Abstract
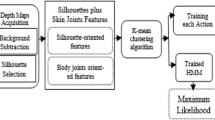
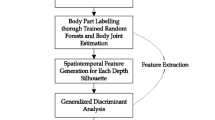
The increasing number of elderly people living independently needs especial care in the form of smart home monitoring system that provides monitoring, recording and recognition of daily human activities through video cameras, which offer smart lifecare services at homes. Recent advancements in depth video technologies have made human activity recognition (HAR) realizable for elderly healthcare applications. This study proposes a depth video-based HAR system to utilize skeleton joints features which recognize daily activities of elderly people in indoor environments. Initially, depth maps are processed to track human silhouettes and produce body joints information in the form of skeleton, resulting in a set of 23 joints per each silhouette. Then, from the joints information, skeleton joints features are computed as a centroid point with magnitude and joints distance features. Finally, using these features, hidden Markov model is trained to recognize various human activities. Experimental results show superior recognition rate, resulting up to the mean recognition rate of 84.33% for nine daily routine activities of the elderly.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JS, Yeom DH, Joo YH (2011) Fast and robust algorithm of tracking multiple moving objects for intelligent video surveillance systems. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 57:1165–1170
Jalal A, Kim S (2005) The mechanism of edge detection using the block matching criteria for the motion estimation. In: Proceedings of human computer interaction, pp 484–489
Lee Y, Choi T-J, Ahn C-W (2017) Multi-objective evolutionary approach to select security solutions. CAAI Trans Intell Technol 2(2):64–67
Ming JL-C, Armenakis C (2018) UAV navigation system using line-based sensor pose estimation. Geo-Spat Inf Sci 21(1):2–11
Jalal A, Kim Y, Kamal S, Farooq A, Kim D (2015) Human daily activity recognition with joints plus body features representation using Kinect sensor. In: Proceedings IEEE conference on Informatics, electronics and vision, pp 1–6
Otero RP (2003) Induction of the effects of actions by monotonic methods. In: Proceedings of the international conference on inductive logic programming, pp 299–310
Kamal S, Jalal A, Kim D (2016) “Depth Images-based human detection, tracking and activity recognition using spatiotemporal features and modified HMM. J Electr Eng Technol 11:1921–1926
Liu M, Chen C, Liu H (2017) Learning informative pairwise joints with energy-based temporal pyramid for 3D action recognition. In: Proceedings of the international conference on multimedia and expo, pp 901–906
Bakli MS, Sakr MA, Soliman THA (2018) A spatiotemporal algebra in Hadoop for moving objects. Geo-Spat Inf Sci 21(2):102–114
Jalal A, Kamal S, Kim D (2016) Human depth sensors-based activity recognition using spatiotemporal features and hidden Markov model for smart environments. J Comput Netw Commun 2016:1–11
Zhao W, Yan L, Zhang Y (2018) Geometric-constrained multi-view image matching method based on semi-global optimization. Geo-Spat Inf Sci 21(2):115–126
Weng E-J, Fu L-C (2012) On-line human action recognition by combining joint tracking and key pose recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on intelligent robots and systems, pp 4112–4117
Chang Z, Cao J, Zhang Y (2018) A novel image segmentation approach for wood plate surface defect classification through convex optimization. J For Res 29(6):1789–1795
Jalal A, Kamal S, Kim D (2015) Individual detection-tracking-recognition using depth activity images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on ubiquitous robots and ambient intelligence, pp 450–455
Jalal A, Uddin MZ, Kim JT, Kim T (2011) Daily human activity recognition using depth silhouettes and R transformation for smart home. In: Proceedings smart homes health telematics, pp 25–32
Hongye X, Zhuoya H (2015) Gait recognition based on gait energy image and linear discriminant analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on signal processing, communications and computing, pp 1–4
Rajput H, Som T, Kar S (2016) Using radon transform to recognize skewed images of vehicular license plates. Computer 49:59–65
Kim Y-N, Park J-H, Kim M-H (2018) Spatio-temporal analysis of trajectory for pedestrian activity recognition. J Electr Eng Technol 13(2):961–968
Jalal A, Kamal S, Kim D (2015) Depth silhouettes context: a new robust feature for human tracking and activity recognition based on embedded HMMs. In: Proceedings 12th IEEE conference on ubiquitous robots and ambient intelligence, pp 294–299
Muller M, Roder T (2006) Motion templates for automatic classification and retrieval of motion capture data. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on computer animation, pp 479–485
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (no. 2018R1D1A1A02085645). Also, it was supported by a grant (19CTAP-C152247-01) from Technology Advancement Research Program funded by Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korean government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K., Jalal, A. & Mahmood, M. Vision-Based Human Activity Recognition System Using Depth Silhouettes: A Smart Home System for Monitoring the Residents. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 14, 2567–2573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-019-00278-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-019-00278-8