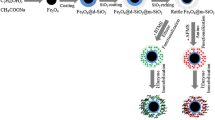
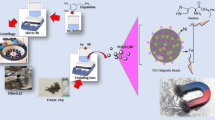
Abstract
New efficient protein purification methods need to be developed to overcome product loss during purification and to lower its final price. Magnetic adsorbents emerge as a potential support which can easily separate target biomolecules from crude biological medium. The hydrophobic adsorption of recombinant lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus (BTL-2) in novel silica magnetic microparticles (SMMp) was investigated aiming to directly recover it from cell lysate. The adsorbent surface of SMMp was modified by activation with octyl groups (25%–100%). Adsorptions on silica-octyl (non-magnetic) were also performed to understand the process better. Using centrifuged and dialyzed enzyme, under low ionic strength, the highest enzyme adsorption (92%) and desorption yields (50%) were obtained using SMMp-octyl-75% and SMMp-octyl-25%, respectively, due to simultaneous hydrophobic and ionic interaction between charged silanol groups and the enzyme. Direct enzyme adsorption from cell lysates under high ionic strength conditions led to a high yield of enzyme adsorption with 100% desorption using SMMp-octyl-25%. Therefore, the use of SMMp-octyl allows for a simple and highly efficient BTL-2 recovery by a one-step purification technique that can even be extended to other applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data presented in this article, including Supplementary Material, are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abol-Fotouh D, AlHagar OEA, Hassan MA (2021) Optimization, purification, and biochemical characterization of thermoalkaliphilic lipase from a novel Geobacillus stearothermophilus FMR12 for detergent formulations. Int J Biol Macromol 181:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.111
Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (2001) Protein purification handbook. Amersham Pharmacia Biotech Ltd.
Arana-Peña S, Lokha Y, Fernández-Lafuente R (2018) Immobilization on octyl-agarose beads and some catalytic features of commercial preparations of lipase a from Candida antarctica (Novocor ADL): comparison with immobilized lipase b from candida antarctica. Biotechnol Prog 35:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2735
Ariffin MFK, Idris A, Ngadiman NHA (2019) Optimization of lipase immobilization on maghemite and its physico-chemical properties. Braz J Chem Eng 36(01):171–179. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20190361s20180168
Atiroğlu V (2020) Lipase immobilization on synthesized hyaluronic acid-coated magnetic nanoparticle-functionalized graphene oxide composites as new biocatalysts: improved reusability, stability, and activity. Int J Biol Macromol 145:456–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.233
Bao J, Chen W, Liu T, Zhu Y, Jin P, Wand L, Liu J, Wei Y, Li Y (2007) Bifunctional Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles for protein separation. ACS Nano 1(4):293–298. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn700189h
Beisson F, Tiss A, Rivière C, Verger R (2000) Methods for lipase detection and assay: a critical review. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 102(2):133–153. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1438-9312(200002)102:2%3c133::AID-EJLT133%3e3.0.CO;2-X
Boudrant J, Woodle JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2020) Parameters necessary to define an immobilized enzyme preparation. Process Biochem 90:66–80
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (2013) Sol-Gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing. Academc Press
Carrasco-Lopez C, Godoy C, Rivas B, Fernandez-Lorente G, Palomo JM, Guisan JM, Hermoso JA (2009) Activation of bacterial Thermoalkalophilic Lipases Is spurred by dramatic structural rearrangements. J Biol Chem 284(7):4365–4372. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M808268200
Ding SS, Zhu JP, Wang Y, Yu Y, Zhao Z (2020) Recent progress in magnetic nanoparticles and mesoporous materials for enzyme immobilization: an update. Br J Biol 82:e244496. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.244496
Fernandez-Lorente G, Cabrera Z, Godoy C, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Palomo JM, Guisan JM (2008) Interfacially activated lipases against hydrophobic supports: effect of the support nature on the biocatalytic properties. Process Biochem 43(10):1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.05.009
Godoy CA, Fernández-Lorente G, Rivas B, Filice M, Guisan JM, Palomo JM (2011) Medium engineering on modified Geobacillus thermocatenulatus lipase to prepare highly active catalysts. J Mole Cataly b: Enzymatic 70(3):144–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2011.03.001
Gurkok S, Ozdal M (2021) Purification and characterization of a novel extracellular, alkaline, thermoactive, and detergent-compatible lipase from Aeromonas caviae LipT51 for application in detergent industry. Protein Expr Purif 180:105819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2021.105819
Harrison RG, Todd P, Rudge SR, Petrides DP (2015) Bioseparations science and engineering. Oxford University Press
Healthcare GE (2012) Hydrophobic interaction and reversed phase chromatography: principles and methods, 1st edn. Uppsala
Heebøll-Nielsen A, Choe WS, Middelberg APJ, Thomas ORT (2003) Efficient inclusion body processing using chemical extraction and high gradient magnetic fishing. Biotechnol Prog 19(3):887–898. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp025553n
Hernández-Garcia S, García-García MI, García-Carmona F (2014) Purification, immobilization and characterization of lipase isoenzyme from Aspergillus niger with C8 magnetic particles. Avd Biosci Biotechnol 5:633–641. https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2014.57075
Iler RK (1979) The chemistry of silica: solubility, polymerization, colloid and surface pro perties, and biochemistry, 1st edn. John Wiley and Sons
Käppler TE, Hickstein B, Peuker UA, Posten C (2008) Characterization of magnetic ion-exchange composites for protein separation from biosuspensions. J Biosci Bioeng 105(6):579–585. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.105.579
Kilikian BV, Pessoa Jr A (2020) Purificação de produtos biorecnológicos: operações e processos com aplicação industrial. Editora Edgard Blücher Ltda, ISBN: 9788521219460.
Kopp W, Silva FA, Lima LN, Masunaga SH, Tardioli PW, Giordano RC, Giordano RLC (2015) Synthesis and characterization of robust magnetic carriers for bioprocess applications. Mater Sci Eng B 193:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.12.002
Lei L, Zhu Y, Qin X, Chai S, Liu G, Su W (2021) Magnetic biohybrid microspheres for protein purification and chronic wound healing in diabetic mice. Chem Eng J 425:130671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130671
Lima LN, Vieira GNA, Kopp W, Tardioli PW, Giordano RLC (2016) Mono- and heterofunctionalized silica magnetic microparticles (SMMPs) as new carriers for immobilization of lipases. J Mol Catal B Enzym 133:S491–S499
Linke D, Berger RG (2011) Foaming of proteins: new prospects for enzyme purification processes. J Biotechnol 152(4):125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.07.022
Maity D, Agrawal DC (2007) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles under oxidizing environment and their stabilization in aqueous and non-aqueous media. J Magn Magn Mater 308:46–55
Mendes AA, Oliveira PC, Vélez AM, Giordano RC, Giordano RLC, Castro HF (2012) Evaluation of immobilized lipases on poly-hydroxybutyrate beads to catalyze biodiesel synthesis. Int J Biol Macromole 50(3):503–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.01.020
Meyer A, Hansen DB, Gomes CSG, Hobley TJ, Thomas ORT, Franzreb M (2005) Demonstration of a strategy for product purification by high-gradient magnetic fishing: recovery of superoxide dismutase from unconditioned whey. Biotechnol Prog 21(1):244–254. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp049656c
Nawani N, Khurana J, Kaur J (2006) A thermostable lipolytic enzyme from a thermophilic Bacillus sp.: purification and characterization. Mol Cell Biochem 290(1–2):17–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-9076-4
Palomo JM, Muñoz G, Fernández-Lorente G, Mateo C, Fernández-Lafuente R, Guisán JM (2002) Interfacial adsorption of lipases on very hydrophobic support (octadecyl–Sepabeads): immobilization, hyperactivation and stabilization of the open form of lipases. J Mol Catal B Enzym 19:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1177(02)00178-9
Palomo JM, Fernández-Lorente G, Rúa ML, Guisán JM, Fernández-Lafuente R (2003) Evaluation of the lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus as an enantioselective biocatalyst. Tetrahedron Asym 14(23):3679–3687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2003.10.010
Palomo JM, Ortiz C, Fuentes M, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2004) Use of immobilized lipases for lipase purification via specific lipase–lipase interactions. J Chromatogr A 1038(1–2):267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2004.03.058
Palomo JM, Segura RL, Fernández-Lorente G, Pernas M, Rua ML, Guisán JM, Fernández-Lafuente R (2008) Purification, immobilization, and stabilization of a Lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus by interfacial adsorption on hydrophobic supports. Biotechnol Prog 20(2):630–635. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0342957
Pérez-Guzmán AK, Ilyina N, Zugasti-Cruz A, García-García JD, Segura-Ceniceros EP, Martínez-Hernández JL, Ramos-González R (2019) Chitosan–heparin functionalised magnetic nanoparticles for the magnetic recovery of Aspergillus niger lipase enzyme. Micro Nano Letters 14:623–628. https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2018.5490
Quyen DT, Schmidt-Dannert C, Schmid RD (2003) High-level expression of a lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus BTL2 in Pichia pastoris and some properties of the recombinant lipase. Protein Expr Purif 28:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1046-5928(02)00679-4
Rios NS, Arana-Pena S, Mendez-Sanchez C, Lokha Y, Cortes-Corbean V, Gonçalves L, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2019) Increasing the enzyme loading capacity of porous supports by a layer-by-layer immobilization strategy using PEI as Glue. Catalysts 9:576. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9070576
Santos JCS, Barbosa O, Ortiz C, Berenguer-Murcia A, Rodrigues RC, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2015) Importance of the support properties for immobilization or purification of enzymes. Chem Cat Chem 7(16):2413–2432. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201500310
Schmidt-Dannert C, Rúa ML, Schmid RD (1997) Two novel lipases from thermophile Bacillus thermocatenulatus: Screening, purification, cloning, overexpression, and properties. Methods Enzymol 284:194–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(97)84013-X
Schmidt-Dannert C, Sztajer H, Stöcklein W, Menge U, Schmid RD (1994) Screening, purification and properties of a thermophilic lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)/Lipids Metab 1214(1):43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(94)90008-6.
Schmidt-Dannert C, Rúa ML, Atomi H, Schmid RD (1996) Thermoalkalophilic lipase of Bacillus thermocatenulatus I. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Lipids Lipid Meta 1301(1–2):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(96)00027-6
Shi Y, Liu W, Tao QL, Jiang XP, Liu CH, Zeng S, Zhang YW (2016) Immobilization of lipase by adsorption onto magnetic nanoparticles in organic solvents. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16(1):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2016.10694
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150(1):76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7
Vahidi AK, Yang Y, Ngo TPN, Li Z (2015) Simple and efficient immobilization of extracellular his-tagged enzyme directly from cell culture supernatant as active and recyclable nanobiocatalyst: high-performance production of biodiesel from waste grease. ACS Catal 5(6):3157–3161. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b00550
Vélez AM, Horta ACL, Silva AJ, Iemma MRC, Giordano RLC, Zangirolami TC (2013) Enhanced production of recombinant thermo-stable lipase in Escherichia coli at high induction temperature. Protein Expr Purif 90(2):96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2013.05.005
Wang P, Zhao J, Jiang Z, Liu Y, Liu S (2009) Preparation of magnetic iron/mesoporous silica composite spheres and their use in protein immobilization. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 19:s605–s610. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(10)60117-3
Zanardo RT, Ferri ALS, Figueiredo DB, Kraschowetz S, Cabrera-Crespo J, Gonçalves VM (2016) Development of a new process for purification of capsular polysaccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype. Braz J Chem Eng 33(03):435–443. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20160333s20150140
Zhao X, Guan Y, Xia C, Xia T, Qiu X, Wang C, Guo C (2016) Preparation and characterization of magnetic poly(styrene-glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres for highly efficient protein adsorption by two-stage dispersion polymerization. J App Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43005
Zhu YT, Ren XY, Liu YM, Wei Y, Qing LS, Liao X (2014) Covalent immobilization of porcine pancreatic lipase on carboxyl-activated magnetic nanoparticles: characterization and application for enzymatic inhibition assays. Mat Sci Eng C 38:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.02.011
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Laboratory of Biocatalysis (ICP-CSIC, Madrid, Spain) for the donation of recombinant cells of E. coli, and the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP grants #2008/56246-0 and 2016/10636-8), the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for the financial support.
Funding
This work was supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), grants #2008/56246-0 and 2016/10636-8, and the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for their financial support. This work was in part financed by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brazil (CAPES) – Finance code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. LAL performed all experiments with the support of WK. All authors discussed and analysed the data. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LAL and manuscript review and editing were carried out by TSM and TP. RLCG revised the manuscript and supervised the work development. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts and competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, L.A., Kopp, W., Milessi, T.S. et al. Direct recovery of intracellular lipase from cell lysate by adsorption on silica magnetic microparticles activated with Octyl groups. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 39, 789–801 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-021-00190-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-021-00190-7