Abstract
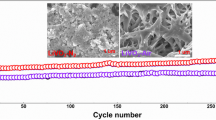
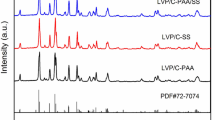
Li3VO4 is a promising electrode material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to its excellent specific capacity (592 mAh g−1), suitable discharge voltage (0.5–1.0 V), and moderate volume change upon charge/discharge, while it still suffers from low electronic conductivity that usually gives a poor rate capability, low initial coulombic efficiency, and large polarization, imposing a challenge on its practical applications. In this work, a partial surface phase transformation of Li3VO4 was initiated via a freeze-drying method followed by a heat treatment in inert gas. Using this method, Li3VO4 was integrated with a conductive layer LiVO2 and carbon matrix. The synergistic effect among Li3VO4, LiVO2 layer, and carbon matrix was systematically studied by optimizing the treatment conditions. When treated at 600 °C in Ar, Li3VO4-based composite delivered outstanding electrochemical properties, as expressed by a specific capacity (689 mAh g−1 at 0.1 A g−1 after 100 cycles), rate performance (i.e., 448 mAh g−1 at 2 A g−1), and longtime cycle stability (523 mAh g−1 after 200 cycles at 0.2 A g−1), which are superior to those without LiVO2 conductive layer when treated at the same temperature in air. The findings reported in this work may offer novel hints of preparing more advanced anodes and promote the applications of vanadate materials such as Li3VO4 for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-021-00115-4
References
Kong H, Wu Y, Hong W, Yan C, Zhao Y, Chen G. Structure-designed synthesis of Cu-doped Co3O4@N-doped carbon with interior void space for optimizing alkali-ion storage. Energy Storage Mater. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2019.06.015.
Zhang D, Xi S, Li G, Li B, Fan J, Liu X, Chen D, Li L. Facile synthesis of Mn2.1V0.9O4/rGO: A novel high-rate anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2019;426:197.
Liu Y, Chen Z, Jia H, Xu H, Liu M, Wu R. Iron-doping-induced phase transformation in dual-carbon-confined cobalt diselenide enabling superior lithium storage. ACS Nano. 2019;13(5):6113.
Zhu Z, Tang Y, Leow W, Xia H, Lv Z, Wei J, Ge X, Cao S, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zhang H, Xi S, Du Y, Chen X. Approaching the lithiation limit of MoS2 while maintaining its layered crystalline structure to improve lithium storage. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(11):3521.
Li X, Li K, Zhu SC, Fan K, Lyu L, Yao H, Li Y, Hu J, Huang H, Mai YW, Goodenough JB. Fiber-in-tube design of Co9S8–carbon/Co9S8: enabling efficient sodium storage. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(19):1.
Hwang S, Yao Z, Zhang L, Fu M, He K, Mai L, Chris W, Su D. Multistep lithiation of tin sulfide: an investigation using in situ electron microscopy. ACS Nano. 2018;12(4):3638.
Wei X, Wang X, Tan X, An Q, Mai L. Nanostructured conversion-type negative electrode materials for low-cost and high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(46):1804458.
Yan Z, Guo J. High-performance silicon-carbon anode material via aerosol spray drying and magnesiothermic reduction. Nano Energy. 2019;63:103845.
Zhang D, Li G, Yu M, Fan J, Li B, Li L. Facile synthesis of Fe4N/Fe2O3/Fe/porous N-doped carbon nanosheet as high-performance anode for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2018;384:34.
Deng J, Yu X, Qin X, Zhou D, Zhang L, Duan H, Kang F, Li B, Wang G. Co–B nanoflakes as multifunctional bridges in ZnCo2O4 micro-/nanospheres for superior lithium storage with boosted kinetics and stability. Adv Energy Mater. 2019;9(14):1803612.
Liu H, Hu P, Yu Q, Liu Z, Zhu T, Luo W, Zhou L, Mai L. Boosting the deep discharging/charging lithium storage performances of Li3VO4 through double-carbon decoration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(28):23938.
Huang Y, Yang H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Tian M, Chen P, Trout R, Ma Y, Wu TH, Wu Y, Liu N. A safe and fast-charging lithium-ion battery anode using MXene supported Li3VO4. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2019;7:11250.
Dompablo MEA, Tartaj P, Amarilla JM, Amador U. Computational investigation of Li insertion in Li3VO4. Chem Mater. 2016;28(16):5643.
Zeng J, Yang Y, Li C, Li J, Huang J, Wang J, Zhao J. Li3VO4: an insertion anode material for magnesium ion batteries with high specific capacity. Electrochim Acta. 2017;247:265.
Liang Z, Zhao Y, Ouyang L, Dong Y, Kuang Q, Lin X, Liu X, Yan D. Synthesis of carbon-coated Li3VO4 and its high electrochemical performance as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2014;252:244.
Yang Y, Li J, He X, Wang J, Sun D, Zhao J. A facile spray drying route for mesoporous Li3VO4/C hollow spheres as an anode for long life lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2016;4:7165.
Liao C, Wen Y, Shan B, Zhai T, Li H. Probing the capacity loss of Li3VO4 anode upon Li insertion and extraction. J Power Sources. 2017;348:48.
Ni S, Zhang J, Ma J, Yang X, Zhang L. Superior electrochemical performance of Li3VO4/N-doped C as an anode for Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015;3(35):17951.
Liu X, Li G, Zhang D, Chen D, Wang X, Li B, Li L. Fe-doped Li3VO4 as an excellent anode material for lithium ion batteries: optimizing rate capability and cycling stability. Electrochim Acta. 2019;308:185.
Shen L, Chen S, Maier J, Yu Y. Carbon-coated Li3VO4 spheres as constituents of an advanced anode material for high-rate long-life lithium-ion batteries. Adv Mater. 2017;29(33):1701571.
Kang T, Shen D, Ni S, Chen Q, Li T, Yang X, Zhao J. Pseudocapacitive charge storage induced by self-enhanced electrical conductivity and Li-ion diffusion in high performance Li3VO4@LiVO2 anode for Li-ion batteries. J Alloy Compd. 2018;741:442.
Li X, Su Z, Tian H, Zhang Y. Rhombohedral-structured LiVO2 prepared by a novel two step method and its electrochemical properties. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2017;12:693.
Armstrong AR, Lyness C, Panchmatia PM, Islam MS, Bruce PG. The lithium intercalation process in the low-voltage lithium battery anode Li1+xV1−xO2. Nature Mater. 2011;10:223.
Liu X, Zhang D, Li G, Xue C, Ding J, Li B, Chen D, Li L. In situ synthesis of V2O3 nanorods anchored on reduced graphene oxide as high-performance lithium ion battery anode. ChemistrySelect. 2018;3(43):12108.
Zhou LL, Shen SY, Peng XX, Wu LN, Wang Q, Shen CH, Tu TT, Huang L, Li JT, Sun SG. New insights into the structure changes and interface properties of Li3VO4 anode for lithium-ion batteries during the initial cycle by in-situ techniques. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:23739.
Zhang CK, Liu CF, Nan XH, Song HQ, Liu YG, Zhang CP, Cao GZ. Hollow-cuboid Li3VO4/C as high-performance anodes for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(36):680.
Zhang C, Wang K, Liu C, Nan X, Fu H, Ma W, Li Z, Cao G. Effects of high surface energy on lithium-ion intercalation properties of Ni-doped Li3VO4. NPG Asia Mater. 2016;8:e287.
Zhou J, Zhao B, Song J, Chen B, Ma X, Dai J, Zhu X, Sun Y. Optimization of rate capability and cyclability performance in Li3VO4 anode material through Ca doping. Chem Eur J. 2017;23(64):16338.
Xu X, Niu F, Wang C, Li Y, Zhao C, Yang J, Qian Y. Li3VO4 nanoparticles in N-doped carbon with porous structure as an advanced anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Eng J. 2019;370:606.
Yang Y, Li J, Huang J, Huang J, Zeng J, Zhao J. Polystyrene-template-assisted synthesis of Li3VO4/C/rGO ternary composite with honeycomb-like structure for durable high-rate lithium ion battery anode materials. Electrochim Acta. 2017;247:771.
Zhang D, Li G, Li B, Fan J, Chen D, Liu X, Li L. Fast synthesis of Co1.8V1.2O4/rGO as a high-rate anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2018;54:7689.
Zhang D, Li G, Fan J, Li B, Li L. Tuning shell thickness of MnO/C core-shell nanowires for optimum performance of lithium-ion batteries. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2017;33(6):924.
Zhao L, Duan H, Zhao Y, Kuang Q, Fan Q, Chen L, Dong Y. High capacity and stability of Nb-doped Li3VO4 as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2018;378:618.
Wang K, Fu H, Li Z, Xia M, Liang X, Qi R, Cao G, Lu X. Enhancing the rate performance of a Li3VO4 anode through Cu doping. ChemElectroChem. 2018;5(3):478.
Li Q, Wei Q, Sheng J, Yan M, Zhou L, Wen L, Sun R, Mai L. Mesoporous Li3VO4/C submicron-ellipsoids supported on reduced graphene oxide as practical anode for high-power lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Sci. 2015;2(12):1500284.
Shao G, Gan L, Ma Y, Li H, Zhai T. Enhancing the performance of Li3VO4 by combining nanotechnology and surface carbon coating for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015;3:11253.
Liang ZY, Zhao YM, Dong YZ, Kuang Q, Lin XH, Liu XD, Yan DL. The low and high temperature electrochemical performance of Li3VO4/C anode material for Li-ion batteries. J Electroanal Chem. 2015;745:1.
Zhao D, Cao MH. Constructing highly graphitized carbon-wrapped Li3VO4 nanoparticles with hierarchically porous structure as a long life and high capacity anode for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:25084.
Qin RH, Shao GQ, Hou JX, Zheng Z, Zhai TY, Li HQ. One-pot synthesis of Li3VO4@C nanofibers by electrospinning with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. Sci Bull. 2017;62:1081.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21571176, 21671077, 21771075 and 21871106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Li, L. & Li, G. Partial surface phase transformation of Li3VO4 that enables superior rate performance and fast lithium-ion storage. Tungsten 1, 276–286 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-019-00028-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-019-00028-3