Abstract
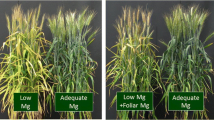
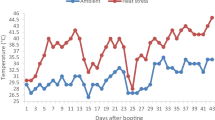
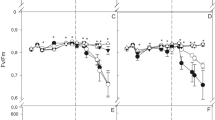
Our previous studies showed that foliar applied magnesium sulfate during the booting stage can effectively increase wheat grain weight. To explore the effects of foliar application of magnesium sulfate during wheat grain filling on photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaf and grain filling, an experiment was conducted using winter wheat cultivars to assess the effects of foliar application of magnesium sulphate on photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaves, carbohydrate metabolism in grains, and dry matter translocation in different organs in the Zhoumai 27 and Aikang 58 cultivars at different growth stages. The results indicated throughout the different stages of growth, the flag leaves exhibited a high net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs) and transpiration (Tr), and a decrease in the concentration of intercellular CO2 (Ci). Therefore, foliar application of magnesium sulfate during the booting stage maintained high canopy photosynthesis after anthesis. Simultaneously, exogenous supply of magnesium sulphate enhanced the sucrose synthase (SUS) and invertase (INV) enzyme activities in detached wheat grains, meanwhile reinforced the activities of most starch synthesis enzyme such as ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and soluble starch synthase, and consequently lead to a higher content of grain starch. Furthermore, field experiment also confirmed foliar application of magnesium sulphate can improve superior dry matter accumulation and translocation in grain.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell CJ, Incoll LD (1990) The redistribution of assimilate in field-grown winter wheat. J Exp Bot 41:949–960
Bonnett GD, Incoll LD (1992) The potential pre-anthesis and post-anthesis contributions of stem internodes to grain yield in crops of winter barley. Ann Bot 69:219–225
Borrill P, Fahy B, Smith AM, Uauy C (2015) Wheat grain filling is limited by grain filling capacity rather than the duration of flag leaf photosynthesis: a case study using NAM RNAi plants. PLoS ONE 10:1–14
Buysse J, Merckx R (1993) An improved colorimetric method to quantify sugar content of plant tissue. J Exp Bot 44:1627–1629
Cakmak I, Marschner H (1992) Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol 98:1222–1229
Cakmak I, Hengeler C, Marschner H (1994) Partitioning of shoot and root dry matter and carbohydrates in bean plants suffering from phosphorus, potassium and magnesium deficiency. J Exp Bot 45:1245–1250
Dai Z, Yin Y, Wang Z (2009) Comparison of starch accumulation and enzyme activity in grains of wheat cultivars differing in kernel type. Plant Growth Regul 57:153–162
Dimassi-Theriou K, Bosabalidis AM (1997) Effects of light, magnesium and sucrose on leaf anatomy, photosynthesis, starch and total sugar accumulation, in kiwifruit cultured in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 47:127–134
Ding Y, Xu G (2011) Low magnesium with high potassium supply changes sugar partitioning and root growth pattern prior to visible magnesium deficiency in leaves of rice. Am J Plant Sci 2:601–608
Evans LT, Fischer RA (1999) Yield potential: its definition, measurement, and significance. Crop Sci 39:1544–1551
Farhat N, Elkhouni A, Zorrig W, Smaoui A, Abdelly C, Rabhi M (2016) Effects of magnesium deficiency on photosynthesis and carbohydrate partitioning. Acta Physiol Plant 38:145–156
Gardner WK (2015) Sodium, calcium and magnesium ratios in soils of NW victoria, australia may restrict root growth and crop production. J Plant Nutr 9:1205–1215
Gebbing T, Schnyder H (1999) Pre-anthesis reserve utilization for protein and carbohydrate synthesis in grains of wheat. Plant Physiol 121:871–878
Hermans C, Verbruggen N (2005) Physiological characterization of Mg deficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 56:2153–2161
Hermans C, Bourgis F, Faucher M, Strasser RJ, Delrot S, Verbruggen N (2005) Magnesium deficiency in sugar beets alters sugar partitioning and phloem loading in young mature leaves. Planta 220:541–549
Keeling PL, Bacon PJ, Holt DC (1993) Elevated temperature reduces starch deposition in wheat endosperm by reducing the activity of soluble starch synthase. Planta 191:342–348
Koonjul PK, Minhas JS, Nunes C, Sheoran IS, Saini HS (2005) Selective transcriptional down-regulation of anther invertases precedes the failure of pollen development in water-stressed wheat. J Exp Bot 56:179–186
Li G, Pan J, Cui K, Yuan M, Hu Q, Wang W, Mohapatra PK, Nie L, Huang J, Peng S (2017a) Limitation of unloading in the developing grains is a possible cause responsible for low stem non-structural carbohydrate translocation and poor grain yield formation in rice through verification of recombinant inbred lines. Front Plant Sci 8:1–15
Li Z, Wang F, Lin W, Zhao Q, Liu J, Cheng F (2017b) Carbon reserve and remobilization in leaf sheaths during the grain-filling stage in response to leaf early senescence. Acta Physiol Plant 39:10–24
Maydup ML, Antonietta M, Guiamet JJ, Graciano C, López JR, Tambussi EA (2010) The contribution of ear photosynthesis to grain filling in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Field Crops Res 119:48–58
Nakamura Y, Yuki K, Park SY, Ohya T (1989) Carbohydrate metabolism in the developing endosperm of rice grains. Plant Cell Physiol 30:833–839
Oliver SN, Van Dongen JT, Alfred SC, Mamun EA, Zhao X, Saini HS, Fernandes SF, Blanchard CL, Sutton BG, Geigenberger P (2005) Cold-induced repression of the rice anther-specific cell wall invertase gene OSINV4 is correlated with sucrose accumulation and pollen sterility. Plant, Cell Environ 28:1534–1551
Pollock CJ, Cairns AJ (1991) Fructan metabolism in grasses and cereals. Annu Rev Plant Biol 42:77–101
Ruuska SA, Rebetzke GJ, van Herwaarden AF, Richards RA, Fettell NA, Tabe L, Cld J (2006) Genotypic variation in water-soluble carbohydrate accumulation in wheat. Funct Plant Biol 33:799–809
Schaffer AA, Petreikov M (1997) Sucrose-to-Starch metabolism in tomato fruit undergoing transient starch accumulation. Plant Physiol 113:739–746
Schnyder H (2010) The role of carbohydrate storage and redistribution in the source-sink relations of wheat and barley during grain filling. New Phytol 123:233–245
Shearman VJ, Sylvesterbradley R, Scott RK, Foulkes MJ (2005) Physiological processes associated with wheat yield progress in the UK. Crop Sci 45:175–185
Sung SJ, Xu DP, Black CC (1989) Identification of actively filling sucrose sinks. Plant Physiol 89:1117–1121
Wang X, Cai J, Liu F, Jin M, Yu H, Jiang D, Wollenweber B, Dai T, Cao W (2012) Pre-anthesis high temperature acclimation alleviates the negative effects of post-anthesis heat stress on stem stored carbohydrates remobilization and grain starch accumulation in wheat. J Cereal Sci 55:331–336
Zhang C, Jiang D, Liu F, Cai J, Dai T, Cao W (2010) Starch granules size distribution in superior and inferior grains of wheat is related to enzyme activities and their gene expressions during grain filling. J Cereal Sci 51:226–233
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1708085QC62), Scientific Research Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Anhui Province, China (KJ2019A0585), National Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201910373033), Anhui University Collaborative Innovation Project (GXXT-2019-033) and the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Huaibei Normal University (15601047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Changes in the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), the transpiration rate (Tr), the stomatal conductance (Gs) and the intercellular CO2 (Ci) in two winter wheat cultivars in both growing seasons in MS0 and MS1 plants. Where MS0 is the control and MS1 denotes the MgSO4 treatment at the booting stage. Bars indicate standard errors of the means of three measurements. Asterisks denote significant differences between treatments at p < 0.05 (*) by the LSD test (PDF 333 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ba, Q., Zhang, L., Chen, S. et al. Effects of foliar application of magnesium sulfate on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and its translocation, and carbohydrate metabolism in grain during wheat grain filling. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 48, 157–163 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-020-00026-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-020-00026-z