Abstract
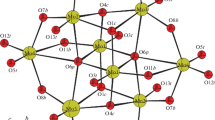
Developing new low-cost and efficient proton-conducting materials remains an attractive and challenging task. Herein, sodium molybdate dihydrate is used as the source of molybdenum, mixed with transition metal chloride and 2-methylimidazole (2-MI), using the "one-pot method" to synthesize two crystalline proton conducting materials based on {P4Mo6} units: H14[C4H6N2]2[M(H2O)5] [M(H2O)2]2{M[(PO3)3(PO4)Mo6O15]2}·4H2O (M=Co and Fe) (1–2). Different from the common {P4Mo6}, we use H3PO3 to adjust the pH value, resulting in two different coordination modes of P atoms in the crystal structure. The structure is expanded into three-dimensional network by metal ions. At 75 °C and 98% relative humidity, the proton conductivity of compounds 1 and 2 are 1.33 × 10–2 S·cm−1 and 1.03 × 10–2 S·cm−1, respectively. The high proton conductivity is mainly attributed to the free state of 2-methylimidazole as the proton carrier, which has a fast migration rate. At the same time, 2-methylimidazole, coordination water, and {P4Mo6} anion form a hydrogen bond network to provide multiple pathways for the transmission of protons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi J, Yeon JH, Yook SH, Shin S, Kim JY, Choi M, Jang S. Multifunctional Nafion/CeO2 dendritic structures for enhanced durability and performance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2021;13(1):806.
Guerrero Moreno N, Cisneros Molina M, Gervasio D, Pérez Robles JF. Approaches to polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and their cost. Renew and Sust Energ Rev. 2015;52:897.
Karim MR, Hatakeyama K, Koinuma M, Hayami S. Proton conductors produced by chemical modifications of carbon allotropes, perovskites and metal organic frameworks. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5(16):7243.
Gui D, Duan W, Shu J, Zhai F, Wang N, Wang X, Xie J, Li H, Chen L, Diwu J, Chai Z, Wang S. Persistent superprotonic conductivity in the order of 10–1 S·cm−1 achieved through thermally induced structural transformation of a uranyl coordination polymer. CCS Chem. 2019;1(2):197.
Ivanchev SS. Fluorinated proton-conduction nafion-type membranes, the past and the future. Russ J Appl Chem. 2008;81(4):569.
Liu B, Hu B, Du J, Cheng D, Zang HY, Ge X, Tan H, Wang Y, Duan X, Jin Z, Zhang W, Li Y, Su Z. Precise molecular-level modification of nafion with bismuth oxide clusters for high-performance proton-exchange membranes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(11):6076.
Luo HB, Ren Q, Wang P, Zhang J, Wang L, Ren XM. High proton conductivity achieved by encapsulation of imidazole molecules into proton-conducting MOF-808. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11(9):9164.
Zhou B, Le J, Cheng Z, Zhao X, Shen M, Xie M, Hu B, Yang X, Chen L, Chen H. Simple transformation of covalent organic frameworks to highly proton-conductive electrolytes. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12(7):8198.
Wu GD, Zhou HL, Fu ZH, Li WH, Xiu JW, Yao MS, Li QH, Xu G. MOF nanosheet reconstructed two-dimensional bionic nanochannel for protonic field-effect transistors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(18):9931.
Huang B, Yang DH, Han BH. Application of polyoxometalate derivatives in rechargeable batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2020;8(9):4593.
Du DY, Yan LK, Su ZM, Li SL, Lan YQ, Wang EB. Chiral polyoxometalate-based materials: from design syntheses to functional applications. Coordin Chem Rev. 2013;257(3–4):702.
Lu J, He P, Niu J, Wang J. Polyoxometalate-supported metal carbonyl derivatives: from synthetic strategies to structural diversity and applications. Inorg Chem Front. 2019;6(11):3041.
Miras HN, Yan J, Long DL, Cronin L. Engineering polyoxometalates with emergent properties. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(22):7403.
Anyushin AV, Kondinski A, Parac-Vogt TN. Hybrid polyoxometalates as post-functionalization platforms: from fundamentals to emerging applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(2):382.
Yang L, Lei J, Fan JM, Yuan RM, Zheng MS, Chen JJ, Dong QF. The Intrinsic Charge Carrier Behaviors and Applications of Polyoxometalate Clusters Based Materials. Adv Mater. 2021;e2005019.
Cheng D, Li B, Sun S, Zhu LJ, Li Y, Wu XL, Zang HY. Proton-conducting polyoxometalates as redox electrolytes synergistically boosting the performance of self-healing solid-state supercapacitors with polyaniline. CCS Chem. 2021;3(3):1649.
Chen Y, Guo ZW, Chen YP, Zhuang ZY, Wang GQ, Li XX, Zheng ST, Yang GY. Two novel nickel cluster substituted polyoxometalates: syntheses, structures and their photocatalytic activities, magnetic behaviors, and proton conduction properties. Inorg Chem Front. 2021;8(5):1303.
Niinomi K, Miyazawa S, Hibino M, Mizuno N, Uchida S. High proton conduction in crystalline composites based on preyssler-type polyoxometalates and polymers under nonhumidified or humidified conditions. Inorg Chem. 2017;56(24):15187.
Gao Q, Wang XL, Xu J, Bu XH. The first demonstration of the gyroid in a polyoxometalate-based open framework with high proton conductivity. Chem Eur J. 2016;22(27):9082.
Zhang S, Lu Y, Sun XW, Li Z, Dang TY, Zhang Z, Tian HR, Liu SX. Purely inorganic frameworks based on polyoxometalate clusters with abundant phosphate groups: single-crystal to single-crystal structural transformation and remarkable proton conduction. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020;56(3):391.
Lin J, Li N, Yang S, Jia M, Liu J, Li XM, An L, Tian Q, Dong LZ, Lan YQ. Self-assembly of giant Mo240 hollow opening dodecahedra. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(32):13982.
Zhang YQ, Zhou LY, Ma YY, Dastafkan K, Zhao C, Wang LZ, Han ZG. Stable monovalent aluminum(I) in a reduced phosphomolybdate cluster as an active acid catalyst. Chem Sci. 2021;12(5):1886.
Han Z, Xin X, Zheng R, Yu H. Influence of Pb element on the catalytic properties of {P4Mo6}-polyoxometalate for redox reactions. Dalton Trans. 2018;47(10):3356.
Xin X, Tian X, Yu H, Han Z. Synthesis of hybrid phosphomolybdates and application as highly stable and effective catalyst for the reduction of Cr(VI). Inorg Chem. 2018;57(18):11474.
Yang H, Duan XY, Lai JJ, Wei ML. Proton-conductive keggin-type clusters decorated by the complex moieties of Cu(II) 2,2’-Bipyridine-4,4’-dicarboxylate/diethyl analogues. Inorg Chem. 2019;58(2):1020.
Iwano T, Shitamatsu K, Ogiwara N, Okuno M, Kikukawa Y, Ikemoto S, Shirai S, Muratsugu S, Waddell PG, Errington RJ, Sadakane M, Uchida S. Ultrahigh proton conduction via extended hydrogen-bonding network in a preyssler-type polyoxometalate-based framework functionalized with a lanthanide ion. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2021;13(16):19138.
Du ZY, Chen Z, Kang RK, Han YM, Ding J, Cao JP, Jiang W, Fang M, Mei H, Xu Y. Two 2D layered P4Mo6 clusters with potential bifunctional properties: proton conduction and CO2 photoreduction. Inorg Chem. 2020;59(17):12876.
Inukai M, Horike S, Itakura T, Shinozaki R, Ogiwara N, Umeyama D, Nagarkar SS, Nishiyama Y, Malon M, Hayashi A, Ohhara T, Kiyanagi R, Kitagawa S. Encapsulating mobile proton carriers into structural defects in coordination polymer crystals: high anhydrous proton conduction and fuel cell application. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(27):8505.
Vilciauskas L, Tuckerman ME, Bester G, Paddison SJ, Kreuer KD. The mechanism of proton conduction in phosphoric acid. Nat Chem. 2012;4(6):461.
Streb C, Long DL, Cronin L. Influence of organic amines on the self-assembly of hybrid polyoxomolybdenum(V) phosphate frameworks. CrystEngComm. 2006;8(8):629.
Li W, Zhu JN, Shen NN, Xiong WW, Huang XY. Assembling [M(P4Mo6)2] (M = Na, Mn, Na/Cu) dimeric clusters via transition metal/sodium ions into 0D to 3D phosphomolybdates. CrystEngComm. 2019;21(6):971.
Zhang L, Li X, Zhou Y, Wang X. Unprecedented formation of a hydrogen-bonded assembly of water–diethylenetriamine molecules within a new solid state supramolecular molybdenum(V) phosphate complex. J Mol Struct. 2009;928(1–3):59.
Xu X, Liu X, Wang D, Liu X, Chen L, Zhao J. HPO3 and {WO4}simultaneously induce the assembly of Tri-Ln(III)-incorporated antimonotungstates and their photoluminescence behaviors. Inorg Chem. 2021;60(2):1037.
Cao Y, Zhou X, Luan L, Zeng H, Zou G, Lin Z. Organically templated metal phosphate-oxalates: Solvent-free synthesis, crystal structure, and proton conduction. Inorg Chem Commun. 2021;124:108403
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21871042, 21471028, 21673098, and 21671036), Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (Grant No. 20200201083JC), Jilin Provincial Education Department (Grant No. JJKH20201169KJ), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2412015KJ012, 2412017BJ004), and the support of the Jilin Provincial Department of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZG and SS designed and wrote the draft; BL and DC collected the data; ZG and SS contributed equally to this work. All authors contributed to the writing and revisions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, ZX., Sun, S., Li, B. et al. Design and synthesis of phosphomolybdate coordination compounds based on {P4Mo6} structural units and their proton conductivity. Tungsten 5, 67–74 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-021-00122-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-021-00122-5