Abstract
Purpose
The management of the temperature and humidity inside greenhouses is essential for optimum crop growth. The temperature and humidity statuses extensively depend on the performance of dehumidifiers and heaters in the greenhouses. The objective of this study was to evaluate the performance of a small-scale suspension-type dehumidifier with a heating module in terms of temperature and humidity changes over time, and monitoring and controlling the status of individual actuating components in summer and winter.
Methods
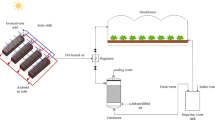
The prototype consisted of a dehumidifier, a fan, and a heating module. Twenty-seven temperature and humidity sensor nodes were placed in three layers (top, middle, and bottom) and in three sections (front, center, and rear sides) for monitoring the temperature and humidity statuses. Two additional temperature and humidity sensor nodes were placed in front of the module and outside the greenhouses. An on/off controller was used to manage the temperature and humidity during the operation of the dehumidifier.
Results
Remote monitoring and controlling was successfully achieved to operate the dehumidifier with a heating module without interruption during the experiments. The time response and change results confirmed the satisfactory performance of the on/off control. The power consumption values varied depending on the status of the actuators. When the dehumidifier, fan, and heater were turned on, the average power consumption values were 556.64 ± 1.94, 125.80 ± 1.26, and 3779.60 ± 2.24 W, respectively. The temperature and humidity showed a considerable amount of spatial and vertical variability, and the temperature and humidity changes were greater in the middle section than in the other sections in both the summer and winter greenhouses.
Conclusion
The outcomes of the research support the need for small-scale suspension-type dehumidifiers for region-specific temperature and humidity management, and may inform possible improvement of the prototype.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, A., Ishaque, K., Lashin, A., & Al Arifi, N. (2017). Modeling of a liquid desiccant dehumidification system for close type greenhouse cultivation. Energy, 118, 578–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2016.10.069.
Ardabili, S. F., Mahmoudi, A., Mesri Gundoshmian, T. M., & Roshanianfard, A. (2016). Modeling and comparison of fuzzy and on/off controller in a mushroom growing hall. Measurement, 90, 127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2016.04.050.
Atia, D. M., & El-madany, H. T. (2017). Analysis and design of greenhouse temperature control using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology, 4(1), 34–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JESIT.2016.10.014.
Bazgaou, A., Fatnassi, H., Bouhroud, R., Gourdo, L., Ezzaeri, K., Tiskatine, R., & Bouirden, L. (2018). An experimental study on the effect of a rock-bed heating system on the microclimate and the crop development under canarian greenhouse. Solar Energy, 176, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2018.10.027.
Benli, H., & Durmuş, A. (2009). Performance analysis of a latent heat storage system with phase change material for new designed solar collectors in greenhouse heating. Solar Energy, 83(12), 2109–2119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2009.07.005.
Bouadila, S., Lazaar, M., Skouri, S., Kooli, S., & Farhat, A. (2014). Assessment of the greenhouse climate with a new packed-bed solar air heater at night, in Tunisia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 35, 31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.03.051.
Boulard, T., Kittas, C., Papadakis, G., & Mermier, M. (1998). Pressure field and airflow at the opening of a naturally ventilated greenhouse. Journal of Agricultural and Engineering Research, 71(1), 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaer.1998.0302.
Chen, J., Xu, F., Tan, D., Shen, Z., Zhang, L., & Ai, Q. (2015). A control method for agricultural greenhouses heating based on computational fluid dynamics and energy prediction model. Applied Energy, 141, 106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2014.12.026.
Dayioğlu, M. A. (2014). Performance analysis of a greenhouse fan-pad cooling system: gradients of horizontal temperature and relative humidity. Journal of Agricultural SciencesTarım Bilimleri Dergisi, 21(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.15832/tbd.25721.
Ghani, S., Bakochristou, F., ElBialy, E. M. A. A., Gamaledin, S. M. A., Rashwan, M. M., Abdelhalim, A. M., & Ismail, S. M. (2019). Design challenges of agricultural greenhouses in hot and arid environments – a review. Engineering in Agriculture, Environment and Food, 12(1), 48–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EAEF.2018.09.004.
Guohong, T., Christopher, D. M., Tianlai, L., & Tieliang, W. (2008). Temperature variations inside Chinese solar greenhouses with external climatic conditions and enclosure materials. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 1(2), 21–26. https://doi.org/10.25165/IJABE.V1I2.44.
Hong, S. J., Park, S. B., Kang, N. R., Kim, Y. J., & Chung, S. O. (2017). Performance evaluation of a 400 W precise window motor for glass houses. Korean Journal of Agricultural Science, 44(4), 595. https://doi.org/10.7744/kjoas.20170067.
Iqbal, Z., Islam, N., Jang, B. E., Ali, M., Kabir, S. N., Lee, D. H., & Chung, S. O. (2019). Monitoring the operating status of an automatic harmful fly collector for smart greenhouses. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 44(4), 258–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-019-00036-8.
Jiang, J. A., Wang, C. H., Liao, M. S., Zheng, X. Y., Liu, J. H., Chuang, C. L., & Chen, C. P. (2016). A wireless sensor network-based monitoring system with dynamic convergecast tree algorithm for precision cultivation management in orchid greenhouses. Precision Agriculture, 17(6), 766–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-016-9448-7.
Kansal, A., Hsu, J., Zahedi, S., & Srivastava, M. B. (2007). Power management in energy harvesting sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 6(4), 32. https://doi.org/10.1145/1274858.1274870.
Kavga, A., Karanastasi, E., Konstas, I., & Panidis, T. (2013). Performance of an infrared heating system in a production greenhouse. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 46(18), 235–240. https://doi.org/10.3182/20130828-2-SF-3019.00017.
Medina-García, J., Sánchez-Rodríguez, T., Galán, J., Delgado, A., Gómez-Bravo, F., & Jiménez, R. (2017). A wireless sensor system for real-time monitoring and fault detection of motor arrays. Sensors, 17(3), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030469.
Mnati, M., Van den Bossche, A., & Chisab, R. (2017). A smart voltage and current monitoring system for three phase inverters using an android smartphone application. Sensors, 17(4), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040872.
Ozgener, O., & Hepbasli, A. (2005). Exergoeconomic analysis of a solar assisted ground-source heat pump greenhouse heating system. Applied Thermal Engineering, 25(10), 1459–1471. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLTHERMALENG.2004.09.015.
Pahuja, R., Verma, H. K., & Uddin, M. (2017). An intelligent wireless sensor and actuator network system for greenhouse microenvironment control and assessment. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 42(1), 23–43. https://doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2017.42.1.023.
Pedersen, T. H., Nielsen, K. U., & Petersen, S. (2017). Method for room occupancy detection based on trajectory of indoor climate sensor data. Building and Environment, 115, 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BUILDENV.2017.01.023 .
Ryu, M. J., Ryu, D. K., Chung, S. O., Hur, Y. K., Hur, S. O., Hong, S. J., & Kim, H. H. (2014). Spatial, vertical, and temporal variability of ambient environments in strawberry and tomato greenhouses in winter. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 39(1), 47–56. https://doi.org/10.5307/jbe.2014.39.1.047.
Shalaby, S. M., Bek, M. A., & Kabeel, A. E. (2017). Design recommendations for humidification-dehumidification solar water desalination systems. Energy Procedia, 107, 270–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EGYPRO.2016.12.148.
Shamshiri, R., & Wan Ishak, W. I. (2013). A review of greenhouse climate control and automation systems in tropical regions. Journal of Agricultural Science and Applications, 2(3), 175–183.
Tarara, J. M., & Hoheisel, G. A. (2007). Low-cost shielding to minimize radiation errors of temperature sensors in the field. American Society for Horticultural Science, 42(6), 1372–1379. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.42.6.1372.
Went, F. W. (1944). Plant growth under controlled conditions. II. Thermoperiodicity in growth and fruiting of the tomato. American Journal of Botany, 31(3), 135–150. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1944.tb08011.x.
Xu, J., Li, Y., Wang, R. Z., Liu, W., & Zhou, P. (2015). Experimental performance of evaporative cooling pad systems in greenhouses in humid subtropical climates. Applied Energy, 138, 291–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.10.061.
Xu, X., Huang, Z., Zhang, X., & Li, Z. (2018). A novel humidity measuring method based on dry-bulb temperatures using artificial neural network. Building and Environment, 139, 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BUILDENV.2018.05.012.
Xu, D., Du, S., & van Willigenburg, G. (2019). Double closed-loop optimal control of greenhouse cultivation. Control Engineering Practice, 85, 90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CONENGPRAC.2019.01.010.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (IPET) through the Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Convergence Technologies Program for Educating Creative Global Leaders funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (Project No. 320001-4), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M., Iqbal, M., Ali, M. et al. Performance Evaluation of a Suspension-Type Dehumidifier with a Heating Module for Smart Greenhouses. J. Biosyst. Eng. 45, 155–166 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00055-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00055-w