Abstract
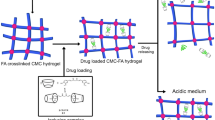
The number of studies of controlled drug-release systems is growing constantly. Bionanocomposite materials which can be prepared from the combination of biopolymers with inorganic solids such as clay minerals offer interesting alternatives for use as drug-delivery systems. In the present study, new bionanocomposite drug-release systems were prepared from the intercalation of the antibiotic drug ciprofloxacin into montmorillonite using an ion-exchange reaction. In order to prepare more stable systems for oral ciprofloxacin release, this ciprofloxacin-clay intercalation compound was incorporated into i-carrageenan-gelatin biopolymer blend to produce bionanocomposite materials. Bionanocomposites of two distinct i-carrageenan and gelatin mass ratios were conformed as beads through an ionic gelification reaction with Ca2+ ions, and dried by freeze-drying where liquid nitrogen or conventional freezing was adopted in the freezing step. The resulting ciprofloxacin-clay hybrid was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, solid state 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), thermal analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The montmorillonite-ciprofloxacin hybrid incorporated into the bionanocomposite beads was evaluated by in vitro release studies which showed a significant difference in the release profiles in the aqueous medium used to simulate the gastrointestinal tract, depending on the blend composition and the freezing method employed in the preparation of the beads. The results point to bionanocomposite systems based on ciprofloxacin-clay hybrids and biopolymers that may be used as devices in the biomedical area.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abdel-Karim, A., El-Naggar, M. E., Radwan, E. K., Mohamed, I. M., Azaam, M., & Kenawy, E.-R. (2021). High-performance mixed-matrix membranes enabled by organically/inorganic modified montmorillonite for the treatment of hazardous textile wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 405, 126964.
Aguzzi, C., Cerezo, P., Viseras, C., & Caramella, C. (2007). Use of clays as drug delivery systems: possibilities and limitations. Applied Clay Science, 36, 22–36.
Aguzzi, C., Cerezo, P., Sandri, G., Ferrari, F., Rossi, S., Bonferoni, C., Caramella, C., & Viseras, C. (2014). Intercalation of tetracycline into layered clay mineral material for drug delivery purposes. Materials Technology, 29, B96–B99 Taylor & Francis.
Akrami-Hasan-Kohal, M., Ghorbani, M., Mahmoodzadeh, F., & Nikzad, B. (2020). Development of reinforced aldehyde-modified kappa-carrageenan/gelatin film by incorporation of halloysite nanotubes for biomedical applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 160, 669–676.
Alcântara, A. C. S., & Darder, M. (2018). Building up functional bionanocomposites from the assembly of clays and biopolymers. The Chemical Record, 18, 696–712 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Alcântara, A. C. S., Aranda, P., Darder, M., & Ruiz-Hitzky, E. (2010). Bionanocomposites based on alginate-zein/layered double hydroxide materials as drug delivery systems. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 20, 9465–9504.
Alcântara, A. C. S., Darder, M., Aranda, P., & Ruiz-hitzky, E. (2016). Effective intercalation of zein into Na-montmorillonite : role of the protein components and use of the developed biointerfaces. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 7, 1772–1782.
Ashe, S., Behera, S., Dash, P., Nayak, D., & Nayak, B. (2020). Gelatin carrageenan sericin hydrogel composites improves cell viability of cryopreserved SaOS-2 cells. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 154, 606–620.
Bergaya, F., & Lagaly, G. (2006). Chapter 1 General introduction: clays, clay minerals, and clay science. In F. Bergaya, B. K. G. Theng, & G. Lagaly (Eds.), Handbook of Clay Science (pp. 1–18). Elsevier.
Bertolino, V., Cavallaro, G., Lazzara, G., Merli, M., Milioto, S., Parisi, F., & Sciascia, L. (2016). Effect of the biopolymer charge and the nanoclay morphology on nanocomposite materials. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 55, 7373–7380 American Chemical Society.
Brigatti, M. F., Galan, E., & Theng, B. K. G. (2006). Structures and mineralogy of clay minerals. In F. Bergaya, B. K. G. Theng, & G. Lagaly (Eds.), Handbook of Clay Science (pp. 19–86). Elsevier.
Cai, J., Han, X., Wang, X., & Meng, X. (2020). Atomic layer deposition of two-dimensional layered materials: processes, growth mechanisms, and characteristics. Matter, 2, 587–630.
Calabrese, I., Cavallaro, G., Scialabba, C., Licciardi, M., Merli, M., Sciascia, L., & Turco Liveri, M. L. (2013). Montmorillonite nanodevices for the colon metronidazole delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 457, 224–236.
Calabrese, I., Gelardi, G., Merli, M., Liveri, M. L. T., & Sciascia, L. (2017). Clay-biosurfactant materials as functional drug delivery systems: Slowing down effect in the in vitro release of cinnamic acid. Applied Clay Science, 135, 567–574.
Camara, M., Liao, H., Xu, J., Zhang, J., & Swai, R. (2019). Molecular dynamics study of the intercalation and conformational transition of poly (N-vinyl caprolactam), a thermosensitive polymer in hydrated Na-montmorillonite. Polymer, 179, 121718.
Carazo, E., Borrego-Sánchez, A., Sánchez-Espejo, R., García-Villén, F., Cerezo, P., Aguzzi, C., & Viseras, C. (2018). Kinetic and thermodynamic assessment on isoniazid/montmorillonite adsorption. Applied Clay Science, 165, 82–90.
Chattah, A. K., Linck, Y. G., Monti, G. A., Levstein, P. R., Manzo, H., Breda, S. A., & Olivera, E. (2007). NMR and IR characterization of the aluminium complexes of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin fluoroquinolones. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 45, 850–859.
Cheng, C. J., & Jones, O. G. (2017). Stabilizing zein nanoparticle dispersions with ι-carrageenan. Food Hydrocolloids, 69, 28–35.
Cunha, V. R. R., De Souza, R. B., Da Fonseca Martins, A. M. C. R. P., Koh, I. H. J., & Constantino, V. R. L. (2016). Accessing the biocompatibility of layered double hydroxide by intramuscular implantation: Histological and microcirculation evaluation. Scientific Reports, 6, 1–10.
Darder, M., Aranda, P., Ferrer, M. L., Gutiérrez, M. C., del Monte, F., & Ruiz-Hitzky, E. (2011). Progress in bionanocomposite and bioinspired foams. Advanced Materials, 23, 5262–5267.
El-Gamel, N. E. A., Hawash, M. F., & Fahmey, M. A. (2012). Structure characterization and spectroscopic investigation of ciprofloxacin drug. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 108, 253–262.
García, M. C. (2018). 12 - Drug delivery systems based on nonimmunogenic biopolymers. In A. Parambath (Ed.), Engineering of Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems (pp. 317–344). Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials. Woodhead Publishing.
Gieseking, J. E. (1939). The mechanism of cation exchange in the montmorillonite-beidellite-nontronite type of clay minerals. Soil Science, 47, 1–14.
Gómez-Mascaraque, L. G., Llavata-Cabrero, B., Martínez-Sanz, M., Fabra, M. J., & López-Rubio, A. (2018). Self-assembledgelatin-ι-carrageenan encapsulation structures for intestinal-targeted release applications. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 517, 113–123.
Gutiérrez, M. C., García-Carvajal, Z. Y., Jobbágy, M., Rubio, F., Yuste, L., Rojo, F., Ferrer, M. L., & del Monte, F. (2007). Poly(vinyl alcohol). scaffolds with tailored morphologies for drug delivery and controlled release. Advanced Functional Materials, 17, 3505–3513.
Kevadiya, B. D., Rajkumar, S., Bajaj, H. C., Chettiar, S. S., Gosai, K., Brahmbhatt, H., Bhatt, A. S., Barvaliya, Y. K., Dave, G. S., & Kothari, R. K. (2014). Biodegradable gelatin–ciprofloxacin–montmorillonite composite hydrogels for controlled drug release and wound dressing application. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 122, 175–183.
Khan, A. K., Saba, A. U., Nawazish, S., Akhtar, F., Rashid, R., Mir, S., Nasir, B., Iqbal, F., Afzal, S., Pervaiz, F., & Murtaza, G. (2017). Carrageenan based bionanocomposites as drug delivery tool with special emphasis on the influence of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2017, 1–13.
Kotal, M., & Bhowmick, A. K. (2015). Polymer nanocomposites from modified clays: Recent advances and challenges. Progress in Polymer Science, 51, 127–187.
Lee, L., Zeng, C., Cao, X., Han, X., Shen, J., & Xu, G. (2005). Polymer nanocomposite foams. Composites Science and Technology, 65, 2344–2363.
Lehn, J.-M., Alberti, G., & Bein, T. (1997). Comprehensive Supramolecular chemistry (Vol. 4). Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK.
Li, J.-R., Wang, Y.-X., Wang, X., Yuan, B., & Fu, M.-L. (2015). Intercalation and adsorption of ciprofloxacin by layered chalcogenides and kinetics study. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 453, 69–78.
Nahin, P. G. (1952). Infrared analysis of clays and related minerals. Clays and Clay Minerals, Bull, 169, Part III, 112–118.
Nascimento, G.M. (2021). Tanushree Choudhury (July 15th 2020). Clay Hybrid Materials, Clay Science and Technology, IntechOpen, https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.92529. Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/clay-science-and-technology/clay-hybrid-materials. Accessed in September 2021.
Nayak, P. L., & Sahoo, D. (2011). Chitosan-alginate composites blended with cloisite 30B as a novel drug delivery system for anticancer drug paclitaxel. International Journal of Plastics Technology, 15, 68–81.
Nouri, A., Tavakkoli Yaraki, M., Ghorbanpour, M., & Wang, S. (2018). Biodegradable κ-carrageenan/nanoclay nanocomposite films containing Rosmarinus officinalis L. extract for improved strength and antibacterial performance. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 115, 227–235.
Oliveira, A. S., Alcântara, A. C. S., & Pergher, S. B. C. (2017). Bionanocomposite systems based on montmorillonite and biopolymers for the controlled release of olanzapine. Materials Science and Engineering C, 75, 1250–1258.
Page, J. B. (1943). Differential thermal analysis of montmorillonite. Soil Science, 56, 273–284.
Rebitski, E. P., Alcântara, A. C. S., Darder, M., Cansian, R. L., Gómez-Hortigüela, L., & Pergher, S. B. C. (2018a). Functional carboxymethylcellulose/zein bionanocomposite films based on neomycin supported on sepiolite or montmorillonite clays. ACS Omega, 3, 13538–13550.
Rebitski, E. P., Aranda, P., Darder, M., Carraro, R., & Ruiz-Hitzky, E. (2018b). Intercalation of metformin into montmorillonite. Dalton Transactions, 47, 3185–3192.
Rebitski, E. P., Souza, G. P., Santana, S. A. A., Pergher, S. B. C., & Alcântara, A. C. S. (2019). Bionanocomposites based on cationic and anionic layered clays as controlled release devices of amoxicillin. Applied Clay Science, 173, 35–45.
Ribeiro, L. N. M., Alcântara, A. C. S., Darder, M., Aranda, P., Herrmann, P. S. P., Araújo-Moreira, F. M., García-Hernández, M., & Ruiz-Hitzky, E. (2014). Bionanocomposites containing magnetic graphite as potential systems for drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 477, 553–563.
Rivera, A., Valdés, L., Jiménez, J., Pérez, I., Lam, A., Altshuler, E., De Ménorval, L. C., Fossum, J. O., Hansen, E. L., & Rozynek, Z. (2016). Smectite as ciprofloxacin delivery system: Intercalation and temperature-controlled release properties. Applied Clay Science, 124–125, 150–156.
Ruiz-Hitzky, E., Darder, M., & Aranda, P. (2005). Functional biopolymer nanocomposites based on layered solids. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 15, 3650–3662.
Salvé, J., Grégoire, B., Imbert, L., Hubert, F., Karpel Vel Leitner, N., & Leloup, M. (2021). Design of hybrid Chitosan-Montmorillonite materials for water treatment: Study of the performance and stability. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 6, 100087.
Sepehr, M. N., Al-Musawi, T. J., Ghahramani, E., Kazemian, H., & Zarrabi, M. (2017). Adsorption performance of magnesium/aluminum layered double hydroxide nanoparticles for metronidazole from aqueous solution. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, 611–623.
Sharma, A., Bhat, S., Vishnoi, T., Nayak, V., & Kumar, A. (2013). Three-dimensional supermacroporous carrageenan-gelatin cryogel matrix cryogel matrix for tissue engineering applications. BioMed Research International, 2013, 1–15.
Svagan, A. J., Berglund, L. A., & Jensen, P. (2011). Cellulose nanocomposite biopolymer foam—hierarchical structure effects on energy absorption. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 3, 1411–1417.
Thai, T., Salisbury, B.H., & Zito, P.M. (2021). Ciprofloxacin. Treasure Island. StatPearls Publishing, Florida, USA.
Varghese, J. S., Chellappa, N., & Fathima, N. N. (2014). Gelatin-carrageenan hydrogels: Role of pore size distribution on drug delivery process. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 113, 346–351.
Viseras, C., Cerezo, P., Sanchez, R., Salcedo, I., & Aguzzi, C. (2010). Current challenges in clay minerals for drug delivery. Applied Clay Science, 48, 291–295.
Wang, C. J., Li, Z., & Jiang, W. T. (2011). Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on 2:1 dioctahedral clay minerals. Applied Clay Science, 53, 723–728.
Wu, Q., Li, Z., Hong, H., Yin, K., & Tie, L. (2010). Adsorption and intercalation of ciprofloxacin on montmorillonite. Applied Clay Science, 50, 204–211.
Wu, W., Chen, W., & Jin, Q. (2016). Oral mucoadhesive buccal film of ciprofloxacin for periodontitis: Preparation and characterization. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 15, 447–451.
Wu, M. J., Wu, J. Z., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Zhou, J. Z., Qian, G. R., Xu, Z. P., Du, Z., & Rao, Q. L. (2018). A review on fabricating heterostructures from layered double hydroxides for enhanced photocatalytic activities. Catalysis Science & Technology, 8, 1207–1228.
Yan, H., Zhang, P., Chen, X., Bao, C., Zhao, R., Hu, J., Liu, C., & Lin, Q. (2020). Preparation and characterization of octyl phenyl polyoxyethylene ether modified organo-montmorillonite for ibuprofen controlled release. Applied Clay Science, 189, 105519.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
M.S.L and W.C.S thank CNPq for masters and undergraduate scholarships, respectively. M.S.L. acknowledges the financial support obtained from the Mobility Program of Master Courses (CAPES) and the Graduate Program of the Federal University of Maranhão (UFMA) for an internship taken at the University of São Paulo (USP) and the Finance Code 001-CAPES. L.R.L acknowledges CAPES for providing the postdoctoral contract from the PROCAD-Amazônia- 88887.472618/2019-00 project.This study was funded by FAPEMA (UNIVERSAL 01118/16 and 00961/18 projects) and CNPq 425730/2018-2.
Funding
Funding sources are as stated in the Acknowledgments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This paper belongs to a special issue on ‘Clay Minerals in Health Applications’
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leite, M.S., Sodré, W.C., de Lima, L.R. et al. BIONANOCOMPOSITE BEADS BASED ON MONTMORILLONITE AND BIOPOLYMERS AS POTENTIAL SYSTEMS FOR ORAL RELEASE OF CIPROFLOXACIN. Clays Clay Miner. 69, 547–560 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-021-00158-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-021-00158-1