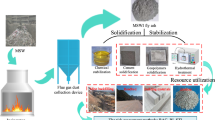
Abstract
Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash (FA) is classified as hazardous waste, which requires additional treatment before disposal or further utilization. Stabilization/solidification (S/S) is regarded as a low-cost and high-efficient method for MSWI FA treatment. “Low-carbon S/S” has captured extensive interest in recent years, which could treat hazardous wastes and enable resource recycling in a sustainable way. This article introduced the state-of-art low-carbon S/S strategies for MSWI FA treatment. The immobilization mechanisms of pollutants in various matrices were also discussed. Prospects were raised to foster the actualization of sustainable management of MSWI FA.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 April 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-023-00149-z
References
Abbà, A., Collivignarelli, M.C., and Sorlini, S. 2014. On the reliability of reusing bottom ash from municipal solid waste incineration as aggregate in concrete. Composites Part B: Engineering 58: 502–509.
National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2019. China statistical yearbook 2019, China Statistics Press, Beijing, China.
Funari, V., Braga, R., Bokhari, S.N.H., et al. 2015. Solid residues from Italian municipal solid waste incinerators: A source for “critical” raw materials. Waste Management 45: 206–216.
Huang, T., Liu, L., Zhou, L., et al. 2018. Operating optimization for the heavy metal removal from the municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes in the three-dimensional electrokinetics. Chemosphere 204: 294–302.
Xue, Y., and Liu, X. 2021. Detoxification, solidification and recycling of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal 420: 130349.
Lan, T., Meng, Y., Ju, T., et al. 2022. Synthesis and application of geopolymers from municipal waste incineration fly ash (MSWI FA) as raw ingredient - a review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 182: 106308.
Cristelo, N., Segadães, L., Coelho, J., et al. 2020. Recycling municipal solid waste incineration slag and fly ash as precursors in low-range alkaline cements. Waste Management 104: 60–73.
Pan, Y., Yang, L., Zhou, J., et al. 2013. Characteristics of dioxins content in fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere 92: 765–771.
Chen, Q.Y., Tyrer, M., Hills, C.D., et al. 2009. Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilisation: A review. Waste Management 29: 390–403.
Chen, L., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., et al. 2022. Roles of biochar in cement-based stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Chemical Engineering Journal 430: 132972.
Sun, J., Wang, L., Yu, J., et al. 2022. Cytotoxicity of stabilized/solidified municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials 424: 127369.
Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Chen, L., et al. 2021. Treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: State-of-the-art technologies and future perspectives. Journal of Hazardous Materials 411: 125132.
Chavda, M.A., Bernal, S.A., Apperley, D.C., et al. 2015. Identification of the hydrate gel phases present in phosphate-modified calcium aluminate binders. Cement and Concrete Research 70: 21–28.
Fan, C., Wang, B., and Zhang, T. 2018. Review on cement stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2018: 5120649.
Olsson, S., van Schaik, J.W.J., Gustafsson, J.P., et al. 2007. Copper(II) binding to dissolved organic matter fractions in municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash leachate. Environmental Science & Technology 41: 4286–4291.
Verhulst, D., Buekens, A., Spencer, P.J., et al. 1996. Thermodynamic behavior of metal chlorides and sulfates under the conditions of incineration furnaces. Environmental Science & Technology 30: 50–56.
Li, Q., Meng, A., Jia, J., et al. 2010. Investigation of heavy metal partitioning influenced by flue gas moisture and chlorine content during waste incineration. Journal of Environmental Sciences 22: 760–768.
Xia, Y., He, P., Shao, L., et al. 2017. Metal distribution characteristic of MSWI bottom ash in view of metal recovery. Journal of Environmental Sciences 52: 178–189.
Yao, Q., Samad, N.B., Keller, B., et al. 2014. Mobility of heavy metals and rare earth elements in incineration bottom ash through particle size reduction. Chemical Engineering Science 118: 214–220.
Luo, H., Wu, Y., Zhao, A., et al. 2017. Hydrothermally synthesized porous materials from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash and their interfacial interactions with chloroaromatic compounds. Journal of Cleaner Production 162: 411–419.
Trauchessec, R., Mechling, J.M., Lecomte, A., et al. 2015. Hydration of ordinary Portland cement and calcium sulfoaluminate cement blends. Cement and Concrete Composites 56: 106–114.
Shi, H.-S., and Kan, L.-L. 2009. Characteristics of municipal solid wastes incineration (MSWI) fly ash–cement matrices and effect of mineral admixtures on composite system. Construction and Building Materials 23: 2160–2166.
Zhang, Y., Cetin, B., Likos, W.J., et al. 2016. Impacts of pH on leaching potential of elements from MSW incineration fly ash. Fuel 184: 815–825.
Dermatas, D., and Meng, X. 2003. Utilization of fly ash for stabilization/solidification of heavy metal contaminated soils. Engineering Geology 70: 377–394.
Du, B., Li, J., Fang, W., et al. 2018. Characterization of naturally aged cement-solidified MSWI fly ash. Waste Management 80: 101–111.
Contessi, S., Calgaro, L., Dalconi, M.C., et al. 2020. Stabilization of lead contaminated soil with traditional and alternative binders. Journal of Hazardous Materials 382: 120990.
López-Zaldívar, O., Lozano-Díez, R.V., Verdú-Vázquez, A., et al. 2017. Effects of the addition of inertized MSW fly ash on calcium aluminate cement mortars. Construction and Building Materials 157: 1106–1116.
Kinoshita, H., Swift, P., Utton, C., et al. 2013. Corrosion of aluminium metal in OPC- and CAC-based cement matrices. Cement and Concrete Research 50: 11–18.
Chen, L., Wang, L., Cho, D.-W., et al. 2019. Sustainable stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by incorporation of green materials. Journal of Cleaner Production 222: 335–343.
Chen, L., Wang, Y.-S., Wang, L., et al. 2021. Stabilisation/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by phosphate-enhanced calcium aluminate cement. Journal of Hazardous Materials 408: 124404.
Walling, S.A., and Provis, J.L. 2016. Magnesia-based cements: A journey of 150 years, and cements for the future? Chemical Reviews 116: 4170–4204.
Ruan, S., Liang, S., Kastiukas, G., et al. 2020. Solidification of waste excavation clay using reactive magnesia, quicklime, sodium carbonate and early-age oven curing. Construction and Building Materials 258: 120333.
Kastiukas, G., Ruan, S., Unluer, C., et al. 2019. Environmental assessment of magnesium oxychloride cement samples: A case study in Europe. Sustainability 11: 6957.
Wang, B., and Fan, C. 2020. Hydration behavior and immobilization mechanism of MgO–SiO2–H2O cementitious system blended with MSWI fly ash. Chemosphere 250: 126269.
Tansel, B., Lunn, G., and Monje, O. 2018. Struvite formation and decomposition characteristics for ammonia and phosphorus recovery: A review of magnesium-ammonia-phosphate interactions. Chemosphere 194: 504–514.
Xie, Y., Lin, X., Pan, X., et al. 2020. Preliminary investigation of the hydration mechanism of MgO-SiO2-K2HPO4 cement. Construction and Building Materials 235: 117471.
Zhang, Q., Cao, X., Ma, R., et al. 2021. Solid waste-based magnesium phosphate cements: Preparation, performance and solidification/stabilization mechanism. Construction and Building Materials 297: 123761.
Wang, L., Chen, L., Guo, B., et al. 2020. Red mud-enhanced magnesium phosphate cement for remediation of Pb and As contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials 400: 123317.
Su, Y., Yang, J., Liu, D., et al. 2016. Effects of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash on solidification/stabilization of Cd and Pb by magnesium potassium phosphate cement, Journal of Environmental. Chemical Engineering 4: 259–265.
Wang, Y.S., Dai, J.G., Wang, L., et al. 2018. Influence of lead on stabilization/solidification by ordinary Portland cement and magnesium phosphate cement. Chemosphere 190: 90–96.
Liu, J., Jin, H., Gu, C., et al. 2019. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on early-age hydration and the mechanical properties of cement paste. Construction and Building Materials 217: 352–362.
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., et al. 2022. Designing novel magnesium oxysulfate cement for stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials 423: 127025.
Shi, C., Qu, B., and Provis, J.L. 2019. Recent progress in low-carbon binders. Cement and Concrete Research 122: 227–250.
Kiventerä, J., Lancellotti, I., Catauro, M., et al. 2018. Alkali activation as new option for gold mine tailings inertization. Journal of Cleaner Production 187: 76–84.
Chartier, D., Muzeau, B., Stefan, L., et al. 2017. Magnesium alloys and graphite wastes encapsulated in cementitious materials: Reduction of galvanic corrosion using alkali hydroxide activated blast furnace slag. Journal of Hazardous Materials 326: 197–210.
Wang, L., Yu, K., Li, J.-S., et al. 2018. Low-carbon and low-alkalinity stabilization/solidification of high-Pb contaminated soil. Chemical Engineering Journal 351: 418–427.
Wang, L., Cho, D.-W., Tsang, D.C.W., et al. 2019. Green remediation of As and Pb contaminated soil using cement-free clay-based stabilization/solidification. Environment International 126: 336–345.
Galiano, Y., Luna, C., Pereira, F., et al. 2011. Stabilization/solidification of a municipal solid waste incineration residue using fly ash-based geopolymers. Journal of hazardous materials 185 (1): 373–381.
Cocke, D., Mollah, M., Hess, T. et al. 2010. Advanced concepts in cement solidification and stabilization technology, In: Advances in Cement and Concrete. ASCE, Reston, VA, USA, pp. 614–615.
Paria, S., and Yuet, P.K. 2006. Solidification–stabilization of organic and inorganic contaminants using portland cement: a literature review. Environmental review 14: 217–255.
Coleman, N.J., Li, Q., and Raza, A. 2014. Synthesis, structure and performance of calcium silicate ion exchangers from recycled container glass. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing 50(1): 5–16.
Gougar, M.L.D., Scheetz, B.E., and Roy, D.M. 1996. Ettringite and C-S-H Portland cement phases for waste ion immobilization: A review. Waste Management 16: 295–303.
Diet, J.N., Moszkowicz, P., and Sorrentino, D. 1998. Behaviour of ordinary Portland cement during the stabilization/solidification of synthetic heavy metal sludge: Macroscopic and microscopic aspects. Waste Management 18: 17–24.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Clean Energy Utilization, Zhejiang University (No. ZJUCEU2022001) for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jianhua Yan is the Editor-in-Chief of Waste Disposal & Sustainable Energy, Qunxing Huang is the Editorial Board member of Waste Disposal & Sustainable Energy. The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised to correct the Conflict of Interest section.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Wang, L., Lin, X. et al. Low-carbon stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 4, 69–74 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-022-00102-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-022-00102-6