Abstract
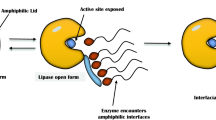
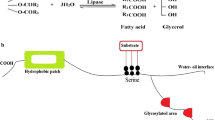
Lipases are enzymes that catalyze the breakdown of lipids into long-chain fatty acids and glycerol in oil-water interface. In addition, they catalyze broad spectrum of bioconversion reactions including esterification, inter-esterification, among others in non-aqueous and micro-aqueous milieu. Lipases are universally produced from plants, animals, and microorganisms. However, lipases from microbial origin are mostly preferred owing to their lower production costs, ease of genetic manipulation etc. The secretion of these biocatalysts by microorganisms is influenced by nutritional and physicochemical parameters. Optimization of the bioprocess parameters enhanced lipase production. In addition, microbial lipases have gained intensified attention for a wide range of applications in food, detergent, and cosmetics industries as well as in environmental bioremediation. This review provides insights into strategies for production of microbial lipases for potential biotechnological applications.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Patel N, Rai D, Shivam SS, Mishra U (2019) Lipases: sources, production, purification, and applications. Recent Patents Biotechnol 13(1):45–56
Joseph B, Ramteke PW, Thomas G (2008) Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments. Biotechnol Adv 26(5):457–470
Hassan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Influence of culture conditions on lipase production by Bacillus sp. FH5. Ann Microbiol 56:247–252
Borrelli GM, Trono D (2015) Recombinant lipases and phospholipases and their uses as biocatalysts for industrial applications. Int J Mol Sci 16(9):20774–20840
Kanmani P, Aravind J, Kumaresan K (2015a) An insight into microbial lipases and their environmental facet. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(3):1147–1162
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(6):763–781
de Pascale D, Cusano AM, Autore F, Parrilli E, Di Prisco G, Marino G, Tutino ML (2008) The cold-active Lip 1 lipase from the antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 is a member of a new bacterial lipolytic enzyme family. Extremophiles 12(3):311–323
Nardini M, Dijkstra BW (1999) α/β hydrolase fold enzyme: the family keeps growing. Curr Opin Struct Biol 9(6):732–737
Jaeger K-E, Dijkstra BW, Reetz MT (1999) Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:315–351
Beisson F, Tiss A, Riviére C, Verger R (2000) Methods for lipase detection and assay: a critical review. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 2:133–153
Chandra P, Singh ER, Arora PK (2020) Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: a comprehensive review. Microb Cell Factories 19:169
Bharathi D, Rajalakshmi G (2019) Microbial lipases: an overview of screening, production and purification. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 22:101368
Gururaj P, Ramalingam S, Devi GN, Gautam P (2016) Process optimization for production and purification of a thermostable, organic solvent tolerant lipase from Acinetobacter sp. AU07. Braz J Microbiol 47(3):647–657
Adetunji AI, Olaniran AO (2018a) Optimization of culture conditions for enhanced lipase production by an indigenous Bacillus aryabhattai SE3-PB using response surface methodology. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32(6):1514–1526
Lo C-F, Yu C-Y, Kuan I-C, Lee S-L (2012) Optimization of lipase production by Burkholderia sp. using response surface methodology. Int J Mol Sci 13(11):14889–14897
Faisal PA, Hareesh ES, Priji P, Unni KN, Sajith S, Sreedevi S, Josh MS, Benjamin S (2014) Optimization of parameters for the production of lipase from Pseudomonas sp. BUP6 by solid state fermentation. Adv Enzyme Res2:125-133.
Kalyani N, Saraswathy N (2014) Production of extracellular lipase by a new strain Staphylococcus aureus NK-LB37 isolated from oil-contaminated soil. Afr J Biotechnol 13 (28):2858-2866.
Tripathi R, Singh J, Bharti RK, Thakur IS (2014) Isolation, purification and characterization of lipase from Microbacterium sp. and its application in biodiesel production. Energy Procedia 54:518–529
Lopes MF, Leitão AL, Regalla M, Marques JJ, Carrondo MJ, Crespo MT (2002) Characterization of a highly thermostable extracellular lipase from Lactobacillus plantarum. Int J Food Microbiol 76(1-2):107–115
Abdou AM (2003) Purification and partial characterization of psychrotrophic Serratia marcescens lipase. J Dairy Sci 86(1):127–132
Mahdi BA, Bhattacharya A, Gupta A (2012) Enhanced lipase production from Aeromonas sp. S1 using Sal deoiled seed cake as novel natural substrate for potential application in dairy wastewater treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87(3):418–426
Sharma A, Bardhan D, Patel R (2009) Optimization of physical parameters for lipase production from Arthrobacter sp. BGCC#490. Indian J Biochem Biophys 46:178–183
Hasan-Beikdashti M, Forootanfar H, Safiarian MS, Ameri A, Ghahremani MH, Khoshay MR, Faramarzi MA (2012) Optimization of culture conditions for production of lipase by a newly isolated bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43(5):670–677
Gumerov VM, Mardanov AV, Kolosov PM, Ravin NV (2012) Isolation and functional characterization of lipase from the thermophilic alkali-tolerant bacterium Thermosyntropha lipolytica. Appl Biochem Microbiol 48(4):338–343
Teng Y, Xu Y, Wang D (2009) Changes in morphology of Rhizopus chinensis in submerged fermentation and their effect on production of mycelium-bound lipase. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32(3):397–405
Naqvi SH, Dahot MU, Ali A, Khan MY, Rafiq M (2011) Production and characterization of extracellular lipase secreted by Mucor geophillus. Afr J Biotechnol 10(84):19598–19606
Oliveira BH, Coradi GV, Attili-Angelis D, Scauri C, Luques AHPG, Barbosa AM, Dekker RFH, Neto PO, Lima VMG (2013) Comparison of lipase production on crambe oil and meal by Fusarium sp. (Gibberella fujikuroi complex). Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 115(12):1413–1425
Loo JL, Khoramnia A, Lai OM, Long K, Ghazali HM (2014) Mycelium-bound lipase from a locally isolated strain of Geotrichum candidum. Molecules 19(6):8556–8570
Colla LM, Primaz AL, Benedetti S, Loss RA, de Lima M, Reinehr CO, Bertolin TE, Costa JAV (2016) Surface response methodology for the optimization of lipase production under submerged fermentation by filamentous fungi. Braz J Microbiol 47(2):461–467
Turati DFM, Morais Júnior WG, Terrasan CRF, Moreno-Perez S, Pessela BC, Fernandez-Lorente G, Guisan JM, Carmona EC (2017) Immobilization of lipase from Penicillium sp. Section Gracilenta (CBMAI 1583) on different hydrophobic supports: modulation of functional properties. Molecules 22(2):339
Liu Z, Chi Z, Wang L, Li J (2008) Production, purification and characterization of an extracellular lipase from Aureobasidium pullulans HN2.3 with potential application for the hydrolysis of edible oils. Biochem Eng J 40(3):445–451
Potumarthi R, Subhakar C, Vanajakshi J, Jetty A (2008) Effect of aeration and agitation regimes on lipase production by newly isolated Rhodotoru lamucilaginosa MTCC 8737 in stirred tank reactor using molasses as sole production medium. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 151(2-3):700–710
Laachari F, Elabed S, Sayari A, Mohammed I, Harchali E, Boubendir A, Ibnsouda SK (2013) Biochemical characterization of a thermoactive and thermostable lipase from a newly isolated Trichosporon coremiiforme strain. Afr J Biotechnol 12(28):4503–4511
Oliveira ACD, Fernandes ML, Mariano AB (2014) Production and characterization of an extracellular lipase from Candida guilliermondii. Braz J Microbiol 45(4):1503–1511
Thirunavukarasu K, Purushothaman S, Gowthaman MK, Nakajima-Kambe T, Rose C, Kamini NR (2015) Utilization of fishmeal and fish oil for production of Cryptococcus sp. MTCC 5455 lipase and hydrolysis of polyurethane thereof. J Food Sci Technol 52(9):5772–5780
Sharma R, Chisti Y, Banerjee UC (2001) Production, purification, characterization, and application of lipases. Biotechnol Adv 19(8):627–662
Adetunji AI, Olaniran AO (2018c) Immobilization and characterization of lipase from an indigenous Bacillus aryabhattai SE3-PB isolated from lipid-rich wastewater. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 48(10): 898–905
Bora L, Bora M (2012) Optimization of extracellular thermophilic highly alkaline lipase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. isolated from hot springs of Arunachal Pradesh India. Braz J Microbiol 43(1):30–42
Lee LP, Karbul HM, Citartan M, Gopinath SCB, Lakshmipriya T, Tang T-H (2015) Lipase-secreting Bacillus species in an oil-contaminated habitat: promising strains to alleviate oil pollution. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–9
Daouadji KL, Reffas FZI, Benine ML, Abbouni B (2015) Optimization of various physical and chemical parameters for lipase production by Bacillus coagulans. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 15(5):962–968
Shariff FM, Abd Rahman RNZR, Basri M, Salleh AB (2011) A newly isolated thermostable lipase from Bacillus sp. Int J Mol Sci 12(5):2917–2934
Ghori MI, Iqbal MJ, Hameed A (2011) Characterization of a novel lipase from Bacillus sp. isolated from tannery wastes. Braz J Microbiol 42(1):22–29
Kumar S, Kikon K, Upadhyay A, Kanwar SS, Gupta R (2005) Production, purification, and characterization of lipase from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus coagulans BTS-3. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):38–44
Castro-Ochoa LD, Rodríguez-Gómez C, Valerio-Alfaro G, Ros RO (2005) Screening, purification and characterization of the thermoalkalophilic lipase produced by Bacillus thermoleovorans CCR11. Enzym Microb Technol 37(6):648–654
Kumar R, Sharma A, Kumar A, Singh D (2012) Lipase from Bacillus pumilus RK31: production and some properties. World Appl Sci J16(7):940–948
Anbu P, Noh M-J, Kim D-H, Seo J-S, Hur B-K, Min KH (2011) Screening and optimization of extracellular lipases by Acinetobacter species isolated from oil-contaminated soil in South Korea. Afr J Biotechnol 10(20):4147–4156
Jagtap SC, Chopade BA (2015) Purification and characterization of lipase from Acinetobacter haemolyticus TA 106 isolated from human skin. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 37(1):7–13
Sarac N, Ugur A (2015) A green alternative for oily wastewater treatment: lipase from Acinetobacter haemolyticus NS02-30. Desalin Water Treat 1(42):19750–19759
Kumari A, Mahapatra P, Banerjee R (2009) Statistical optimization of culture conditions by response surface methodology for synthesis of lipase with Enterobacter aerogenes. Braz Arch Biol Technol 52(6):1349–1356
Abdel-Fattah YF (2002) Optimization of thermostable lipase production from a thermophilic Geobacillus sp. using Box-Behnken experimental design. Biotechnol Lett 24(14):1217–1222
Ebrahimpour A, Abd Rahman RNZR, Ch’ng DHE, Basri M, Salleh A (2008) A modeling study by response surface methodology and artificial neural network on culture parameters optimization for thermostable lipase production from a newly isolated thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. BMC Biotechnol 8:96
Abd Rahman RNZR, Leow TC, Salleh A, Basri M (2007) Geobacillus zalihae sp. nov., a thermophilic lipolytic bacterium isolated from palm oil mill effluent in Malaysia. BMC Microbiol 7:77
Boran R, Ugur A (2010) Partial purification and characterization of the organic solvent-tolerant lipase produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens RB02-3 isolated from milk. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 40(4):229–241
Mobarak-Qamsari E, Kasra-Kermanshahi R, Moosavi-nejad Z (2011) Isolation and identification of a novel, lipase-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa KM110. Iranian J Microbiol 3(2):92–98
Sreelatha B, Rao VK, Kumar RR, Girisham S, Reddy SM (2017) Culture conditions for the production of thermostable lipase by Thermomyces lanuginosus. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 6(1):87–95
Das A, Shivakumar S, Bhatttacharya S, Shakya S, Swathi SS (2016) Purification and characterization of a surfactant-compatible lipase from Aspergillus tamarii JGIFO6 exhibiting energy-efficient removal of oil stains from polycotton fabric. 3. Biotech 6(2):131
Sethi BK, Nanda PK, Sahoo S (2016) Characterization of biotechnologically relevant extracellular lipase produced by Aspergillus terreus NCFT 4269.10. Braz J Microbiol 47(1):143–149
Pacheco SMV, Cruz Júnior A, Morgado AF, FurigoJúnior A, Amadi OC, Guisán JM, Pessela B (2015) Isolation and screening of filamentous fungi producing extracellular lipase with potential in biodiesel production. Adv Enzyme Res 3:101–114
Pereira MG, Vici AC, Facchini FDA, Tristão AP, Cursino-Santos JR, Sanches PR, Jorge JA, Polizeli MLTM (2014) Screening of filamentous fungi for lipase production: Hypocrea pseudokoningiia new producer with a high biotechnological potential. Biocatal Biotransform 32(1):74–83
de Almeida AF, Dias KB, da Silva ACC, Terrasan CRF, Tauk-Tornisielo SM, Carmona EC (2016) Agroindustrial wastes as alternative for lipase production by Candida viswanathii under solid-state cultivation: purification, biochemical properties, and its potential for poultry fat hydrolysis. Enzyme Res 2016:1–15
Nair S, Kumar P (2007) Molecular characterization of a lipase-producing Bacillus pumilus strain (NMSN-1d) utilizing colloidal water-dispersible polyurethane. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(10):1441–1449
Singh M, Singh RS, Banerjee UC (2010) Enantioselective transesterification of racemic phenyl ethanol and its derivatives in organic solvent and ionic liquid using Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipase. Process Biochem 45(1):25–29
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2009) Methods for detection and characterization of lipases: a comprehensive review. Biotechnol Adv 27(6):782–798
Ertuğrul S, Dönmez G, Takaç S (2007) Isolation of lipase producing Bacillus sp. from olive mill wastewater and improving its enzyme activity. J Hazard Mater 149(3):720–724
Bora L, Kalita MC (2007) Production and optimization of thermostable lipase from a thermophilic Bacillus sp. LBN 4. Internet J Microbiol 4(1):1–6
Kim EK, Jang WH, Ko JH, Kang JS, Noh MJ, Yoo OJ (2001) Lipase and its modulator from Pseudomonas sp. strain KFCC 10818: proline-to-glutamine substitution at position 112 induces formation of enzymatically active lipase in the absence of the modulator. J Bacteriol 183(20):5937–5941
Emmanuel G, Esakkiraj P, Jebadhas A, Iyapparaj P, Palavesam A (2008) Investigation of lipase production by milk isolate Serratia rubidaea. Food Technol Biotechnol 46(1):60–65
Kashmiri MA, Ahmad A, Butt BW (2006) Production, purification and partial characterization of lipase from Trichoderma viride. Afr J Biotechnol 5(10):878–882
Rasmey AM, Aboseidah AA, Gaber S, Mahran F (2017) Characterization and optimization of lipase activity produced by Pseudomonas monteilli 2403-KY120354 isolated from ground beef. Afr J Biotechnol 16(2):96–105
Alkan H, Baysal Z, Uyar F, Dogru M (2007) Production of lipase by a newly Bacillus coagulans under solid-state fermentation using melon wastes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 136(2):183–192
Melani NB, Tambourgi EB, Silveira E (2019) Lipases: from production to applications. Sep Purif Rev 49(2):143–158
Martínez-Corona R, Banderas-Martínez FJ, Pérez-Castillo JN, Cortés-Penagos C, González-Hernández JC (2020) Avocado oil as an inducer of the extracellular lipase activity of Kluyveromyces marxianus L-2029. Food Sci Technol 40:121–129
Niyonzima FN, More SS, Muddapur U (2013) Optimization of fermentation culture conditions for alkaline lipase production by Bacillus flexus XJU-1.Curr. Trends Biotechnol Pharm 7(3):793–803
Khoramnia A, Ebrahimpour A, Beh BK, Lai OM (2011) Production of a solvent, detergent, and thermotolerant lipase by a newly isolated Acinetobacter sp. in submerged and solid-state fermentations. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:1–12
Nerurkar M, Manasi J, Sujata P, Ravindra A (2013) Application of lipase from marine bacteria Bacillus sonorensis as an additive in detergent formulation. J Surfactant Deterg 16(3):435–443
Chauhan M, Chauhan RS, Garlapati VK (2013) Evaluation of a new lipase from Staphylococcus sp. for detergent additive capability. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–6
Gulati R, Isar J, Kumar V, Prasad AK, Parmar VS, Saxena RK (2005) Production of a novel alkaline lipase by Fusarium globulosum using neem oil, and its applications. Pure Appl Chem 77(1):251–262
Ghanem EH, Al-Sayed HA, Saleh KM (2000) An alkalophilic thermostable lipase produced by a new isolated of Bacillus alcalophilus.World. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16(5):459–464
Rashid N, Shimada Y, Ezaki S, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2001) Low temperature lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas sp. strain KB700A. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(9):4064–4069
Gunalakshmi B, Sahu M, Sivakumar K, Thangaradjou T, Sudha S, Kanan L (2008) Investigation on lipase producing actinomycete stain LE-1, isolated from shrimp pond. Res J Microbiol 3:73–81
Thirunavukarasu K, Edwinoliver NG, Anbarasan S, Gowthaman MK, Iefuji H, Kamini NR (2008) Removal of triglyceride soil from fabrics by a novel lipase from Cryptococcus sp. S-2. Process Biochem 43(7):701–706
Kumar SS, Kumar L, Sahai V, Gupta R (2009) A thiol-activated lipase from Trichosporon asahii MSR 54: detergent compatibility and presoak formulation for oil removal from soiled cloth at ambient temperature. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 26(3):427–432
Wang J-Y, Ma C-L, Bao Y-M, Xu P-S (2012) Lipase entrapment in protamine-induced bio-zirconia particles: characterization and application to the resolution of (R, S)-1-phenylethanol. Enzym Microb Technol 51(1):40–46
Aravindan R, Anbumathi P, Viruthagiri T (2007) Lipase applications in food industry. Indian J Biotechnol 6:141–158
Romdhane IB, Fendri A, Gargouri Y, Gargouri A, Belghith HA (2010) novel thermoactive and alkaline lipase from Talaromyces thermophilus fungus for use in laundry detergents. Biochem Eng J 53(1):112–120
Ilesanmi OI, Adekunle AE, Omolaiye JA, Olorode EM, Ogunkanmi AL (2020) Isolation, optimization and molecular characterization of lipase producing bacteria from contaminated soil. Sci Afr 8:e00279
Cherif S, Mnif S, Hadrich F, Abdelkafi S, Sayadi S (2011) A newly high alkaline lipase: an ideal choice for application in detergent formulations. Lipids Health Dis 10:221–228
Wang X, Yu X, Xu Y (2009) Homologous expression, purification and characterization of a novel high-alkaline and thermal stable lipase from Burkholderia cepacia ATCC 25416. Enzym Microb Technol 45(2):94–102
Wang H, Shao J, Wei YJ, Zhang J, Qi W (2011) A novel low temperature alkaline lipase from Acinetobacter johnsonii LP28 suitable for detergent formulation. Food Technol Biotechnol 49(1):96–102
Lailaja VP, Chandrasekaran M (2013) Detergent compatible alkaline lipase produced by marine Bacillus smithii BTMS11.World. J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(8):1349–1360
Rathi P, Saxena RK, Gupta R (2001) A novel alkaline lipase from Burkholderia cepacia for detergent formulation. Process Biochem 37(2):187–192
Bayoumi RA, El-louboudey SS, Sidkey NM, Abd-El-Rahman MA (2007) Production, purification and characterization of thermos-alkalophilic lipase for application in bio-detergent industry. J Appl Sci Res 3(12):1752–1765
Brozzoli,V, Crognale S, Sampedro I, Federici F, D’Annibale A, Petruccioli M (2009) Assessment of olive-mill wastewater as a growth medium for lipase production by Candida cylindracea in bench-top reactor. Bioresour Technol 100 (13):3395-3402.
Ghosh PK, Saxena RK, Gupta R, Yadav RP, Davidson S (1996) Microbial lipases: production and applications. Sci Prog 79:119–157
Niyonzima FN, More SS (2015) Microbial detergent compatible lipases. J Sci Ind Res 74:105–113
Sharma R, Soni SK, Vohra RM, Jolly RS, Gupta LK, Gupta JK (2002) Production of extracellular alkaline lipase from a Bacillus sp. RSJ1 and its application in ester hydrolysis. Indian J Microbiol 42:49–54
El-Batal AI, Farrag AA, Elsayed MA, El-Khawaga AM (2016) Effect of environmental and nutritional parameters on the extracellular lipase production by Aspergillus niger. Int Lett Nat Sci 60:18–29
Bharathi D, Rajalakshmi G, Komathi S (2019) Optimization and production of lipase enzyme from bacterial strains isolated from petrol spill soil. J King Saud Univ --Sci 31:898–901
Zheng C (2018) Growth characteristics and enzyme production optimization of lipase producing strain. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 108:042087
Taskin M, Ucar MH, Unver Y, Kara AA, Ozdemir M, Ortucu S (2016) Lipase production with free and immobilized cells of cold-adapted yeast Rhodotorula glutinis HL25. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 8:97–103
Furini G, Berger JS, Campos JAM, van der Sand ST, Germani JC (2018) Production of lipolytic enzymes by bacteria isolated from biological effluent systems. Ann Braz Acad Sci 90:2955–2965
Salwoom L, Abd Rahman RNZR, Salleh AB, Shariff FM, Convey P, Pearce D, Ali MSM (2019) Isolation, characterization, and lipase production of a cold-adapted bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. LSK 25 isolated from Signy Island, Antarctica. Molecules 24:715
Kanwar L, Gogoi BK, Goswami P (2002) Production of a Pseudomonas lipase in n-alkane substrate and its isolation using an improved ammonium sulfate precipitation technique. Bioresour Technol 84:207–211
Mazhar H, Abbas N, Ali S, Sohai LA, Hussain Z, Ali SS (2017) Optimized production of lipase from Bacillus subtilis PCSIRNL-39. Afr J Biotechnol 16:1106–1115
Geoffry K, Achur RN (2018) Screening and production of lipase from fungal organisms. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 14:241–253
Adetunji AI, Olaniran AO (2020) Statistical modeling and optimization of protease production by an autochtonous Bacillus aryabhattai Ab15-ES: a response surface methodology approach. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 24:101528
Puri S, Beg QK, Gupta R (2002) Optimization of alkaline protease production from Bacillus sp. by response surface methodology. Curr Microbiol 44:286–290
Bas D, Boyaci IH (2007) Modeling and optimization I: usability of response surface methodology. J Food Eng 78(3):836–845
Papagora C, Roukas T, Kotzekidou P (2013) Optimization of extracellular lipase production by Debaryomyces hansenii isolates from dry-salted olives using response surface methodology. Food Bioprod Process 91(4):413–420
Yang F, Long L, Sun X, Wu H, Li T, Xiang W (2014) Optimization of medium using response surface methodology for lipid production by Scenedesmus sp. Mar Drugs 12(3):1245–1257
Rathi P, Goswami VK, Sahai V, Gupta R (2002) Statistical medium optimization and production of a hyperthermostable lipase from Burkholderia cepacia in a bioreactor. J Appl Microbiol 93(6):930–936
Khoramnia A, Lai OM, Ebrahimpour A, Tanduba CJ, Voon TS, Mukhlis S (2010) Thermostable lipase from a newly isolated Staphylococcus xylosus strain; process optimization and characterization using RSM and ANN. Electron J Biotechnol 13(5):15–16
Samaei-Nouroozi A, Rezaei S, Khoshnevis N, Doosti M, Hajihoseini R, Khoshayand MR, Faramarzi MA (2015) Medium-based optimization of an organic solvent-tolerant extracellular lipase from the isolated halophilic Alkalibacillus salilacus. Extremophiles 19(5):933–947
Kai W, Peisheng Y (2016) Optimization of lipase production from a novel strain Thalassospira permensis M35-15 using response surface methodology. Bioengineered 7(5):298–303
Ruchi G, Anshu G, Khare SK (2008) Lipase from solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain: production optimization by response surface methodology and application. Bioresour Technol 99(11):4796–4802
Jia J, Yang X, Wu Z, Zhang Q, Lin Z, Guo H, Lin CSK, Wang J, Wang Y (2015) Optimization of fermentation medium for extracellular lipase production from Aspergillus niger using response surface methodology. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–8
Kanmani P, Karthik S, Aravind J, Kumaresan K (2013) The use of response surface methodology as a statistical tool for media optimization in lipase production from the dairy effluent isolate Fusarium solani. ISRN Biotechnol 2013:1–8
Facchini FDA, Vici AC, Pereira MG, Jorge JA, Polizeli MLTM (2015) Enhanced lipase production of Fusarium verticillioides by using response surface methodology and wastewater pretreatment application. J Biochem Technol 6(3):996–1002
Rajendran A, Thangavelu V (2007) Optimization of medium composition for lipase production by Candida rugosa NCIM 3462 using response surface methodology. Can J Microbiol 53(5):643–655
de Menezes LHS, Carneiro LL, Tavares IMC, Santos PH, das Chagas TP, Mendes AA, da Silva EGP, Franco M, de Oliveira JR (2020) Artificial neural network hybridized with genetic algorithm for optimization of lipase production from Penicillium roqueforti ATCC 10110 in solid-state fermentation. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101885, 31, 101885.
Saxena R, Singh R (2010) Statistical optimization of conditions for protease production from Bacillus sp. Acta Biol Szeged 54:135–141
Singh V, Haque S, Niwas R, Srivastava A, Pasupuleti M, Tripathi CKM (2017) Strategies for fermentation medium optimization: an in-depth review. Front Microbiol 7:2087
Adinarayana K, Ellaiah P (2002) Response surface optimization of the critical medium components for the production of alkaline protease by a newly isolated Bacillus sp. J. Pharm Pharm Sci 5:272–278
Singh V, Tripathi C (2008) Production and statistical optimization of a novel olivanic acid by Streptomyces olivaceus MTCC 6820. Process Biochem 43:1313–1317
Rajeswari P, Arul JP, Amiya R, Jebakumar SRD (2014) Characterization of saltern based Streptomyces sp. and statistical media optimization for its improved antibacterial activity. Front Microbiol 5:753
Mehta A, Sharma R, Gupta R (2019) Statistical optimization by response surface methodology to enhance lipase production by Aspergillus fumigatus. Open Microbiol J 13:86–93
Oskouie SFG, Tabandeh F, Yakhchali B, Eftekhar F (2008) Response surface optimization of medium composition for alkaline protease production by Bacillus clausii. Biochem Eng J 39:37–42
Queiroga AC, Pintado ME, Malcata FX (2012) Use of response surface methodology to optimize protease synthesis by a novel strain of Bacillus sp. isolated from Portuguese sheep wool. J Appl Microbiol 113:36–43
Shabbiri K, Adnan A, Jamil S, Ahmad W, Noor B, Rafique HM (2012) Medium optimization of protease production by Brevibacterium lihens DSM 20158 using statistical approach. Braz J Microbiol 2012:1051–1061
Li Y, Liu Z, Cui F, Liu Z, Zhao H (2007) Application of Plackett-Burman design and Doehlert design to evaluate nutritional requirements for xylanase production by Alternaria mali ND-16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:285–291
Priyanka P, Tan Y, Kinsella GK, Henehan GT, Ryan BJ (2019) Solvent stable microbial lipases: current understanding and biotechnological applications. Biotechnol Lett 41(2):203–220
Wang Y, Ma R, Li S (2018) An alkaline and surfactant-tolerant lipase from Trichoderma lentiforme ACCC30425 with high application potential in the detergent industry. AMB Express 8:95
Hasan F, Shah AA, Javed S, Hameed A (2010) Enzymes used in detergents: lipases. Afr J Biotechnol 9(31):4836–4844
Bacha AB, Al-Assaf A, Moubayed NM, Abid I (2018) Evaluation of a novel thermo-alkaline Staphylococcus aureus lipase for application in detergent formulations. Saud J Biol Sci 25(3):409–417
Devi R, Nampoothiri KM, Sukumaran RK, Sindhu R, Arumugam M (2019) Lipase of Pseudomas guariconesis as an additive in laundry detergents and transesterification biocatalysts. J Basic Microbiol 60:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201900326
Andualema B, Gessesse A (2012) Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: review. Biotechnol 11:100–118
Gupta R, Rathi P, Bradoo S (2003) Lipase mediated upgradation of dietary fats and oils. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 43(6):635–644
Raveedran S, Parameswaran B, Ummalyma SB, Abraham A, Mathew AK, Madhavan A, Rebello S, Pandey A (2018) Applications of microbial enzymes in food industry. Food Technol Biotechnol 56(1):16–30
Kazlauskas RJ, Bornscheur UT (1998) Biotransformations with lipases. In: Rehm HJ, Pihler G, Stadler A, Kelly PJW (eds) Biotechnology. VCH, New York, pp 37–192
Guerrand D (2017) Lipases industrial applications: focus on food and agroindustries. OCL 24(4):D403
Ansorge-Schumacher MB, Thum O (2013) Immobilized lipases in cosmetics industry. Chem Soc Rev 42(15):6475–6490
Lehtinen T, Efimova E, Santala S, Santala V (2018) Improved fatty aldehyde and wax ester production by overexpression of fatty acyl-CoA reductases. Microb Cell Factories 17(1):19
Zasada M, Budzisz E (2019) Retinoids: active molecules influencing skin structure formation in cosmetic and dermatological treatments. Adv Dermatol Allergol 36(4):392–397
Jaeger KE, Reetz MT (1998) Microbial lipases from versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 16(9):396–403
Fakuda S, Hayashi S, Ochiai H, Iiizumi T, Nakamura K (1990) Improvers for deinking of wastepaper. Japanese Patent 2:229–290
Bajpai P (1999) Application of enzymes in paper and pulp industry. Biotechnol Prog 15(2):147–157
Demuner BJ, Pereira JN, Antunes A (2011) Technology prospecting on enzymes for the pulp and paper industry.J. Technol Manag Innov 6(3):148–158
Adetunji AI, Olaniran AO (2018b) Treatment of lipid-rich wastewater using a mixture of free or immobilized bioemulsifier and hydrolytic enzymes from indigenous bacterial isolates. Desalin Water Treat 132:274–280
Ferreira-Leitão VS, Cammarota MS, Aguieiras ECG, Vasconcelos de Sá LR, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Freire DMG (2017) The protagonism of biocatalysis in green chemistry and its environmental benefits. Catalysts 7(1):9
Kanmani P, Kumaresan K, Aravind J (2015b) Pretreatment of coconut mill effluent using celite-immobilized hydrolytic enzyme preparation from Staphylococcus pasteuri and its impact in anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol Prog 31:1249–1258
Rosa DR, Cammarota MC, Freire DMG (2006) Production and utilization of a novel solid enzymatic preparation produced by Penicillium restrictum in activated sludge systems treating wastewater with high levels of oil and grease. Environ Eng Sci 23(5):814–823
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the National Research Foundation (NRF) of South Africa toward this research is hereby acknowledged. Opinions expressed and conclusions arrived at are those of the authors and are not necessarily to be attributed to the NRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AIA conceived and drafted the manuscript while AOO edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Adalberto Pessoa
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adetunji, A.I., Olaniran, A.O. Production strategies and biotechnological relevance of microbial lipases: a review. Braz J Microbiol 52, 1257–1269 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00503-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00503-5