Abstract
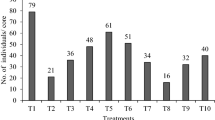
Assessment of the potential effects of insecticides on the natural enemies is an important part of IPM. The use of natural enemies in combination with selected insecticides which have no effect on them is effective in depressing the population density of the insect pest. In this context, an effort was made to know the diversity of predatory fauna and effect of seed dressers, soil applied chemicals and foliar spraying insecticides on their abundance in wheat during rabi, 2019–20. The investigation registered the activity of green lacewing (Chrysoperla zastrowi sillemi), coccinellids (Coccinella transversalis, Cheilomenes sexmaculata, Illeis cincta), syrphid (Ischiodon scutellaris) and spider (Oxyopes lineatus). Meanwhile, the results also revealed the peak activity of green lacewing, coccinellids, syrphids and spiders in seed treatment with thiamethoxam 30 FS @ 5 ml/kg seeds (1.20, 1.40, 0.73 and 0.67 per meter square area, respectively) followed by soil application of carbofuran 3G @ 30 kg/ha (1.17, 1.37, 0.70 and 0.62 per meter square, respectively) and both were found on par with untreated check (1.39, 1.51, 0.81 and 0.78 per meter square, respectively). Whereas, the least population was recorded in soil application of carbofuran 3G @ 30 kg/ha followed by a foliar application of cypermethrin 10 EC @ 0.5 ml/l (0.22, 0.24, 0.14 and 0.12 per meter square, respectively) over rest of the treatments. These results endorsed the biocompatibility of seed dressers (Thiamethoxam 30 FS), soil applied chemicals (Carbofuran 3G) and detrimental effects of foliar spraying insecticides (Cypermethrin 10 EC, Emamectin benzoate 5SG and Nimbecidine 1500 ppm) on population dynamics of natural enemy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated during this study are included in this manuscript and available with corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahire RV (2008) Evaluation of newer insecticide thiamethoxam as seed dresser for the management of early season pests in soybean. Doctoral dissertation, Vasantrao Naik Krishi Vidyapeeth, Parbhani
Anita VS (2009) Non-chemical approaches for the management of shoot fly Atherigona soccata Rondani in kharif sorghum. Dissertation, University of Agricultural Sciences Dharwad, Karnataka, India
Anonymous (2013) Hundred years wheat research in India. Directorate of Wheat Research, Karnal, India, pp. 171–172
Anonymous (2014) Satyagopal K, SN Sushil, P Jeyakumar, G Shankar, OP Sharma, SK Sain, DR Boina, D Chattopadhyay, N Srinivasa Rao, BS Sunanda, Ram Asre, R Murali, KS Kapoor, Sanjay Arya, Subhash Kumar, CS Patni, Indu Sharma, H Ravindra, BK Shivanna, MS Saharan, Damanjit Kaur, Beant Singh, RK Sharma, RS Chokar, AK Karnatak, Ruchira Tiwari, Deepshikha, BR Patel, Surajit Khalko, Nripendra Laskar, Ayon Roy, Tapan Kumar Hath, LV Ghetiya, N Sathyanarayana, S Latha (2014) AESA based IPM package for Wheat. pp 58. https://farmer.gov.in/imagedefault/ipm/wheat.pdf
Balasaheb BA (2014) Bio efficacy of different insecticides against sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rondani in Rabi season. Dissertation, MPKV, Rahuri, Maharashtra, India
Biradar A (2015) Management of shoot fly (Atherigona soccata Rondani) in Rabi sorghum. Dissertation, University of Agricultural Sciences Dharwad, Karnataka, India
Brown GW, Bifulco A, Veiel HOF, Andrews B (1990) Self-esteem and depression. Social Psych Psych Epidem 25(5):225–234
Croft BA, Whalon ME (1982) Selective toxicity of pyrethroid insecticides to arthropod natural enemies and pests of agricultural crops. Entomophaga 27(1):3–21
Dinter A (1995) Untersuchungen zur Populationsdynamik von Spinnen (Arachnida: Araneae) in Winterweizen und deren Beeinflussung durch insektizide Wirkstoffe [dissertation]. [Göttingen]: Cuvillier Publisher, Goettingen Universität. ISBN 3–89588–171–6 Cuvillier Verlag Göttingen 383 p
Duffield SJ, Aebischer NJ (1994) The effect of spatial scale of treatment with dimethoate on invertebrate population recovery in winter wheat. J Appl Ecol 31:263–281
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11(1):1–42
Duveiller E, Ravi P, Singh E, Julie MN (2007) The challenges of maintain wheat productivity: pests, disease and potential epidemics. Euphytica 157:417–430
El-Wakeil NE, Gaafar N, Vidal S (2006) Side effect of some Neem products on natural enemies of Helicoverpa, Trichogramma spp. and Chrysoperla carnea. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 39:445–455
El-Wakeil N, Gaafar N, Sallam A, Volkmar C (2013) Side effects of insecticides on natural enemies and possibility of their integration in plant protection strategies. Insecticides: Development of Safer and More Effective Technologies Agricultural and Biological Sciences (S. Trdan, ed.). InTech Open Access Publisher, 1–56
El-Wakeil N, Volkmar C (2013) Monitoring of wheat insects and their natural enemies using sticky traps in wheat. Arch Phytopathol Pflanzenschutz 46(13):1523–1532
Freier B, Triltsch H, Möwes M, Moll E (2007) The potential of predators in natural control of aphids in wheat: Results of a ten-year field study in two German landscapes. Biocontrol 52:775–788
Hassan SA, Albert R, Bigler F, Blaisinger P, Bogenschütz H, Boller E, Vanwetswinkel G (1987) Results of the third joint pesticide testing programme by the IOBC/WPRS-Working Group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms.” J Appl Entomol 103(1–5):92–107
Holland JM, Winder L, Perry JN (2000) The impact of dimethoate on the spatial distribution of beneficial arthropods in winter wheat. Ann Appl Biol 136(2):93–105
Jambagi SR (2020) Status and management of shoot fly in wheat. Dissertation, University of Agricultural Sciences Dharwad, Karnataka, India
Jambagi SR, Kambrekar DN, Mallapur CP, Naik VR (2021) Status of shoot fly (Atherigona spp.) incidence in wheat in major wheat growing districts of North Karnataka. J Pharm Innov. SP-10 (11):2032–2035
Jambagi SR, Kambrekar DN, Mallapur CP, Naik VR (2022) Morphological traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) associated with resistance to shoot fly, Atherigona approximata Malloch. J Asia-Pacific Entomol 25(4):101990
Jambagi SR, Kambrekar DN, Mallapur CP, Naik VR (2023) Novel insecticides for the management of shoot fly, Atherigona approximata Malloch (Diptera: Muscidae): an emerging insect pest of wheat in India. Int J Trop Ins Sci 1–10
Kaethner M (1991) No side effects of neem on the aphidophagous predators Chrysoperla carnea and Coccinella septempunctata. Anz Schädlngskde Planzenschutz Umweltschutz 64:97–99
Katole SR, Patil PJ (2000) Biosafety of imidacloprid and thiamethoxam as seed treatment and foliar sprays to some predators. Pestology 24(11):11–13
Malschi D (2008) Environment, agriculture, sustainable development. Optimization of integrated wheat pest management technologies under the dynamics of agroecological changes in Transylvania. Ed. Argonaut, Cluj-Napoca, 250
Meena BL, Dadhich SR, Kumawat RL (2002) Efficacy of some insecticides against ladybird beetle, Coccinella septumpunctata L. feeding on fenugreek aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris.). Ann Biol 18:171–173
Pimentel D (1997) Techniques for reducing pesticide use: economic and environmental benefits. John Wiley and Sons
Ranjith M, Bajya DR, Manoharan T, Ramya RS (2018) Biodiversity of insect pests and natural enemies affiliated with wheat (Triticum aestivum) ecosystem in Haryana. Indian J Agril Sci 88(1):157–158
Prakash KS (2014) Efficacy of different seed dressers on sorghum shoot fly Atherigona soccata (Rondani). Dissertation, University of Agricultural Sciences Dharwad, Karnataka, India
Schmidt MH, Thewes U, Thies C, Tscharntke T (2004) Aphid suppression by natural enemies in mulched cereals. Entomol Experiment Et Applicata 113(2):87–93
Schmutterer H (1997) Side effects of neem (Azadirachta indica) products on insect pathogens and natural enemies of spider mites and insects. J Appl Entomol 121:121–128
Smith TM, Stratton GW (1986) Effects of synthetic pyrethroid insecticides on non-target organisms. Residue Rev 97:93–120
Solangi BK, Lanjar AG, Lohar MK (2007) Comparative toxicity of some insecticides on 4th instar grub of Coccinella septempunctata L. under laboratory conditions. Sarhad J Agric 23:1091–1096
Srinivasan G, Babu PCS (2000) Effect of neem products on predatory green lacewing, Chrysoperla carnea. Pest Res J 12:123–126
Swaran D (1999) Effect of some important insecticides on the adults of Coccinella septempunctata L. Predating on different aphid species. J Entomol Res 23:127–131
Thomas CFG, Hol EHA, Everts JW (1990) Modelling the diffusion component of dispersal during recovery of a population of linyphiid spiders from exposure to an insecticide. Func Ecolo 4:357–368
Way MJ, Heong KL (1994) The role of biodiversity in the dynamics and management of insect pests of tropical irrigated rice—a review. Bull Entomol Res 84(4):567–587
Wiles JA, Jepson PC (1994) Sub-lethal effects of deltamethrin residues on the within-crop behaviour and distribution of Coccinella septempunctata. Entomol Exp Appl 72:33–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors were contributed to the study where, first author was Post Graduate student who conducted the experiment while, second author was advisory committee chairman and rest of the two authors were the members of advisory committee of the student and actively involved in analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jambagi, S.R., Kambrekar, D.N., Mallapur, C.P. et al. Insecticide compatibility with abundance and diversity of predatory fauna in wheat (Triticum aestivum) ecosystem. Int J Trop Insect Sci 43, 1749–1755 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01088-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01088-2