Abstract
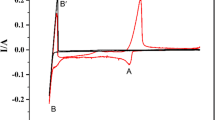
Magnesium (Mg) production via electrolysis can offer an efficient and sustainable alternative to conventional metallothermic processes. However, electrolytic systems contain impurities like manganese (Mn) that significantly influence efficiency and product quality. This study investigates the local structure of Mn2+ and the intricate electrochemical behavior of Mn(II) within MgCl2-NaCl-KCl melts, aiming to explore its impacts on electrode kinetics. Deep Potential Molecular Dynamics (DPMD) method is applied for structure introduction, and a strange chloride layer around Mn2+ is observed. Furthermore, cyclic voltammetry, chronopotentiometry, and other techniques are employed for study using tungsten electrodes with introduced MnCl2. Results reveal the quasi-reversible reduction of Mn(II) on tungsten. The diffusion coefficients (D) of Mn(II) at different temperatures are summarized, and an activation energy of 30.60 kJ·mol-1 for diffusion is found. Mn electrodeposition follows instantaneous nucleation. While limited in scope, these findings provide important insights into Mn(II) interactions that could inform efforts to optimize Mg electrolysis. Further research on Mn(II) effects on melt structure is still needed to understand electrolytic systems comprehensively. This work significantly furthers the fundamental comprehension of Mn(II) electrochemistry within industrial Mg production.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
References
Abbott T B (2015) Magnesium: industrial and research developments over the last 15 years,Corrosion.71 120.
Bu M., Feng T., Lu G.,Prediction on Local Structure and Properties of LiCl-KCl-AlCl3 Ternary Molten Salt with Deep Learning Potential,Journal of Molecular Liquids.(2022) 120689.
Feng T., Zhao J., Liang W., Lu G.,Molecular dynamics simulations of lanthanum chloride by deep learning potential,Computational Materials Science.210 (2022) 111014.
Gao F., Nie Z.-r., Wang Z.-h., Gong X.-z., Zuo T.-y.,Assessing environmental impact of magnesium production using Pidgeon process in China,Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China.18 (2008) 749.
Ha HY, Kim HJ, Baek SM, Kim B, Sohn SD, Shin HJ, Jeong HY, Park SH, Yim CD, You BS, Lee JG, Park SS (2015) Improved corrosion resistance of extruded Mg-8Sn-1Zn-1Al alloy by microalloying with Mn. Scripta Mater 109:38
Halmann M, Frei A, Steinfeld A (2008) Magnesium production by the pidgeon process involving dolomite calcination and MgO Silicothermic reduction: Thermodynamic and environmental analyses. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:2146
Hillis JE, Reichek KN (1986) High purity magnesium AM60 Alloy: The critical contaminant limits and the salt water corrosion performance, SAE transactions. 227
Kim JI, Nguyen HN, You BS, Kim YM (2019) Effect of Y addition on removal of Fe impurity from magnesium alloys. Scripta Mater 162:355
Lee T-H, Okabe TH, Lee J-Y, Kim YM, Kang J (2021) Development of a novel electrolytic process for producing high-purity magnesium metal from magnesium oxide using a liquid tin cathode. J Magnes Alloys 9:1644
Liang W, Lu G, Yu J (2021) Machine-Learning-Driven Simulations on Microstructure and Thermophysical Properties of MgCl2–KCl Eutectic. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:4034
Liang W, Lu G, Yu J (2022) Machine learning accelerates molten salt simulations: Thermal conductivity of MgCl2-NaCl Eutectic. Adv Theory Simul 5:2200206
Liu M, Song G-L (2013) Impurity control and corrosion resistance of magnesium–aluminum alloy. Corros Sci 77:143
Liu Z, Lu G, Yu J (2021) Investigation on electrochemical behaviors of MnCl2 impurity in LiCl-KCl melts. Ionics 27:2979
Matsuda H, Ayabe Y (1955) Zur Theorie der Randles-Sevčikschen Kathodenstrahl-Polarographie, Zeitschrift für Elektrochemie, Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische. Chemie 59:494
Nwaogu UC, Blawert C, Scharnagl N, Dietzel W, Kainer KU (2010) Effects of organic acid pickling on the corrosion resistance of magnesium alloy AZ31 sheet. Corros Sci 52:2143
Ramakrishnan S, Koltun P (2016) A comparison of the greenhouse impacts of magnesium produced by electrolytic and Pidgeon processes. Essent Read Magn Technol 169–174
Reichek KN, Clark KJ, Hillis JE (1985) Controlling the salt water corrosion performance of magnesium AZ91 alloy. SAE Trans 318–329
Sahoo DK, Satpati AK, Krishnamurthy N (2015) Electrochemical properties of Ce (iii) in an equimolar mixture of LiCl–KCl and NaCl–KCl molten salts. RSC Adv 5:33163
Sridharan K, Allen TR (2013) Molten salts chemistry, Elsevier, 241–267
Wang H, Zhang L, Han J, Weinan E (2018) DeePMD-kit: A deep learning package for many-body potential energy representation and molecular dynamics. Comput Phys Commun 228:178
Xiong N, Friedrich S, Mohamed SR, Kirillov I, Ye X, Tian Y, Friedrich B (2022) The Separation behavior of impurities in the purification of high-purity magnesium via vacuum distillation. J Sustain Metall 8:1561
Xu T, Yang Y, Peng X, Song J, Pan F (2019) Overview of advancement and development trend on magnesium alloy. J Magnes Alloys 7:536
Xu J, Zhang T, Li X (2023) Research on the process, energy consumption and carbon emissions of different magnesium refining processes. Materials 16(9):3340
Yang Y, Xiong X, Chen J, Peng X, Chen D, Pan F (2021) Research advances in magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2020. J Magnes Alloys 9:705
Zhang L, Han J, Wang H, Car R, Weinan E (2018) Deep potential molecular dynamics: a scalable model with the accuracy of quantum mechanics. Phys Rev Lett 120:143001
Zhao J, Feng T, Lu G, Yu J (2023) Insights into the local structure evolution and thermophysical properties of NaCl–KCl–MgCl2–LaCl3 melt driven by machine learning. J Mater Chem A 11:23999
Zhu S, Liu Z, Qu R, Wang L, Li Q, Guan S (2013) Effect of rare earth and Mn elements on the corrosion behavior of extruded AZ61 system in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution and salt spray test. J Magnes Alloys 1:249
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFB3709300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, T., Liu, Z. & Lu, G. Deep potential molecular dynamic and electrochemical experiments to reveal the structure and behavior of Mn(II) in magnesium electrolysis. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-024-00465-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-024-00465-9