Abstract
Aim
This systematic review was performed to evaluate the role of laparoscopy in cases of recurrent intussusception in children.
Methods
The literature was reviewed for articles on Pubmed and Web of Science with search terms “laparoscopy”, “recurrent intussusception” and “children”.
Results
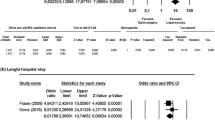
There were 12 articles describing 164 children (9 months to 13 years old) that underwent laparoscopy for recurrent intussusception. The site of intussusception was ileocolic in 94.51% of cases. Non-surgical reduction was initially performed in 89 cases, while in only 4 cases laparoscopy was used as a first-line treatment. Manual reduction was required between 2 and 8 times for each child, with a median of 3.29 procedures prior to laparoscopic intervention. A lead point was identified in 5 cases: Meckel’s diverticulum in 3, appendicitis in 2 and juvenile polyps in 1. Procedures included: appendectomies (n = 149), ileocolonic pexies (n = 118), folding of ileum (n = 2), resection of Meckel’s diverticulum (n = 3) and cecectomy (n = 2). Laparoscopy was unsuccessful in 20 children, who needed subsequent surgery. There were no morbidities.
Conclusions
In conclusion, laparoscopy is successfully used in recurrent intussusception in children. The procedure is usually done after 3 recurrences. Only 3% of patients with recurrent intussusception are reported to have a lead point. The rate of reoperation after laparoscopy is approximately 12%, with no morbidities.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Holcomb GW III, Murphy JP (2012) Ashcraft’s pediatric surgery, 5th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 508–516
Demir M, Akin M, Ünal A, Kaba M, Sever N, Dokucu A (2022) Our treatment approaches in recurrent chronic intussusceptions. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 28:1317–1322. https://doi.org/10.14744/tjtes.2022.56954
Waseem M, Rosenberg HK (2008) Intussusception. Pediatr Emerg Care 24:793–800
Applegates KE (2009) Intussusception in children: evidence-based diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Radiol 39:S140–S143
Wang SM, Huang FC, Wu CH, Ko SF, Lee SY, Hsiao CC (2010) Ileocecal Burkitt’s lymphoma presenting as ileocolic intussusception with appendiceal invagination and acute appendicitis. J Formos Med Assoc 109:476–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-6646(10)60080-0
Puri P, Höllwarth M (eds) (2009) Pediatric surgery. Springer, Berlin, pp 313–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69560-8
Chang YT, Lee JY, Wang JY, Chiou CS, Lin JY (2009) Early laparoscopy for ileocolic intussusception with multiple recurrences in children. Surg Endosc 23:2001–2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-9977-x
Boehm R, Till H (2003) Recurrent intussusceptions in an infant that were terminated by laparoscopic ileocolonic pexie. Surg Endosc 17:831–832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-002-4280-8
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Okamura K, Taniguchi N, Hino Y, Hayashida M (2020) Preoperative diagnosis of appendiceal intussusception. Pediatr Int 62:992–993. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.14182
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Hu X, Li B, Ming G (2020) Laparoscopic ileopexy versus laparoscopic simple reduction in children with multiple recurrences of ileocolic intussusception: a single-institution retrospective cohort study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 30:576–580. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2019.0641
Lipskar A, Telem D, Masseaux J, Midulla P, Dolgin S (2008) Failure of appendectomy to resolve appendiceal intussusception. J Pediatr Surg 43:1554–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.03.038
Li B, Sun CX, Chen WB, Zhang FN (2018) Laparoscopic ileocolic pexy as preventive treatment alternative for ileocolic intussusception with multiple recurrences in children. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 28:314–317. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0000000000000564
Human M, Hawu Y, Tshifularo N (2020) Diffuse juvenile polyposis causing recurrent small bowel intussusception. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep 61:101624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsc.2020.101624
Fecteau A, Flageole H, Nguyen LT, Laberge JM, Shaw KS, Guttman FM (1996) Recurrent intussusception: safe use of hydrostatic enema. J Pediatr Surg 31:859–861
Gray MP, Li SH, Hoffmann RG, Gorelick MH (2014) Recurrence rates after intussusception enema reduction: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics 134:110–119
Chen SC-C, Wang J-D, Hsu H-Y et al (2010) Epidemiology of childhood intussusception and determinants of recurrence and operation: analysis of national health insurance data between 1998 and 2007 in Taiwan. Pediatr Neonatol 2010(51):285–291
Niramis R, Watanatittan S, Kruatrachue A et al (2010) Management of recurrent intussusception: Nonoperative or operative reduction? J Pediatr Surg 45:2175–2180
Wu P, Huang P, Fu Y, Lv Y, Feng S, Lou Y (2022) Laparoscopic versus open reduction of intussusception in infants and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pediatr Surg 32:469–476. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1749437
Li SM, Wu XY, Luo CF, Yu LJ (2022) Laparoscopic approach for managing intussusception in children: analysis of 65 cases. World J Clin Cases 10:830–839. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.830
Anand RJ, Shah SR, Kane TD (2007) Laparoscopic management of delayed recurrent intussusception in an older child. JSLS 11:106–108
Chui CH, Ong LY, Chua JH, Yap T (2007) “Chinese fan spread” distraction technique of laparoscopic reduction of intussusception. JSLS 11:238–241
Wei CH, Fu YW, Wang NL, Du YC, Sheu JC (2015) Laparoscopy versus open surgery for idiopathic intussusception in children. Surg Endosc 29:668–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3717-1
van der Laan M, Bax NM, van der Zee DC, Ure BM (2001) The role of laparoscopy in the management of childhood intussusception. Surg Endosc 15:373–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004640090044
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical concerns
None.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alqadi, G.O., Saxena, A.K. Role of laparoscopy in recurrent pediatric intussusceptions: systematic review. J Ped Endosc Surg 5, 153–157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42804-023-00204-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42804-023-00204-w