Abstract
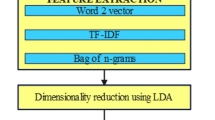
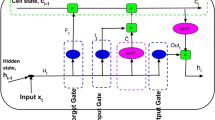
Natural Language Processing (NLP) with Deep Learning (DL) for Tweets Classification includes use of advanced neural network designs to analyse and classify Twitter messages. DL techniques like recurrent neural network (RNN) or transformer-based frameworks like BERT are used to mechanically learn difficult linguistic patterns and contextual info from tweet data. These techniques able to capture subtleties of language with sarcasm, sentiment, and context-specific meanings and making them suitable for tasks like sentiment analysis or topic classification in realm of social media. Leveraging deep symbols learned from great amounts of textual data, these NLP techniques permit precise and nuanced classification of tweets, donating to enhanced information retrieval, sentiment tracking, and trend analysis in dynamic and fast-paced world of social media communication. In this view, this research develops an arithmetic optimization algorithm with deep learning based tweets classification (AOADL-TC) approach for sustainable living. The goal of the AOADL-TC technique is to identify and discriminate different kinds of sentiments that exist in the tweet data. At the initial stage, the AOADL-TC model pre-processes tweet data to convert uniform data into a useful format. For sentiment detection, the AOADL-TC technique applies a parallel bidirectional gated recurrent unit (BiGRU) model. At last, tuning of parameters related to parallel BiGRU model performed by AOA. An wide set of tests carried out to illustrate better performance of AOADL-TC model. The experimental outcomes portrayed that AOADL-TC technique demonstrates the supremacy of the AOADL-TC technique in terms of different evaluation metrics.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated during the current study.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Materials Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ainapure BS, Pise RN, Reddy P, Appasani B, Srinivasulu A, Khan MS, Bizon N. Sentiment analysis of COVID-19 tweets using deep learning and lexicon-based approaches. Sustainability. 2023;15:2573.
Fattoh IE, Kamal Alsheref F, Ead WM, Youssef AM. Semantic sentiment classification for COVID-19 tweets using universal sentence encoder. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022;2022:6354543.
Stitini O, Twil A, Kaloun S, Bencharef O. How can we analyse emotions on Twitter during an epidemic situation? A features engineering approach to evaluate people’s emotions during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Tianjin Univ Sci Technol. 2021;54.
Sitaula C, Basnet A, Mainali A, Shahi TB. Deep learning-based methods for sentiment analysis on Nepali COVID-19-related tweets. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021;2021:2158184.
Anuradha K, Parvathy M. Multi-label emotion classification of COVID-19 tweets with deep learning and topic modelling. Comput Syst Sci Eng. 2023;46:3005–21.
Deva Priya M, Saranya M, Sharaha N. Tamizharasi S. Classification of COVID-19 tweets using deep learning classifiers. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Recent Trends in Computing: ICRTC 2021. Singapore: Springer; 2022. p. 213–25.
Bangyal WH, Qasim R, Rehman NU, Ahmad Z, Dar H, Rukhsar L, Aman Z, Ahmad J. Detection of fake news text classification on COVID-19 using deep learning approaches. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021;2021:1–14.
Oumaima S, Soulaimane K, Omar B. Artificial intelligence in predicting the spread of coronavirus to ensure healthy living for all age groups. In: Emerging trends in ICT for sustainable development: the proceedings of NICE2020 International Conference. Cham: Springer; 2021. p. 11–8.
Wang T, Deng XN. User characteristics, social media use, and fatigue during the coronavirus pandemic: a stressor–strain–outcome framework. Comput Hum Behav Rep. 2022;7: 100218.
Sak S, Yavuzyi ğit BB. Striving for wellbeing digitally in the city amidst the pandemic: Solidarity through Twitter in Ankara. Habitat Int. 2023;137:102846.
Lakshmi SD, Velmurugan T. Classification of disaster tweets using natural language processing pipeline. Acta Sci Comput Sci. 2023;5(3).
Kuber A, Kulthe S, Kosamkar P. Detecting depression in tweets using natural language processing and deep learning. In: Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies (ICTCS 2021) ICT: applications and social interfaces. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore; 2022. p. 453–61.
Arbane M, Benlamri R, Brik Y, Alahmar AD. Social media-based COVID-19 sentiment classification model using Bi-LSTM. Expert Syst Appl. 2023;212: 118710.
Kumar VS, Alemran A, Karras DA, Gupta SK, Dixit CK, Haralayya B. Natural language processing using graph neural network for text classification. In: 2022 International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Communication Systems (ICKES). IEEE; 2022. p. 1–5.
Tam S, Said RB, Tanriöver ÖÖ. A ConvBiLSTM deep learning model-based approach for Twitter sentiment classification. IEEE Access. 2021;9:41283–93.
Kaur G, Sharma A. A deep learning-based model using hybrid feature extraction approach for consumer sentiment analysis. J Big Data. 2023;10(1):5.
Pardhi PR, Rout JK, Ray NK, Sahu SK. Classification of malware from the network traffic using hybrid and deep learning based approach. SN Comput Sci. 2024;5(1):162.
Duraisamy P, Natarajan Y. Twitter disaster prediction using different deep learning models. SN Comput Sci. 2024;5(1):179.
Sahoo BB, Panigrahi B, Nanda T, Tiwari MK, Sankalp S. Multi-step ahead urban water demand forecasting using deep learning models. SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(6):752.
Poomagal S, Malar B, Visalakshi P, Hassan JI, Kishor R. Opinion mining using optimized K-means algorithm and a word weighting technique. SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(6):736.
Gaye B, Zhang D, Wulamu A. A tweet sentiment classification approach using a hybrid stacked ensemble technique. Information. 2021;12(9):374.
Zaoad MS, Mannan MR, Mandol AB, Rahman M, Islam MA, Rahman MM. An attention-based hybrid deep learning approach for Bengali video captioning. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. 2023;35(1):257–69.
Lei X, Shilin D, Shangqin T, Changqiang H, Kangsheng D, Zhuoran Z. Beyond visual range maneuver intention recognition based on attention enhanced tuna swarm optimization parallel BiGRU. Complex Intell Syst. 2023;10:2151–72.
Jokić A, Petrović M, Miljković Z. The arithmetic optimization algorithm for multi-objective mobile robot scheduling. In: 39th International Conference on Production Engineering of Serbia (ICPES 2023). 2023. p. 9–15.
https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/sentiment-analysis-of-covid-19-related-tweets/overview.
Almasoud AS, Alshahrani HJ, Hassan AQA, Almalki NS, Motwakel A. Modified aquila optimizer with stacked deep learning-based sentiment analysis of COVID-19 tweets. Electronics. 2023;12:4125. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12194125.
Funding
This project is sponsored by Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University (PSAU) as part of funding for its SDG Roadmap Research Funding Programme project number PSAU-2023/SDG/38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Manar Ahmed Hamza, Aisha Hassan Abdalla Hashim, Abdelwahed Motwakel,, Elmouez Samir Abd Elhameed, is responsible for designing the framework, analyzing the performance, validating the results, and writing the article. Mohammed Osman, Arun Kumar, Chinu Singla and Muskaan Munjal, is responsible for collecting the information required for the framework, provision of software, critical review, and administering the process.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors do not have any conflicts.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Critiques of the Implementation of Process Analysis in Information Theory” guest edited by Asefeh Asemi, Abu Bakar Munir and Shamsollah Ghanbari.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamza, M.A., Hashim, A.H.A., Motwakel, A. et al. Robust Tweets Classification Using Arithmetic Optimization with Deep Learning for Sustainable Urban Living. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 549 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-02899-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-02899-x