Abstract
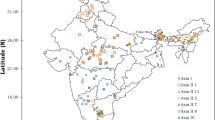
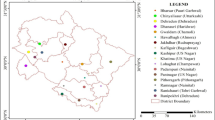
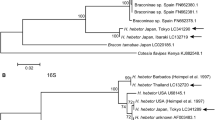
Whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) is a cryptic species complex that infests various plant species and act as a vector for many plant viruses all over the world. To understand the B. tabaci cryptic species diversity in Bihar more comprehensively, interhost and interlocation surveys were conducted during the year 2020-2021. The genetic variability among 29 populations (16 interhost and 13 interlocation) was explored using nuclear markers viz. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD), Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) along with mitochondrial marker, mtCOI. The dissimilarity coefficients of 29 populations clustered in a dendrogram with RAPD and SSR primers showed that interlocation populations were less diverged than the interhost populations. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of 657 bp mtCOI sequences identified the presence of four cryptic species viz. Asia I, Asia II 1, Asia II 7 and China 3 belonging to two genetic groups (Asia and China) with high variations in interhost unlike in interlocation. Among the four cryptic species, Asia I was the most prevalent in Bihar, establishing 86.20% of all the sequenced samples and Asia II 7 and China 3 were reported for the first time in Bihar region. We believe that the information generated in this study is important from the perspective of identifying cryptic species diversity and to develop long term pest management strategies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data relevant to the study are included in the article.
References
Anderson A, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1139/g93-024
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Baig MM, Dubey AK, Ramamurthy VV (2015) Biology and morphology of life stages of three species of whiteflies (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) from India. Pan-Pac Entomol 91:168–183. https://doi.org/10.3956/2015-91.2.168
Ben Abdelkrim A, Hattab T, Fakhfakh H, Belkadhi MS, Gorsane F (2017) A landscape genetic analysis of important agricultural pest species in Tunisia: The whitefly Bemisia tabaci. PLoS One 12:e0185724. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185724
Boykin LM, Shatters RG Jr, Rosell RC, McKenzie CL, Bagnall RA, De Barro P, Frohlich DR (2007) Global relationships of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) revealed using Bayesian analysis of mtCOI DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:1306–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2007.04.020
Calvert LA, Cuervo M, Arroyave JA, Constantino LM, Bellotti A, Frohlich D (2001) Morphological and mitochondrial DNA marker analyses of whiteflies (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) colonizing cassava and beans in Colombia. Ann Entomol Soc Am 94:512–519. https://doi.org/10.1603/0013-8746(2001)094[0512:MAMDMA]2.0.CO;2
Chowda-Reddy RV, Kirankumar M, Seal SE, Muniyappa V, Valand GB, Govindappa MR, Colvin J (2012) Bemisia tabaci phylogenetic groups in India and the relative transmission efficacy of Tomato leaf curl Bangalore virus by an indigenous and an exotic population. J Integr Agric 11:235–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(12)60008-2
Cock MJW (1993) Bemisia tabaci: An update 1986-1992 on the cotton whitefly with an annotated bibliography. International Institute of Biological Control. Ascot, UK
Costa HS, Brown JK, Byrne DN (1991) Life history traits of the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) on six virus-infected or healthy plant species. Environ Entomol 20:1102–1107. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/20.4.1102
De Barro PJ, Driver F (1997) Use of RAPD PCR to distinguish the B biotype from other biotypes of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius)(Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Aust J Entomol 36:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-6055.1997.tb01447.x
De Barro PJ, Scott KD, Graham GC, Lange CL, Schutze MK (2003) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in Bemisia tabaci. Mol Ecol Notes 3:40–43. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2003.00344.x
De Barro PJ, Trueman JWH, Frohlich DR (2005) Bemisia argentifolii is a race of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae): the molecular genetic differentiation of Bemisia tabaci populations around the world. Bull Entomol Res 95:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1079/BER2004351
De Lima TCA, da Silva PF, Oliveira MD, Aires ES, Seabra S Jr, Lima GPP, de Oliveira RC (2021) Change in the physiological and biochemical aspects of tomato caused by infestation by Cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci MED and MEAM1. Insects 12:1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12121105
Dinsdale A, Cook L, Riginos C, Buckley YM, De Barro P (2010) Refined global analysis of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Sternorrhyncha: Aleyrodoidea: Aleyrodidae) mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I to identify species level genetic boundaries. Ann Entomol Soc Am 103:196–208. https://doi.org/10.1603/AN09061
Ellango R, Singh ST, Rana VS, Gayatri PN, Raina H, Chaubey R, Naveen NC, Mahmood R, Ramamurthy VV, Asokan R, Rajagopal R (2015) Distribution of Bemisia tabaci genetic groups in India. Environ Entomol 44:1258–1264. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/nvv062
Fakrudin B, Prakash SH, Krishnareddy KB, Prasad PB, Patil BV, Kuruvinashetti MS (2004) Genetic variation of cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) of South Indian cotton ecosystem using RAPD markers. Curr Sci 87:1654–1657
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Fisher RA (1935) The fiducial argument in statistical inference. Ann Eugen 6:391–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1935.tb02120.x
Frohlich DR, Torres-Jerez I, Bedford ID, Markham PG, Brown JK (1999) A phylogeographical analysis of the Bemisia tabaci species complex based on mitochondrial DNA markers. Mol Ecol 8:1683–1691. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.1999.00754.x
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3784–3788. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg563
Gauthier N, Dalleau-Clouet C, Bouvret ME (2008) Twelve new polymorphic microsatellite loci and PCR multiplexing in the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Mol Ecol Resour 8:1004–1007. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2008.02163.x
Hameed S, Hameed S, Sadia M, Malik SA (2012) Genetic diversity analysis of Bemisia tabaci populations in Pakistan using RAPD markers. Electron J Biotechnol 15:6. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol15-issue6-fulltext-5
Hopkinson J, Pumpa S, van Brunschot S, Fang C, Frese M, Tay WT, Walsh T (2020) Insecticide resistance status of Bemisia tabaci MEAM1 (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in Australian cotton production valleys. Austral Entomol 59:202–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/aen.12436
Kanakala S, Ghanim M (2019) Global genetic diversity and geographical distribution of Bemisia tabaci and its bacterial endosymbionts. PLoS One 14:e0213946. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213946
Kumar M, Mishra GP, Singh R, Kumar J, Naik PK, Singh SB (2009) Correspondence of ISSR and RAPD markers for comparative analysis of genetic diversity among different apricot genotypes from cold arid deserts of trans-Himalayas. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 15:225–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-009-0026-6
Kunz D, Tay WT, Elfekih S, Gordon KHJ, De Barro PJ (2019) Take out the rubbish–removing NUMTs and pseudogenes from the Bemisia tabaci cryptic species mtCOI database. BioRxiv 724765. https://doi.org/10.1101/724765
Lestari SM, Hidayat P, Hidayat SH, Shim JK, Lee KY (2021) Bemisia tabaci in Java, Indonesia: genetic diversity and the relationship with secondary endosymbiotic bacteria. Symbiosis 83:317–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-021-00752-w
Lopes HM, Bastos CS, Boiteux LS, Foresti J, Suinaga FA (2017) A RAPD-PCR-based genetic diversity analysis of Helicoverpa armigera and H. zea populations in Brazil. Genet Mol Res 16:gmr16038757. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr16038757
Lynch M (2008) Estimation of nucleotide diversity, disequilibrium coefficients, and mutation rates from high-coverage genome-sequencing projects. Mol Biol Evol 25:2409–2419. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn185
Maurya RP, Brijwal L, Patwal H, Suyal P (2020) Genetic variability in predatory stink bug Andrallus spinidens (F.) from North-west Himalaya. Indian J Entomol 3:523–527
Misra CS, Lamba KS (1929) The cotton whitefly (Bemisia gossypiperda n.sp.). Bulletin of the Agricultural Research Institute of Pusa, Bihar 196:1–7
Mugerwa H, Seal S, Wang HL, Patel MV, Kabaalu R, Omongo CA, Colvin J (2018) African ancestry of New World, Bemisia tabaci-whitefly species. Sci Rep 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20956-3
Murali P, Hilda K, Ramakrishnan M, Ganesh A, Bhuvaragavan S, Janarthanan S (2021) Molecular genotypic diversity of populations of brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis and development of SCAR marker for pesticide resistance. Mol Biol Rep 48:7787–7800
Perrier X, Flori A, Bonnot F (2003) Data Analysis Methods. Hamon P, Seguin PM, Perrier X, Glaszmann JC, [Eds] Genetic Diversity of Cultivated Tropical Plants. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 43–76
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of Potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051046
Queiroz PR, Lima LH, Sujii ER, Monnerat RG (2017) Description of the molecular profiles of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in different crops and locations in Brazil. J Entomol Nematol 9:36–45. https://doi.org/10.5897/JEN2017.0170
Ramos RS, Kumar L, Shabani F, Picanço MC (2018) Mapping global risk levels of Bemisia tabaci in areas of suitability for open field tomato cultivation under current and future climates. PLoS One 13:e0198925. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198925
Rangaswamy KT, Nagaraju N, Prameela HA, Achari R, Jagadish KS, Govin K, Karkale B, Shankarappa KS, Ramegowda GK, Rathod TS, Babu DR (2019) First report of the invasive MEAM1 whitefly [Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius)], vector of tomato leaf curl viruses in a major tomato-growing region of Maharashtra, India. In: VI International Symposium on Tomato Diseases: Managing Tomato Diseases in the Face of Globalization and Climate Change, pp 113–120. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2021.1316.16
Reddy MSS, Agnihotri M, Jaiswal JP, Subbanna AR, Karthik S (2022) Intra species diversity of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in relation to geography and host plants affiliation in Uttarakhand Himalayan population, India. Phytoparasitica 50:359–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-021-00972-2
Rehman M, Chakraborty P, Tanti B, Mandal B, Ghosh A (2021) Occurrence of a new cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae): an updated record of cryptic diversity in India. Phytoparasitica 49:869–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-021-00909-9
Roopa HK, Asokan R, Rebijith KB, Hande RH, Mahmood R, Kumar NK (2015) Prevalence of a new genetic group, MEAM-K, of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in Florida Entomol Karnataka, India, as evident from mtCOI sequences. Fla Entomol 98:1062–1071
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
Simón B, Cenis JL, La De, Rúa P (2007) Distribution patterns of the Q and B biotypes of Bemisia tabaci in the Mediterranean basin based on microsatellite variation. Entomol Exp Appl 124:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1570-7458.2007.00586.x
Sneath PH, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practice of numerical classification, p 573
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. – Genetics 123:585–595. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/123.3.585
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tay WT, Evans GA, Boykin LM, De Barro PJ (2013) Demonstrating the value of voucher specimens to help resolve modern whitefly taxonomy. In: Abstract 1st International Whitefly Symposium, p 71
Tocko-Marabena BK, Silla S, Simiand C, Zinga I, Legg J, Reynaud B, Delatte H (2017) Genetic diversity of Bemisia tabaci species colonizing cassava in Central African Republic characterized by analysis of cytochrome c oxidase subunit I. PloS One 12:e0182749. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182749
Valle GE, Lourenção AL, Zucchi MI, Pinheiro JB (2012) Low polymorphism revealed in new microsatellite markers for Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Genet Mol Res 11:3899–3903. https://doi.org/10.4238/2012.November.12.7
Wosula EN, Chen W, Fei Z, Legg JP (2017) Unravelling the genetic diversity among Cassava Bemisia tabaci whiteflies using NextRAD sequencing. Gen Biol Evol 9:2958–2973. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evx219
Zitoudi K, Margaritopoulos JT, Mamuris Z, Tsitsipis JA (2001) Genetic variation inMyzus persicae populations associated with host-plant and life cycle category. Entomol Exp Appl 99:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1570-7458.2001.00829.x
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Department of Entomology, Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, and Department of Biotechnology, Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University for their unwavering support throughout the research. This research is part of Gummudala Yashaswini M.Sc dissertation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yashaswini, G., Karthik, S., Reddy, B.D. et al. Genotyping of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) affirmed a new record of Asia II 7, China 3 and dominance of Asia I cryptic species in Bihar, India. Int J Trop Insect Sci 43, 1123–1133 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01004-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-023-01004-8