Abstract
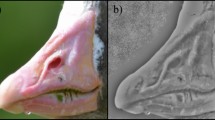
Especially in species with complex social systems, the relatedness between individuals is important information. Visual phenotypic cues present one way to identify closely related conspecifics. Humans are capable of recognizing such visual cues in the faces of their own as well as several primate species, but to which degree this applies to non-primate species is largely unexplored. Here we demonstrate the capability of 110 test persons to recognize faces of 47 male Asian elephants based on 186 photographs. The human examiners were not only able to recognize an individual based on its face after several years, but also to identify, at decreasing accuracy, full brother pairs and paternal kinship. People regularly working with elephants were more successful than laypersons. However, even laypersons recognized 73.3% of the same individuals. The identification of individual elephants by a look at their faces presents a simple approach which can be a valuable tool for in situ research.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Alvergne A, Huchard E, Caillaud D, Charpentier JE, Setchell JM, Ruppli C, Féjan D, Martinez L, Cowlishaw G, Raymond M (2009) Human ability to recognize kin visually within primates. Int J Primatol 30:199–210
Alvergne A, Perreau F, Mazur A, Mueller U, Raymond M (2014) Identification of visual paternity cues in humans. Biol Lett 10:20140063
Barton K (2009) MuMIn:multi-model inference, R package version 0.12.0
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48
Burnham K, Anderson D (2001) Kullback–Leibler information as a basis for strong inference in ecological studies. Wildl Res 28:111–119
Burnham K, Anderson D (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach. Springer-Verlag, New York
de Silva S, Ranjeewa ADG, Weerakoon D (2011) Demography of Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) at Uda Walawe National Park, Sri Lanka based on identified individuals. Biol Conserv 144:1742–1752
de Silva E, Kumarasinghe P, Indrajith K, Pushpakumara T, Vimukthi R, de Zoysa K, Gundawardana K, de Silva S (2022a) Feasibility of using convolutional neural networks for individual-identification of wild Asian elephants. Mamm Biol 102:931–941
de Silva M, Kumarasinghe P, De Zoysa K, Keppitiyagama C (2022b) Reidentifying Asian elephants from ear images using a cascade of convolutional neural networks and explaining with GradCAM. SN Comput Sci 3:192
EAZA E (2020) EAZA elephant best practice guidelines 2020. European Association of Zoos and Aquaria
Fernando P, Ekanayaka SKK, Pastorini J (2020) The elephant at the fence: almsman, panhandler, friend or foe? Eur J Wildl Res 66:e97
Fernando P, Vijayakrishnan S, Ranjeewa ADG, Pastorini J (2022) Size-age class scale for Asian elephants. Gajah 55:30–39
Hepper P (1991) Kin recognition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Highfill L, Fad O, Makecha R, Kuczaj S (2013) Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) may demonstrate stable personalities. Int J Comp Psychol 26:233–240
Kazem AJN, Widdig A (2013) Visual phenotype matching: cues to paternity are present in rhesus macaque faces. PLoS ONE 8:e55846
Prager P (2023) Elefanten-Fotolexikon. https://elefanten-fotolexikon.eu. Retrieved 01 Nov 2023
R Core Team (2021) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
Ranjeewa ADG, Tharanga YJS, Sandanayake GHNA, Perera BV, Fernando P (2015) Camera traps unveil enigmatic crop raiders in Udawalawe, Sri Lanka. Gajah 42:7–14
Seltmann MW, Helle S, Adams MJ, Mar KU, Lahdenperä M (2018) Evaluating the personality structure of semi-captive Asian elephants living in their natural habitat. R Soc Open Sci 5:e172026
Shen J, Mack M, Palmeri T (2014) Studying real-world perceptual expertise. Front Psychol 5:857
Vidya TNC, Prasad D, Ghosh A (2014) Individual identification in Asian Elephants. Gajah 40:3–17
Yasui S, Konno A, Tanaka M, Idani G, Ludwig A, Lieckfeldt D, Inoue-Murayama M (2013) Personality assessment and its association with genetic factors in captive Asian and African elephants. Zoo Biol 32:70–78
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the examiners who contributed to this research.
Funding
No funding to be declared. On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Christian Schiffmann, Marcus Clauss; methodology: Christian Schiffmann, Marcus Clauss; formal analysis and investigation: Marcus Clauss, Daryl Codron, Jennifer Pastorini, Petra Prager, Christian Schiffmann, Linda Schiffmann; writing—original draft preparation: Christian Schiffmann, Marcus Clauss, Daryl Codron; writing—review and editing: Marcus Clauss, Daryl Codron, Jennifer Pastorini, Petra Prager, Christian Schiffmann, Linda Schiffmann.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Heiko Georg Rödel.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Schiffmann, C., Schiffmann, L., Prager, P. et al. Face to face: human recognition of Asian elephant facial features. Mamm Biol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42991-024-00415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42991-024-00415-5