarzi H, Chen HY (2011) IgE, mast cells, and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 41:298–310
Leung DY, Bieber T (2003) Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 361:151–160
Hay RJ, Johns NE, Williams HC, Bolliger IW, Dellavalle RP, Margolis DJ, Marks R, Naldi L, Weinstock MA, Wulf SK, Michaud C, Murray JLC, Naghavi M (2014) The global burden of skin disease in 2010: an analysis of the prevalence and impact of skin conditions. J Investig Dermatol 134:1527–1534
Weidinger S, Novak N (2016) Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 387:1109–1122
Rios JL, Bas E, Recio MC (2005) Effects of natural products on contact dermatitis. Curr Med Chem Anti-Inflamm Anti-Allergy Agents 4:65–80
Dawid-Pac R (2013) Medicinal plants used in treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Postepy Dermatol Alergol 30:170–177
Cho HD, Lee KW, Won YS, Shin DY, Seo KI (2019) Studies on the anti-angiogenic activities of wild and cultivated Orostachys japonicus extracts in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Food Sci 84:1764–1775
Lee KS, Kim SW, Lee HS (2018) Orostachys japonicus induce p53-dependent cell cycle arrest through the MAPK signaling pathway in OVCAR-3 human ovarian cancer cells. Food Sci Nutr 6:2395–2401
Lee SG, Kim JS, Lee HS, Lim YM, So JH, Hahn D, Ha YS, Nam JO (2017) Bioconverted Orostachys japonicas extracts suppress angiogenic activity of Ms-1 endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci 18:E2615
Kim YI, Park SW, Yoon YK, Lee KW, Lee JH, Woo HJ, Kim Y (2015) Orostachys japonicus inhibits the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA and modulates the expression of iNOS and COX-2 genes in human PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells via inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK activation. Mol Med Rep 12:657–662
Lee WS, Yun JW, Nagappan A, Jung JH, Yi SM, Kim DH, Kim HJ, Kim G, Ryu CH, Shin SC, Hong SC, Choi YH, Jung JM (2015) Flavonoids from Orostachys japonicus A. Berger induces caspase-dependent apoptosis at least partly through activation of p38 MAPK pathway in U937 human leukemic cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:465–469
Ryu DS, Kim SH, Kwon JH, Lee DS (2014) Orostachys japonicus induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway in AGS human gastric cancer cells. Int J Oncol 45:459–469
Shin DY, Lee WS, Jung JH, Hong SH, Park C, Kim HJ, Kim GY, Hwang HJ, Kim GS, Jung JM, Ryu CH, Shin SC, Hong SC, Choi YH (2013) Flavonoids from Orostachys japonicus A. Berger inhibit the invasion of LnCaP prostate carcinoma cells by inactivating Akt and modulating tight junctions. Int J Mol Sci 14:18407–18420
Ryu DS, Lee HS, Lee GS, Lee DS (2012) Effects of the ethylacetate extract of Orostachys japonicus on induction of apoptosis through the p53-mediated signaling pathway in human gastric cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull 35:660–665
Ryu DS, Baek GO, Kim EY, Kim KH, Lee DS (2010) Effects of polysaccharides derived from Orostachys japonicus on induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death in human colon cancer cells. BMB Rep 43:750–755
Jang M, Choi HY, Kim GH (2019) Phenolic components rich ethyl acetate fraction of Orostachys japonicus inhibits lipid accumulation by regulating reactive oxygen species generation in adipogenesis. J Food Biochem 43:e12939
Jeong H, Kim JW, Yang D, Jeong TW, Zhao J, Seo JH, Shin DG, Cha JD, Han KM, Lim CW, Kim B (2019) Orostachys japonicus A. Berger (Crassulaceae) exerts antidiabetic activity by improving glucose and lipid levels in Type 2 diabetic mice. J Med Food 22:797–809
Lee SJ, Zhang GF, Sung NJ (2011) Hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects of Orostachys japonicus A. Berger extracts in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Nutr Res Pract 5:301–307
Koppula S, Yum MJ, Kim JS, Shin GM, Chae YJ, Yoon T, Chun CS, Lee JD, Song M (2017) Anti-fibrotic effects of Orostachys japonicus A. Berger (Crassulaceae) on hepatic stellate cells and thioacetamide-induced fibrosis in rats. Nutr Res Pract 11:470–478
Kim YI, Park SW, Choi IH, Lee JH, Woo HJ, Kim Y (2011) Effect of Orostachys japonicus on cell growth and apoptosis in human hepatic stellate cell line LX2. Am J Chin Med 39:601–613
Yoon YK, Woo HJ, Kim Y (2015) Orostachys japonicus inhibits expression of the TLR4, NOD2, iNOS, and COX-2 genes in LPS-stimulated human PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:682019
Lee HS, Ryu DS, Lee GS, Lee DS (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of dichloromethane fraction from Orostachys japonicus in RAW 264.7 cells: suppression of NF-κB activation and MAPK signaling. J Ethnopharmacol 140:271–276
Jeong JH, Ryu DS, Suk DH, Lee DS (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol extract from Orostachys japonicus on modulation of signal pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. BMB Rep 44:399–404
Im DS, Lee JM, Lee J, Shin HJ, No KT, Park SH, Kim K (2017) Inhibition of collagenase and melanogenesis by ethanol extracts of Orostachys japonicus A. Berger: possible involvement of Erk and Akt signaling pathways in melanoma cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 49:945–953
Lee HS, Lee GS, Kim SH, Kim HK, Suk DH, Lee DS (2014) Anti-oxidizing effect of the dichloromethane and hexane fractions from Orostachys japonicus in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells via upregulation of Nrf2 expression and activation of MAPK signaling pathway. BMB Rep 47:98–103
Yoon Y, Kim KS, Hong SG, Kang BJ, Lee MY, Cho DW (2000) Protective effects of Orostachys japonicus A. Berger (Crassulaceae) on H2O2-induced apoptosis in GT1-1 mouse hypothalamic neuronal cell line. J Ethnopharmacol 69:73–78
Jung HJ, Choi J, Nam JH, Park HJ (2007) Anti-ulcerogenic effects of the flavonoid-rich fraction from the extract of Orostachys japonicus in mice. J Med Food 10:702–706
Shim KS, Ha H, Kim T, Lee CJ, Ma JY (2015) Orostachys japonicus suppresses osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting NFATc1 expression. Am J Chin Med 43:1013–1030
Hur JM, Park JC (2006) Effects of the aerial parts of Orostachys japonicus and its bioactive component on hepatic alcohol-metabolizing enzyme system. J Med Food 9:336–341
Park JC, Han WD, Park JR, Choi SH, Choi JW (2005) Changes in hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes and lipid peroxidation by methanol extract and major compound of Orostachys japonicus. J Ethnopharmacol 102:313–318
Lee HY, Park YM, Kim J, Oh HG, Kim KS, Kang HJ, Kim RR, Kim MJ, Kim SH, Yang HJ, Oh J (2019) Orostachys japonicus A. Berger extracts induce immunity-enhancing effects on cyclophosphamide-treated immunosuppressed rats. Biomed Res Int 2019:9461960
Park HJ, Yang HJ, Kim KH, Kim SH (2015) Aqueous extract of Orostachys japonicus A. Berger exerts immunostimulatory activity in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 170:210–217
Choi JH, Jin SW, Park BH, Kim HG, Khanal T, Han HJ, Hwang YP, Choi JM, Chung YC, Hwang SK, Jeong TC, Jeong HG (2013) Cultivated ginseng inhibits 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice and TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced TARC activation in HaCaT cells. Food Chem Toxicol 56:195–203
Fusenig NE, Boukamp P (1998) Multiple stages and genetic alterations in immortalization, malignant transformation, and tumor progression of human skin keratinocytes. Mol Carcinog 23:144–158
Choi JH, Hwang YP, Han EH, Kim HG, Park BH, Lee HS, Park BK, Lee YC, Chung YC, Jeong HG (2011) Inhibition of acrolein-stimulated MUC5AC expression by Platycodon grandiflorum root-derived saponin in A549 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2157–2166
Kabashima-Kubo R, Nakamura M, Sakabe J, Sugita K, Hino R, Mori T, Kobayashi M, Bito T, Kabashima K, Ogasawara K, Nomura Y, Nomura T, Akiyama M, Shimizu H, Tokura Y (2012) A group of atopic dermatitis without IgE elevation or barrier impairment shows a high Th1 frequency: possible immunological state of the intrinsic type. J Dermatol Sci 67:37–43
Choi JH, Jin SW, Han EH, Park BH, Kim HG, Khanal T, Hwang YP, Do MT, Lee HS, Chung YC, Kim HS, Jeong TC, Jeong HG (2014) Platycodon grandiflorum root-derived saponins attenuate atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions via suppression of NF-κB and STAT1 and activation of Nrf2/ARE-mediated heme oxygenase-1. Phytomedicine 21:1053–1061
Jin H, Kumar L, Mathias C, Zurakowski D, Oettgen H, Gorelik L, Geha R (2009) Toll-like receptor 2 is important for the T(H)1 response to cutaneous sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123:875–882
Werfel T, Morita A, Grewe M, Renz H, Wahn U, Krutmann J, Kapp A (1996) Allergen specificity of skin-infiltrating T cells is not restricted to a type-2 cytokine pattern in chronic skin lesions of atopic dermatitis. J Investig Dermatol 107:871–876
Tamaki K, Kakinuma T, Saeki H, Horikawa T, Kataoka Y, Fujisawa T, Sato S, Takehara K, Nakahara T, Fukagawa S, Furue M (2006) Serum levels of CCL17/TARC in various skin diseases. J Dermatol 33:300–302
Han NR, Moon PD, Kim HM, Jeong HJ (2012) Effect of Pyeongwee-San (KMP6) on 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Life Sci 90:147–153
Jung BG, Cho SJ, Ko JH, Lee BJ (2010) Inhibitory effects of interleukin-10 plasmid DNA on the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. J Vet Sci 11:213–220
Yang G, Lee K, Lee MH, Kim SH, Ham IH, Choi HY (2011) Inhibitory effects of Chelidonium majus extract on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. J Ethnopharmacol 138:398–403
Yatagai T, Shimauchi T, Yamaguchi H, Sakabe JI, Aoshima M, Ikeya S, Tatsuno K, Fujiyama T, Ito T, Ojima T, Tokura Y (2018) Sensitive skin is highly frequent in extrinsic atopic dermatitis and correlates with disease severity markers but not necessarily with skin barrier impairment. J Dermatol Sci 89:33–39
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421
Yoon NY, Min BS, Lee HK, Park JC, Choi JS (2009) A potent anti-complementary acylated sterol glucoside from Orostachys japonicus. Arch Pharm Res 28:892–896
Je Ma C, Jung WJ, Lee KY, Kim YC, Sung SH (2009) Calpain inhibitory flavonoids isolated from Orostachys japonicus. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 24:676–679
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research fund of Chungnam National University
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.H., Jin, S.W., Lee, G.H. et al. Orostachys japonicus ethanol extract inhibits 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice and TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced TARC expression in HaCaT cells. Toxicol Res. 36, 99–108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-019-00026-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-019-00026-0