Abstract
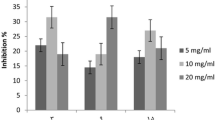
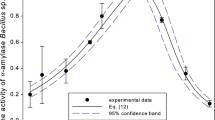
Chilo partellus is a serious pest of agricultural crops. The present investigation was carried out to characterize the gut α-amylase from C. partellus and to explore its inhibition kinetics with various α-amylase inhibitors. α-amylase eluted at ve/vo of 1.38–1.48 on sephadex G-100 column chromatography with 15.58 folds purification. It had a single isoform of 65 KDa with an optimum pH of 8.0. It was thermally stable up to 50 °C and showed the highest activity with starch. A critical analysis of Lineweaver–Burk plot showed that the Michaelis constant, Km, of α-amylase for starch was 0.32 mg/ml while Vmax was observed to be 1.47 nmoles of reducing sugars formed/min/ml of enzyme. Among the various chemicals studied, citric acid, salicylic acid, oxalic acid, zinc chloride and calcium nitrate were found to be the potent inhibitors of α-amylase activity. Through a concerted study of the primary and secondary plots of Lineweaver–Burk, fractional velocity and combination plots, it was revealed that citric acid, salicylic acid, oxalic acid, zinc chloride and calcium nitrate caused complete inhibition of α-amylase activity by mixed- non-competitive-uncompetitive mode.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Aghajari N, Feller G, Gerday C, Haser R (2002) Structural basis of α-amylase activation by chloride. Prot Sci 11:1435–1441
Asadi A, Ghadamyari M, Sajedi RH, Sendi JJ, Tabari M (2010) Biochemical characterization of midgut, salivary glands and haemolymph α-amylases of Naranga aenescens. Bull Insectology 63:175–181
Bamaiyi LJ, Joan MI (2011) Management of stem borers on same quality protein maize varieties. J Agric Sci 56:197–205
Bode W, Huber R (2000) Structural basis of the endoproteinase protein inhibitor interaction. Biochem Biophys Acta 1477:241–252
Boyd JRDW (2002) Digestive enzymes and stylet morphology of Deraeocoriss nigritulus (Uhler) (Hemiptera: Miridae) reflect adaptations for predatory habits. Ann Entomol Soc America 96:667–671
Chan WWC (1995) Combination plots as graphical tools in the study of enzyme inhibition. Biochem J 311:981–985
Chapman RF (2013) The Insects: Structure and Function. Cambridge University Press
Da Lage JL, Danchin EGJ, Casane D (2007) Where do animal α-amylases come from? An inter kingdom trip. FEBS Lett 581:3927–3935
Dejen A, Getu E, Azerefegne F, Ayalew A (2014) Distribution and impact of Busseola fusca (Fuller) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Chilo partellus (Swinhoe) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in northeastern Ethiopia. J Entomol Nematol 6:1–13
Giri AP, Kachole MV (1998) Amylase inhibitors of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) seeds. Phytochem 49:197–202
Guofa Z, Overholt WA, Mochiah MB (2001) Changes in the distribution of lepidopteran maize stemborers in Kenya from the 1950s to 1990s. Int J Trop Insect Sci 21:395–402
Jakovljevic D, Vrvic MM, Radulovic M, Hranisavljevic-Jakovljevic M (2001) Fine structural analysis of the fungal polysaccharide pullulan elaborated by Aureobasidium pullulans, CH-1 strain. J Serbian Chem Soc 66:377–383
Kaur R, Gupta AK, Taggar GK (2015) Characterization and inhibition studies of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) gut α-amylase. Pest Manag Sci 71:1228–1237
Kfir R, Overholt WA, Khan ZR, Polaszek A (2002) Biology and management of economically important lepidopteran cereal stem borers in Africa. Ann Rev Entomol 47:701–731
Kotkar HM, Sarate PJ, Tamhane VA, Gupta VS, Giri AP (2009) Responses of midgut amylases of Helicoverpa armigera to feeding on various host plants. J Insect Physiol 55:663–670
Laidler KJ, Bunting PS (1973) The Chemical Kinetics of Enzyme Action. Clarendon Press
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mailafiya DM, Le-Ru BP, Kairu EW, Calatayud PA, Dupas S (2009) Species diversity of lepidopteran stem borer parasitoids in cultivated and natural habitats in Kenya. J Appl Entomol 133:416–429
Mehrabadi M, Bandani AR, Kwon O (2011) Biochemical characterization of digestive α-D glucosidase and β-D-glucosidase from labial glands and midgut of wheat bug Eurygaster Maura (Hemiptera: Scutelleridae). Entomol Res 41:81–87
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Paquet V, Croux C, Goma G, Soucaille P (1991) Purification and characterization of the extracellular alpha-amylase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:212–218
Pascual-Ruizy S, Carrillo L, Alfageme A, Ruiz M, Castanera P, Ortego F (2009) The effects of different prey regimes on the proteolytic digestion of nymphs of the spined soldier bug, Podisus maculiventris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Bull Entomol Res 99:487–491
Priya S, Kaur N, Gupta AK (2010) Purification, characterization and inhibition studies of α-amylase of Rhyzopertha dominica. Pestic Biochem Physiol 98:231–237
Ravan S, Mehrabadi M, Bandani AR (2009) Biochemical characterization of digestive amylase of wheat bug, Eurygaster maura (Hemiptera: Scutelleridae). Afr J Biotechnol 8:3640–3648
Segel H (1973) Enzyme Kinetics. John Wiley and Sons, New York and London, pp 100–226
Sharifloo A, Zibaee A, Sendi JJ, Jahroumi KT (2016) Characterization of a digestive α-amylase in the midgut of Pieris brassicae L. (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). Front Physiol 7:96
Sharma P, Nain V, Lakhanpaul S, Kumar PA (2011) Binding of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 A toxins with brush border membrane vesicles of maize stem borer (C. partellus Swinehoe). J Invert Pathol 106:333–335
Singh K, Kayastha AM (2014) α-Amylase from wheat (Triticum aestivum) seeds: Its purification, biochemical attributes and active site studies. Food Chem 162:1–9
Singh R, Channappa RK, Deeba F, Nagaraj NJ, Sukavaneasswaran MK, Manjunath TM (2005) Tolerance of Bt Corn (MON810) to Maize stem borer C. partellus (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Plant Cell Rep 24:556–560
Sivakumar S, Mohan M, Franco OL, Thayumanavan B (2006) Inhibition of insect pest α-amylases by little and finger millet inhibitors. Pestic Biochem Physiol 85:155–160
Sorkhabi-Abdolmaleki S, Zibaee A, Hoda H, Fazeli-Dinan M (2014) Purification and characterization of midgut α-amylase in a predatory bug, Andralus spinidens. J Insect Sci 14:1–13
Terra WR, Ferreira C (1994) Insect digestive enzymes: Properties, compartmentalization and function. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Comp Biochem 109:1–62
Terra WR, Ferreira C (2005) 'Biochemistry of digestion' in comprehensive molecular insect science. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K and Gill SS (eds) Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, vol 4. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam, pp 171–224
Trevelyan WE, Procter DP, Harrison JS (1950) Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nat 166:444–445
Xu W, Huang Q, Wu X, Yu X, Wang X, Tao L (2014) Property of Midgut α-Amylase From Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and Its Responses to Potential Inhibitors In Vitro. J Insect Sci 14:1–5
Yonow T, Kriticos DJ, Ota N, Berg JVD, Hutchison WD (2017) The potential global distribution of Chilo partellus, including consideration of irrigation and cropping patterns. J Pest Sci 90:459–477
Yoshino M (1987) A graphical method for determining inhibition parameters for partial and complete inhibitors. Biochem J 248:815–820
Zibaee A (2012) Digestive enzymes of large cabbage white butterfly, Pieris brassicae L. (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) from developmental and site of activity perspectives. Itallian J Zool 79:13–26
Zibaee A, Bandani AR, Kafil M, Ramzi S (2008) Characterization of α-amylase in the midgut and the salivary glands of rice striped stemborer, C. suppressalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Asia-Pacific Entomol 11:201–205
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by Rajiv Gandhi National Fellowship from University Grant Commission, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, S., Kaur, K., Jindal, J. et al. Characterization and inhibition kinetics of gut α-amylase from Chilo partellus through Lineweaver- Burk, fractional velocity and combination plots. Int J Trop Insect Sci 43, 1987–2000 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01101-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01101-8